mirror of https://github.com/ARMmbed/mbed-os.git
Squashed 'littlefs/' changes from 454b588..2ab150c
2ab150c Removed toolchain specific warnings 0825d34 Adopted alternative implementation for lfs_ctz_index 46e22b2 Adopted lfs_ctz_index implementation using popcount 4fdca15 Slight name change with ctz skip-list functions git-subtree-dir: littlefs git-subtree-split: 2ab150cc500d5b8233ec8ef6109efa363bf1d38cpull/6179/head
parent
3c3b0329d4
commit
0171b57a04
96
DESIGN.md
96
DESIGN.md
|
|
@ -290,31 +290,32 @@ The path to data block 0 is even more quick, requiring only two jumps:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
We can find the runtime complexity by looking at the path to any block from
|
We can find the runtime complexity by looking at the path to any block from
|
||||||
the block containing the most pointers. Every step along the path divides
|
the block containing the most pointers. Every step along the path divides
|
||||||
the search space for the block in half. This gives us a runtime of O(log n).
|
the search space for the block in half. This gives us a runtime of O(logn).
|
||||||
To get to the block with the most pointers, we can perform the same steps
|
To get to the block with the most pointers, we can perform the same steps
|
||||||
backwards, which keeps the asymptotic runtime at O(log n). The interesting
|
backwards, which puts the runtime at O(2logn) = O(logn). The interesting
|
||||||
part about this data structure is that this optimal path occurs naturally
|
part about this data structure is that this optimal path occurs naturally
|
||||||
if we greedily choose the pointer that covers the most distance without passing
|
if we greedily choose the pointer that covers the most distance without passing
|
||||||
our target block.
|
our target block.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
So now we have a representation of files that can be appended trivially with
|
So now we have a representation of files that can be appended trivially with
|
||||||
a runtime of O(1), and can be read with a worst case runtime of O(n logn).
|
a runtime of O(1), and can be read with a worst case runtime of O(nlogn).
|
||||||
Given that the the runtime is also divided by the amount of data we can store
|
Given that the the runtime is also divided by the amount of data we can store
|
||||||
in a block, this is pretty reasonable.
|
in a block, this is pretty reasonable.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Unfortunately, the CTZ skip-list comes with a few questions that aren't
|
Unfortunately, the CTZ skip-list comes with a few questions that aren't
|
||||||
straightforward to answer. What is the overhead? How do we handle more
|
straightforward to answer. What is the overhead? How do we handle more
|
||||||
pointers than we can store in a block?
|
pointers than we can store in a block? How do we store the skip-list in
|
||||||
|
a directory entry?
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
One way to find the overhead per block is to look at the data structure as
|
One way to find the overhead per block is to look at the data structure as
|
||||||
multiple layers of linked-lists. Each linked-list skips twice as many blocks
|
multiple layers of linked-lists. Each linked-list skips twice as many blocks
|
||||||
as the previous linked-list. Or another way of looking at it is that each
|
as the previous linked-list. Another way of looking at it is that each
|
||||||
linked-list uses half as much storage per block as the previous linked-list.
|
linked-list uses half as much storage per block as the previous linked-list.
|
||||||
As we approach infinity, the number of pointers per block forms a geometric
|
As we approach infinity, the number of pointers per block forms a geometric
|
||||||
series. Solving this geometric series gives us an average of only 2 pointers
|
series. Solving this geometric series gives us an average of only 2 pointers
|
||||||
per block.
|
per block.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
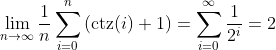
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Finding the maximum number of pointers in a block is a bit more complicated,
|
Finding the maximum number of pointers in a block is a bit more complicated,
|
||||||
but since our file size is limited by the integer width we use to store the
|
but since our file size is limited by the integer width we use to store the
|
||||||
|
|
@ -322,7 +323,7 @@ size, we can solve for it. Setting the overhead of the maximum pointers equal
|
||||||
to the block size we get the following equation. Note that a smaller block size
|
to the block size we get the following equation. Note that a smaller block size
|
||||||
results in more pointers, and a larger word width results in larger pointers.
