9.0 KiB
Create Index
Index system is the core part of Milvus, which is used to speed up the searches, this document introduces which components are involved in Create Index,and what these components do.
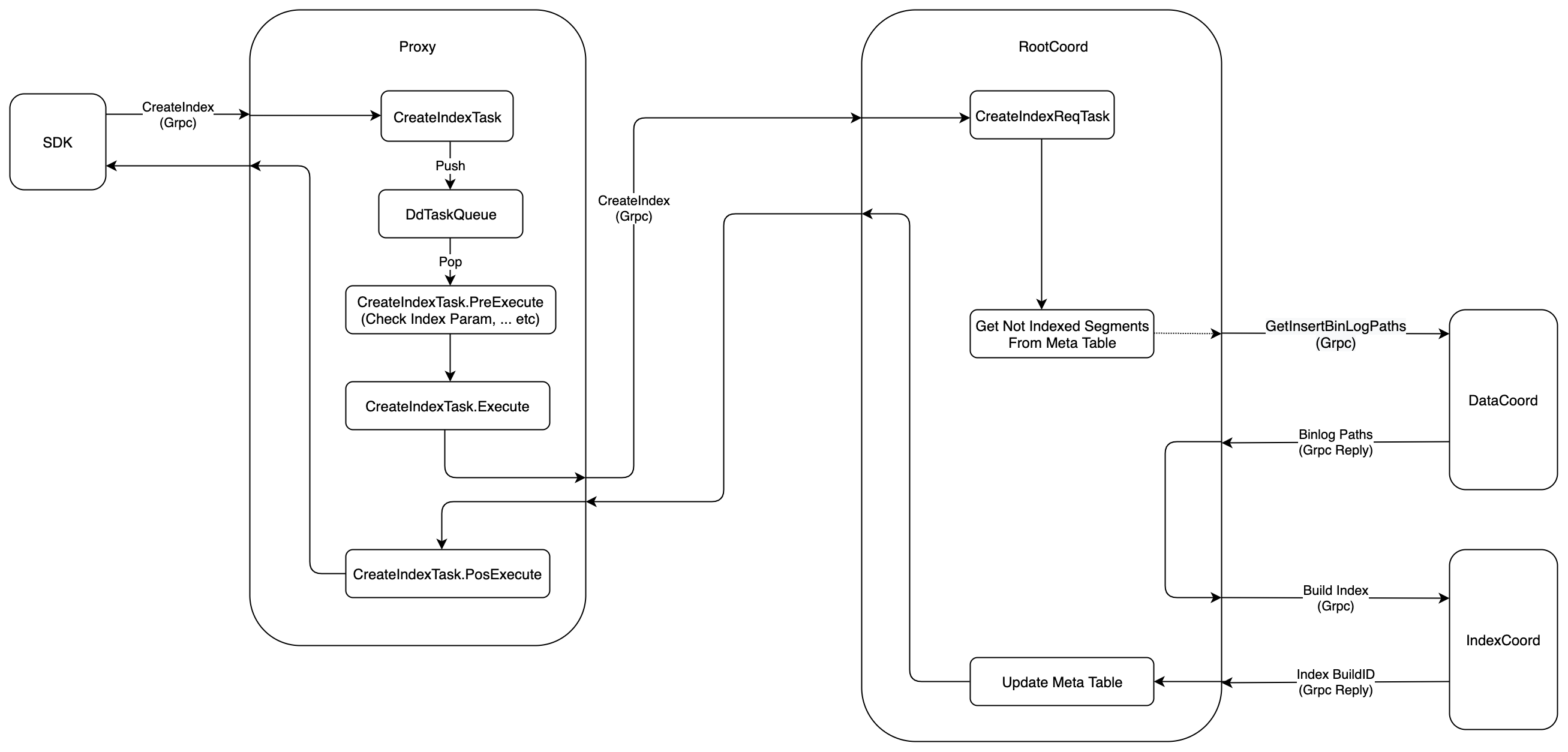
The execution flow of Create Index is shown in the following figure:
- Firstly,
SDKstarts aCreateIndexrequest toProxyviaGrpc, theprotois defined as follows:
service MilvusService {
...
rpc CreateIndex(CreateIndexRequest) returns (common.Status) {}
...
