5.0 KiB
Create Collection
Milvus 2.0 uses Collection to represent a set of data, like Table in a traditional database. User can create or drop Collection.
This article introduces the execution path of CreateCollection, at the end of this article, you should know which components are involved in CreateCollection.
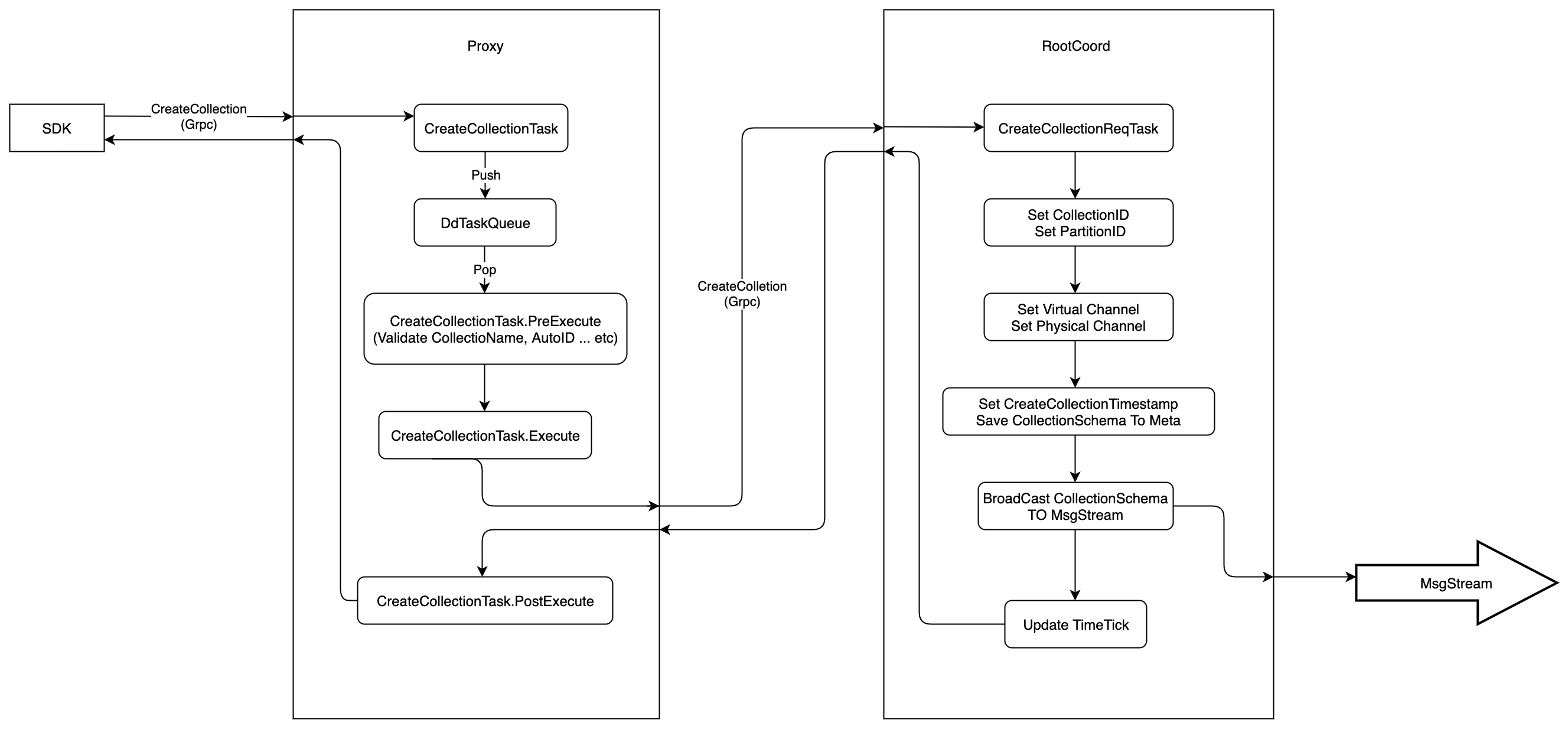
The execution flow of CreateCollection is shown in the following figure:
- Firstly,
SDKstarts aCreateCollectionrequest toProxyviaGrpc, theprotois defined as follows:
service MilvusService {
...
rpc CreateCollection(CreateCollectionRequest) returns (common.Status) {}
...