|
results in more pointers, and a larger word width results in larger pointers.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
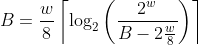
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
where:
|
where:
|
||||||
B = block size in bytes
|
B = block size in bytes
|
||||||
|
|
@ -335,8 +336,83 @@ widths:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Since littlefs uses a 32 bit word size, we are limited to a minimum block
|
Since littlefs uses a 32 bit word size, we are limited to a minimum block
|
||||||
size of 104 bytes. This is a perfectly reasonable minimum block size, with most
|
size of 104 bytes. This is a perfectly reasonable minimum block size, with most
|
||||||
block sizes starting around 512 bytes. So we can avoid the additional logic
|
block sizes starting around 512 bytes. So we can avoid additional logic to
|
||||||
needed to avoid overflowing our block's capacity in the CTZ skip-list.
|
avoid overflowing our block's capacity in the CTZ skip-list.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
So, how do we store the skip-list in a directory entry? A naive approach would
|
||||||
|
be to store a pointer to the head of the skip-list, the length of the file
|
||||||
|
in bytes, the index of the head block in the skip-list, and the offset in the
|
||||||
|
head block in bytes. However this is a lot of information, and we can observe
|
||||||
|
that a file size maps to only one block index + offset pair. So it should be
|
||||||
|
sufficient to store only the pointer and file size.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
But there is one problem, calculating the block index + offset pair from a
|
||||||
|
file size doesn't have an obvious implementation.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
We can start by just writing down an equation. The first idea that comes to
|
||||||
|
mind is to just use a for loop to sum together blocks until we reach our
|
||||||
|
file size. We can write equation equation as a summation:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
where:
|
||||||
|
B = block size in bytes
|
||||||
|
w = word width in bits
|
||||||
|
n = block index in skip-list
|
||||||
|
N = file size in bytes
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
And this works quite well, but is not trivial to calculate. This equation
|
||||||
|
requires O(n) to compute, which brings the entire runtime of reading a file
|
||||||
|
to O(n^2logn). Fortunately, the additional O(n) does not need to touch disk,
|
||||||
|
so it is not completely unreasonable. But if we could solve this equation into
|
||||||
|
a form that is easily computable, we can avoid a big slowdown.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Unfortunately, the summation of the CTZ instruction presents a big challenge.
|
||||||
|
How would you even begin to reason about integrating a bitwise instruction?
|
||||||
|
Fortunately, there is a powerful tool I've found useful in these situations:
|
||||||
|
The [On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences (OEIS)](https://oeis.org/).
|
||||||
|
If we work out the first couple of values in our summation, we find that CTZ
|
||||||
|
maps to [A001511](https://oeis.org/A001511), and its partial summation maps
|
||||||
|
to [A005187](https://oeis.org/A005187), and surprisingly, both of these
|
||||||
|
sequences have relatively trivial equations! This leads us to the completely
|
||||||
|
unintuitive property:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
where:
|
||||||
|
ctz(i) = the number of trailing bits that are 0 in i
|
||||||
|
popcount(i) = the number of bits that are 1 in i
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
I find it bewildering that these two seemingly unrelated bitwise instructions
|
||||||
|
are related by this property. But if we start to disect this equation we can
|
||||||
|
see that it does hold. As n approaches infinity, we do end up with an average
|
||||||
|
overhead of 2 pointers as we find earlier. And popcount seems to handle the
|
||||||
|
error from this average as it accumulates in the CTZ skip-list.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Now we can substitute into the original equation to get a trivial equation
|
||||||
|
for a file size:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Unfortunately, we're not quite done. The popcount function is non-injective,
|
||||||
|
so we can only find the file size from the block index, not the other way
|
||||||
|
around. However, we can solve for an n' block index that is greater than n
|
||||||
|
with an error bounded by the range of the popcount function. We can then
|
||||||
|
repeatedly substitute this n' into the original equation until the error
|
||||||
|
is smaller than the integer division. As it turns out, we only need to
|
||||||
|
perform this substitution once. Now we directly calculate our block index:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Now that we have our block index n, we can just plug it back into the above
|
||||||
|
equation to find the offset. However, we do need to rearrange the equation
|
||||||
|
a bit to avoid integer overflow:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
The solution involves quite a bit of math, but computers are very good at math.