}
message CreateIndexRequest {
common.MsgBase base = 1;
string db_name = 2;
string collection_name = 3;
string field_name = 4;
int64 dbID = 5;
int64 collectionID = 6;
int64 fieldID = 7;
repeated common.KeyValuePair extra_params = 8;
}
- When received the
CreateIndexrequest, theProxywould wrap this request intoCreateIndexTask, and push this task intoDdTaskQueuequeue. After that,Proxywould call method ofWatiToFinishto wait until the task finished.
type task interface {
TraceCtx() context.Context
ID() UniqueID // return ReqID
SetID(uid UniqueID) // set ReqID
Name() string
Type() commonpb.MsgType
BeginTs() Timestamp
EndTs() Timestamp
SetTs(ts Timestamp)
OnEnqueue() error
PreExecute(ctx context.Context) error
Execute(ctx context.Context) error
PostExecute(ctx context.Context) error
WaitToFinish() error
Notify(err error)
}
type createIndexTask struct {
Condition
*milvuspb.CreateIndexRequest
ctx context.Context
rootCoord types.RootCoord
result *commonpb.Status
}
-
There is a background service in
Proxy, this service would get theCreateIndexTaskfromDdTaskQueue, and execute it in three phases.PreExecute, do some static checking at this phase, such as check if the index param is legal, etc.Execute, at this phase,Proxywould sendCreateIndexrequest toRootCoordviaGrpc, and wait the response, theprotois defined as the following:
service RootCoord { ... rpc CreateIndex(milvus.CreateIndexRequest) returns (common.Status) {} ... }PostExecute,CreateIndexTaskdoes nothing at this phase, and returns directly.
-
RootCoordwould wrap theCreateIndexrequest intoCreateIndexReqTask, and then call functionexecuteTask.executeTaskwould return until thecontextis done orCreateIndexReqTask.Executereturned.
type reqTask interface {
Ctx() context.Context
Type() commonpb.MsgType
Execute(ctx context.Context) error
Core() *Core
}
type CreateIndexReqTask struct {
baseReqTask
Req *milvuspb.CreateIndexRequest
}
-
According to the index type and index parameters,
RootCoordlists all theSegmentsthat need to be indexed on thisCollection.RootCoordwould only check thoseSegmentswhich have been flushed at this stage. We will describe how to deal with those newly added segments and growing segments later. -
For each
Segment,RootCoordwould start aGrpcrequest toDataCoordto getBinlogpaths of thatSegment, theprotois defined as following:
service DataCoord {
...
rpc GetInsertBinlogPaths(GetInsertBinlogPathsRequest) returns (GetInsertBinlogPathsResponse) {}
...
}
message GetInsertBinlogPathsRequest {
common.MsgBase base = 1;
int64 segmentID = 2;
}
message GetInsertBinlogPathsResponse {
repeated int64 fieldIDs = 1;
repeated internal.StringList paths = 2;
common.Status status = 3;
}
- After getting the
Segment'sBinlogpaths,RootCoordwould send aGrpcrequest toIndexCoord, askIndexCoordto build index on thisSegment, theprotois defined as the follow:
service IndexCoord {
...
rpc BuildIndex(BuildIndexRequest) returns (BuildIndexResponse){}
...
}
message BuildIndexRequest {
int64 indexBuildID = 1;
string index_name = 2;
int64 indexID = 3;
repeated string data_paths = 5;
repeated common.KeyValuePair type_params = 6;
repeated common.KeyValuePair index_params = 7;
}
message BuildIndexResponse {
common.Status status = 1;
int64 indexBuildID = 2;
}
- The execution flow of
BuildIndexonIndexCoordis shown in the following figure
-
IndexCoordwould wrap theBuildIndexrequest intoIndexAddTask, then alloc a global unique ID asIndexBuildID, and write thisSegment'sindex mateintoIndexCoord'smetaTable. When finish these operations,IndexCoordwould send response toRootCoord, the response includes theIndexBuildID. -
When
RootCooodreceives theBuildIndexResponse, it would extract theIndexBuildIDfrom the response, updateRootCoord'smetaTable, then send responses toProxy. -
There is a background service,
assignTaskLoop, inIndexCoord.assignTaskLoopwould callGetUnassignedTaskperiodically, the default interval is 3s.GetUnassignedTaskwould list these segments whoseindex metahas been updated, but index has not been created yet. -
The previous step has listed the segments whose index has not been created, for each those segments,
IndexCoordwould callPeekClientto get an availableIndexNode, and sendCreateIndexrequest to thisIndexNode. Theprotois defined as follows.