}
message CreateCollectionRequest {
// Not useful for now
common.MsgBase base = 1;
// Not useful for now
string db_name = 2;
// The unique collection name in milvus.(Required)
string collection_name = 3;
// The serialized `schema.CollectionSchema`(Required)
bytes schema = 4;
// Once set, no modification is allowed (Optional)
// https://github.com/milvus-io/milvus/issues/6690
int32 shards_num = 5;
}
message CollectionSchema {
string name = 1;
string description = 2;
bool autoID = 3; // deprecated later, keep compatible with c++ part now
repeated FieldSchema fields = 4;
}
- When receiving the
CreateCollectionrequest,Proxywould wrap this request intoCreateCollectionTask, and pushes this task intoDdTaskQueuequeue. After that,Proxywould callWaitToFinishmethod to wait until the task is finished.
type task interface {
TraceCtx() context.Context
ID() UniqueID // return ReqID
SetID(uid UniqueID) // set ReqID
Name() string
Type() commonpb.MsgType
BeginTs() Timestamp
EndTs() Timestamp
SetTs(ts Timestamp)
OnEnqueue() error
PreExecute(ctx context.Context) error
Execute(ctx context.Context) error
PostExecute(ctx context.Context) error
WaitToFinish() error
Notify(err error)
}
type createCollectionTask struct {
Condition
*milvuspb.CreateCollectionRequest
ctx context.Context
rootCoord types.RootCoord
result *commonpb.Status
schema *schemapb.CollectionSchema
}
-
There is a background service in
Proxy, this service would get theCreateCollectionTaskfromDdTaskQueue, and execute it in three phases.PreExecute, do some static checking at this phase, such as check ifCollection NameandField Nameare legal, if there are duplicate columns, etc.Execute, at this phase,Proxywould sendCreateCollectionrequest toRootCoordviaGrpc, and wait for response, theprotois defined as follows:
service RootCoord { ... rpc CreateCollection(milvus.CreateCollectionRequest) returns (common.Status){} ... }PostExecute,CreateCollectionTaskdoes nothing at this phase, and return directly.
-
RootCoordwould wrap theCreateCollectionrequest intoCreateCollectionReqTask, and then call functionexecuteTask.executeTaskwould return until thecontextis done orCreateCollectionReqTask.Executeis returned.
type reqTask interface {
Ctx() context.Context
Type() commonpb.MsgType
Execute(ctx context.Context) error
Core() *Core
}
type CreateCollectionReqTask struct {
baseReqTask
Req *milvuspb.CreateCollectionRequest
}
-
CreateCollectionReqTask.Executewould allocCollectionIDand defaultPartitionID, and setVirtual ChannelandPhysical Channel, which are used byMsgStream, then write theCollection's meta intometaTable -
After
Collection's meta written intometaTable,Milvuswould consider this collection has been created successfully. -
RootCoordwould alloc a timestamp fromTSObefore writingCollection's meta intometaTable, and this timestamp is considered as the point when the collection was created -
At last
RootCoordwill send a message ofCreateCollectionRequestintoMsgStream, and other components, who have subscribed to theMsgStream, would be notified. TheProtoofCreateCollectionRequestis defined as follows:
message CreateCollectionRequest {
common.MsgBase base = 1;
string db_name = 2;
string collectionName = 3;
string partitionName = 4;
int64 dbID = 5;
int64 collectionID = 6;
int64 partitionID = 7;
// `schema` is the serialized `schema.CollectionSchema`
bytes schema = 8;
repeated string virtualChannelNames = 9;
repeated string physicalChannelNames = 10;
}
- After the above operations,
RootCoordwould update the internal timestamp and return, soProxywould get the response.
Notes:
-
In
Proxy, allDDLrequests will be wrapped intotask, and push thetaskintoDdTaskQueue. A background service will read a newtaskfromDdTaskQueueonly when the previous one is finished. So all theDDLrequests are executed serially onProxy. -
In
RootCoord, allDDLrequests will be wrapped intoreqTask, but there is no task queue, so theDDLrequests will be executed in parallel onRootCoord.