|
||||||
|
We can now solve for the block index + offset while only needed to store the
|
||||||
|
file size in O(1).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Here is what it might look like to update a file stored with a CTZ skip-list:
|
Here is what it might look like to update a file stored with a CTZ skip-list:
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
@ -1129,7 +1205,7 @@ So, to summarize:
|
||||||
metadata block is active
|
metadata block is active
|
||||||
4. Directory blocks contain either references to other directories or files
|
4. Directory blocks contain either references to other directories or files
|
||||||
5. Files are represented by copy-on-write CTZ skip-lists which support O(1)
|
5. Files are represented by copy-on-write CTZ skip-lists which support O(1)
|
||||||
append and O(n logn) reading
|
append and O(nlogn) reading
|
||||||
6. Blocks are allocated by scanning the filesystem for used blocks in a
|
6. Blocks are allocated by scanning the filesystem for used blocks in a
|
||||||
fixed-size lookahead region is that stored in a bit-vector
|
fixed-size lookahead region is that stored in a bit-vector
|
||||||
7. To facilitate scanning the filesystem, all directories are part of a
|
7. To facilitate scanning the filesystem, all directories are part of a
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
321
lfs.c
321
lfs.c
|
|
@ -373,8 +373,8 @@ static int lfs_dir_alloc(lfs_t *lfs, lfs_dir_t *dir) {
|
||||||
// set defaults
|
// set defaults
|
||||||
dir->d.rev += 1;
|
dir->d.rev += 1;
|
||||||
dir->d.size = sizeof(dir->d)+4;
|
dir->d.size = sizeof(dir->d)+4;
|
||||||
dir->d.tail[0] = -1;
|
dir->d.tail[0] = 0xffffffff;
|
||||||
dir->d.tail[1] = -1;
|
dir->d.tail[1] = 0xffffffff;
|
||||||
dir->off = sizeof(dir->d);
|
dir->off = sizeof(dir->d);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// don't write out yet, let caller take care of that
|
// don't write out yet, let caller take care of that
|
||||||
|
|
@ -455,88 +455,91 @@ static int lfs_dir_commit(lfs_t *lfs, lfs_dir_t *dir,
|
||||||
bool relocated = false;
|
bool relocated = false;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
while (true) {
|
while (true) {
|
||||||
int err = lfs_bd_erase(lfs, dir->pair[0]);
|
if (true) {
|
||||||
if (err) {
|
int err = lfs_bd_erase(lfs, dir->pair[0]);
|
||||||
if (err == LFS_ERR_CORRUPT) {
|
if (err) {
|
||||||
goto relocate;
|
if (err == LFS_ERR_CORRUPT) {
|
||||||
|
goto relocate;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return err;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
return err;
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
uint32_t crc = 0xffffffff;
|
uint32_t crc = 0xffffffff;
|
||||||
lfs_crc(&crc, &dir->d, sizeof(dir->d));
|
lfs_crc(&crc, &dir->d, sizeof(dir->d));
|
||||||
err = lfs_bd_prog(lfs, dir->pair[0], 0, &dir->d, sizeof(dir->d));
|
err = lfs_bd_prog(lfs, dir->pair[0], 0, &dir->d, sizeof(dir->d));
|
||||||
if (err) {
|
if (err) {
|
||||||
if (err == LFS_ERR_CORRUPT) {
|
if (err == LFS_ERR_CORRUPT) {
|
||||||
goto relocate;
|
goto relocate;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return err;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
return err;
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
int i = 0;
|
int i = 0;
|
||||||
lfs_off_t oldoff = sizeof(dir->d);
|
lfs_off_t oldoff = sizeof(dir->d);
|
||||||
lfs_off_t newoff = sizeof(dir->d);
|
lfs_off_t newoff = sizeof(dir->d);
|
||||||
while (newoff < (0x7fffffff & dir->d.size)-4) {
|
while (newoff < (0x7fffffff & dir->d.size)-4) {
|
||||||
if (i < count && regions[i].oldoff == oldoff) {
|
if (i < count && regions[i].oldoff == oldoff) {
|
||||||
lfs_crc(&crc, regions[i].newdata, regions[i].newlen);
|
lfs_crc(&crc, regions[i].newdata, regions[i].newlen);
|
||||||
int err = lfs_bd_prog(lfs, dir->pair[0],