service IndexNode {
...
rpc CreateIndex(CreateIndexRequest) returns (common.Status){}
...
}
message CreateIndexRequest {
int64 indexBuildID = 1;
string index_name = 2;
int64 indexID = 3;
int64 version = 4;
string meta_path = 5;
repeated string data_paths = 6;
repeated common.KeyValuePair type_params = 7;
repeated common.KeyValuePair index_params = 8;
}
-
When receiving
CreateIndexrequest,IndexNodewould wrap this request intoIndexBuildTask, and push this task intoIndexBuildQueue, then send response toIndexCoord. -
There is a background service,
indexBuildLoop, in theIndexNode.indexBuildLoopwould callscheduleIndexBuildTaskto get anIndexBuildTaskfromIndexBuildQueue, and then start anothergoroutineto build index and update meta.
Note: IndexNode will not notify the QueryCoord to load the index files, if a user wants to speed up search by these index files, he should call ReleaseCollection firstly, then call LoadCollection to load these index files.
- As mentioned earlier,
RootCoordwould only search on these flushed segments onCreateIndexrequest, the following figure shows how to deal with the newly added segments.
- When a segment has been flushed,
DataCoordwould notifyRootCoordviaSegmentFlushCompleted, theprotois defined as follows:
service RootCoord {
...
rpc SegmentFlushCompleted(data.SegmentFlushCompletedMsg) returns (common.Status) {}
...
}
message SegmentFlushCompletedMsg {
common.MsgBase base = 1;
SegmentInfo segment = 2;
}
message SegmentInfo {
int64 ID = 1;
int64 collectionID = 2;
int64 partitionID = 3;
string insert_channel = 4;
int64 num_of_rows = 5;
common.SegmentState state = 6;
int64 max_row_num = 7;
uint64 last_expire_time = 8;
msgpb.MsgPosition start_position = 9;
msgpb.MsgPosition dml_position = 10;
repeated FieldBinlog binlogs = 11;
}
-
If a user has called
CreateIndexon thisCollection, then whenRootCoordreceivesSegmentFlushCompletedrequest, it would extract theSegmentIDfrom the request, and send aGetInsertBinlogPathsrequest toDataCoordto get theBinlogpaths, finallyRootCoordwould send aBuildIndexrequest toIndexCoordto notifyIndexCoordto build index on this segment. -
The
Grpccall ofSegmentFlushCompletedmight be failed due to network problem or some others, so how to create an index if theGrpcfailed ? The following figure shows the solution.
-
There is a background service,
checkFlushedSegmentLoop, inRootCoord.checkFlushedSegmentLoopwould periodically check whether there is a segment that needs to be created index but has not been created, the default interval is10 minutes, and callDataCoordandIndexCoord's service to create index on these segments. -
In
Milvus 2.0,Create Indexis an asynchronous operation, so theSDKneeds to sendGetIndexStatesrequest toIndexCoordperiodically to check if the index has been created, theprotois defined as follows.
service IndexCoord {
...
rpc GetIndexStates(GetIndexStatesRequest) returns (GetIndexStatesResponse) {}
...
}
message GetIndexStatesRequest {
repeated int64 indexBuildIDs = 1;
}
message GetIndexStatesResponse {
common.Status status = 1;
repeated IndexInfo states = 2;
}
message IndexInfo {
common.IndexState state = 1;
int64 indexBuildID = 2;
int64 indexID = 3;
string index_name = 4;
string reason = 5;
}
enum IndexState {
IndexStateNone = 0;
Unissued = 1;
InProgress = 2;
Finished = 3;
Failed = 4;
}