|
int err = lfs_bd_prog(lfs, dir->pair[0],
|
||||||
newoff, regions[i].newdata, regions[i].newlen);
|
newoff, regions[i].newdata, regions[i].newlen);
|
||||||
if (err) {
|
if (err) {
|
||||||
if (err == LFS_ERR_CORRUPT) {
|
if (err == LFS_ERR_CORRUPT) {
|
||||||
goto relocate;
|
goto relocate;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return err;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
return err;
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
oldoff += regions[i].oldlen;
|
oldoff += regions[i].oldlen;
|
||||||
newoff += regions[i].newlen;
|
newoff += regions[i].newlen;
|
||||||
i += 1;
|
i += 1;
|
||||||
} else {
|
} else {
|
||||||
uint8_t data;
|
uint8_t data;
|
||||||
int err = lfs_bd_read(lfs, oldpair[1], oldoff, &data, 1);
|
int err = lfs_bd_read(lfs, oldpair[1], oldoff, &data, 1);
|
||||||
if (err) {
|
if (err) {
|
||||||
return err;
|
return err;
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
lfs_crc(&crc, &data, 1);
|
|
||||||
err = lfs_bd_prog(lfs, dir->pair[0], newoff, &data, 1);
|
|
||||||
if (err) {
|
|
||||||
if (err == LFS_ERR_CORRUPT) {
|
|
||||||
goto relocate;
|
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
return err;
|
|
||||||
|
lfs_crc(&crc, &data, 1);
|
||||||
|
err = lfs_bd_prog(lfs, dir->pair[0], newoff, &data, 1);
|
||||||
|
if (err) {
|
||||||
|
if (err == LFS_ERR_CORRUPT) {
|
||||||
|
goto relocate;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return err;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
oldoff += 1;
|
||||||
|
newoff += 1;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
oldoff += 1;
|
|
||||||
newoff += 1;
|
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
err = lfs_bd_prog(lfs, dir->pair[0], newoff, &crc, 4);
|
err = lfs_bd_prog(lfs, dir->pair[0], newoff, &crc, 4);
|
||||||
if (err) {
|
if (err) {
|
||||||
if (err == LFS_ERR_CORRUPT) {
|
if (err == LFS_ERR_CORRUPT) {
|
||||||
goto relocate;
|
goto relocate;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return err;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
return err;
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
err = lfs_bd_sync(lfs);
|
err = lfs_bd_sync(lfs);
|
||||||
if (err) {
|
if (err) {
|
||||||
if (err == LFS_ERR_CORRUPT) {
|
if (err == LFS_ERR_CORRUPT) {
|
||||||
goto relocate;
|
goto relocate;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return err;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
return err;
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// successful commit, check checksum to make sure
|
// successful commit, check checksum to make sure
|
||||||
crc = 0xffffffff;
|
crc = 0xffffffff;
|
||||||
err = lfs_bd_crc(lfs, dir->pair[0], 0, 0x7fffffff & dir->d.size, &crc);
|
err = lfs_bd_crc(lfs, dir->pair[0], 0,
|
||||||
if (err) {
|
0x7fffffff & dir->d.size, &crc);
|
||||||
return err;
|
if (err) {
|
||||||
}
|
return err;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if (crc == 0) {
|
if (crc == 0) {
|
||||||
break;
|
break;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
relocate:
|
relocate:
|
||||||
|
|
@ -554,7 +557,7 @@ relocate:
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// relocate half of pair
|
// relocate half of pair
|
||||||
err = lfs_alloc(lfs, &dir->pair[0]);
|
int err = lfs_alloc(lfs, &dir->pair[0]);
|
||||||
if (err) {
|
if (err) {
|
||||||
return err;
|
return err;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
@ -791,8 +794,6 @@ static int lfs_dir_find(lfs_t *lfs, lfs_dir_t *dir,
|
||||||
return err;
|
return err;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return 0;
|
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -1003,30 +1004,31 @@ int lfs_dir_rewind(lfs_t *lfs, lfs_dir_t *dir) {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
/// File index list operations ///
|
/// File index list operations ///
|
||||||
static int lfs_index(lfs_t *lfs, lfs_off_t *off) {
|
static int lfs_ctz_index(lfs_t *lfs, lfs_off_t *off) {
|
||||||
lfs_off_t i = 0;
|
lfs_off_t size = *off;
|
||||||
|
lfs_off_t b = lfs->cfg->block_size - 2*4;
|
||||||
while (*off >= lfs->cfg->block_size) {
|
lfs_off_t i = size / b;
|
||||||
i += 1;
|
if (i == 0) {
|
||||||
*off -= lfs->cfg->block_size;
|
return 0;
|
||||||
*off += 4*(lfs_ctz(i) + 1);
|
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
i = (size - 4*(lfs_popc(i-1)+2)) / b;
|
||||||
|
*off = size - b*i - 4*lfs_popc(i);
|
||||||
return i;
|
return i;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
static int lfs_index_find(lfs_t *lfs,
|
static int lfs_ctz_find(lfs_t *lfs,
|
||||||
lfs_cache_t *rcache, const lfs_cache_t *pcache,
|
lfs_cache_t *rcache, const lfs_cache_t *pcache,
|
||||||
lfs_block_t head, lfs_size_t size,
|
lfs_block_t head, lfs_size_t size,
|
||||||
lfs_size_t pos, lfs_block_t *block, lfs_off_t *off) {
|
lfs_size_t pos, lfs_block_t *block, lfs_off_t *off) {
|
||||||
if (size == 0) {
|
if (size == 0) {
|
||||||
*block = -1;
|
*block = 0xffffffff;
|
||||||
*off = 0;
|
*off = 0;
|
||||||
return 0;
|
return 0;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
lfs_off_t current = lfs_index(lfs, &(lfs_off_t){size-1});
|
lfs_off_t current = lfs_ctz_index(lfs, &(lfs_off_t){size-1});
|
||||||
lfs_off_t target = lfs_index(lfs, &pos);
|
lfs_off_t target = lfs_ctz_index(lfs, &pos);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
while (current > target) {
|
while (current > target) {
|
||||||
lfs_size_t skip = lfs_min(
|
lfs_size_t skip = lfs_min(
|
||||||
|
|
@ -1047,64 +1049,20 @@ static int lfs_index_find(lfs_t *lfs,
|
||||||
return 0;
|
return 0;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
static int lfs_index_extend(lfs_t *lfs,
|
static int lfs_ctz_extend(lfs_t *lfs,
|
||||||
lfs_cache_t *rcache, lfs_cache_t *pcache,
|
lfs_cache_t *rcache, lfs_cache_t *pcache,
|
||||||
lfs_block_t head, lfs_size_t size,
|
lfs_block_t head, lfs_size_t size,
|
||||||
lfs_off_t *block, lfs_block_t *off) {
|
lfs_off_t *block, lfs_block_t *off) {
|
||||||
while (true) {
|
while (true) {
|
||||||
// go ahead and grab a block
|
if (true) {
|
||||||
int err = lfs_alloc(lfs, block);
|
// go ahead and grab a block
|
||||||
if (err) {
|
int err = lfs_alloc(lfs, block);
|
||||||
return err;
|
if (err) {
|
||||||
}
|
return err;
|
||||||
assert(*block >= 2 && *block <= lfs->cfg->block_count);
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
err = lfs_bd_erase(lfs, *block);
|
|
||||||
if (err) {
|
|
||||||
if (err == LFS_ERR_CORRUPT) {
|
|
||||||
goto relocate;
|
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
return err;
|
assert(*block >= 2 && *block <= lfs->cfg->block_count);
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if (size == 0) {
|
err = lfs_bd_erase(lfs, *block);
|
||||||
*off = 0;
|
|
||||||
return 0;
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
size -= 1;
|
|
||||||
lfs_off_t index = lfs_index(lfs, &size);
|
|
||||||
size += 1;
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// just copy out the last block if it is incomplete
|
|
||||||
if (size != lfs->cfg->block_size) {
|
|
||||||
for (lfs_off_t i = 0; i < size; i++) {
|
|
||||||
uint8_t data;
|
|
||||||
int err = lfs_cache_read(lfs, rcache, NULL, head, i, &data, 1);
|
|
||||||
if (err) {
|
|
||||||
return err;
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
err = lfs_cache_prog(lfs, pcache, rcache, *block, i, &data, 1);
|
|
||||||
if (err) {
|
|
||||||
if (err == LFS_ERR_CORRUPT) {
|
|
||||||
goto relocate;
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
return err;
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
*off = size;
|
|
||||||
return 0;
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// append block
|
|
||||||
index += 1;
|
|
||||||
lfs_size_t skips = lfs_ctz(index) + 1;
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
for (lfs_off_t i = 0; i < skips; i++) {
|
|
||||||
int err = lfs_cache_prog(lfs, pcache, rcache,
|
|
||||||
*block, 4*i, &head, 4);
|
|
||||||
if (err) {
|
if (err) {
|
||||||
if (err == LFS_ERR_CORRUPT) {
|
if (err == LFS_ERR_CORRUPT) {
|
||||||
goto relocate;
|
goto relocate;
|
||||||
|
|
@ -1112,18 +1070,67 @@ static int lfs_index_extend(lfs_t *lfs,
|
||||||
return err;
|
return err;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if (i != skips-1) {
|
if (size == 0) {
|
||||||
err = lfs_cache_read(lfs, rcache, NULL, head, 4*i, &head, 4);
|
*off = 0;
|
||||||
if (err) {
|
return 0;
|
||||||
return err;
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
assert(head >= 2 && head <= lfs->cfg->block_count);
|
size -= 1;
|
||||||
}
|
lfs_off_t index = lfs_ctz_index(lfs, &size);
|
||||||
|
size += 1;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
*off = 4*skips;
|
// just copy out the last block if it is incomplete
|
||||||
return 0;
|
if (size != lfs->cfg->block_size) {
|
||||||
|
for (lfs_off_t i = 0; i < size; i++) {
|
||||||
|
uint8_t data;
|
||||||
|
int err = lfs_cache_read(lfs, rcache, NULL,
|
||||||
|
head, i, &data, 1);
|
||||||
|
if (err) {
|
||||||
|
return err;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
err = lfs_cache_prog(lfs, pcache, rcache,
|
||||||
|
*block, i, &data, 1);
|
||||||
|
if (err) {
|
||||||
|
if (err == LFS_ERR_CORRUPT) {
|
||||||
|
goto relocate;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return err;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
*off = size;
|
||||||
|
return 0;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// append block
|
||||||
|
index += 1;
|
||||||
|
lfs_size_t skips = lfs_ctz(index) + 1;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
for (lfs_off_t i = 0; i < skips; i++) {
|
||||||
|
int err = lfs_cache_prog(lfs, pcache, rcache,
|
||||||
|
*block, 4*i, &head, 4);
|
||||||
|
if (err) {
|
||||||
|
if (err == LFS_ERR_CORRUPT) {
|
||||||
|
goto relocate;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
return err;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if (i != skips-1) {
|
||||||
|
err = lfs_cache_read(lfs, rcache, NULL,
|
||||||
|
head, 4*i, &head, 4);
|
||||||
|
if (err) {
|
||||||
|
return err;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
assert(head >= 2 && head <= lfs->cfg->block_count);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
*off = 4*skips;
|
||||||
|
return 0;
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
relocate:
|
relocate:
|
||||||
LFS_DEBUG("Bad block at %d", *block);
|
LFS_DEBUG("Bad block at %d", *block);
|
||||||
|
|
@ -1133,7 +1140,7 @@ relocate:
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
static int lfs_index_traverse(lfs_t *lfs,
|
static int lfs_ctz_traverse(lfs_t *lfs,
|
||||||
lfs_cache_t *rcache, const lfs_cache_t *pcache,
|
lfs_cache_t *rcache, const lfs_cache_t *pcache,
|
||||||
lfs_block_t head, lfs_size_t size,
|
lfs_block_t head, lfs_size_t size,
|
||||||
int (*cb)(void*, lfs_block_t), void *data) {
|
int (*cb)(void*, lfs_block_t), void *data) {
|
||||||
|
|
@ -1141,7 +1148,7 @@ static int lfs_index_traverse(lfs_t *lfs,
|
||||||
return 0;
|
return 0;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
lfs_off_t index = lfs_index(lfs, &(lfs_off_t){size-1});
|
lfs_off_t index = lfs_ctz_index(lfs, &(lfs_off_t){size-1});
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
while (true) {
|
while (true) {
|
||||||
int err = cb(data, head);
|
int err = cb(data, head);
|
||||||
|
|
@ -1160,8 +1167,6 @@ static int lfs_index_traverse(lfs_t *lfs,
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
index -= 1;
|
index -= 1;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return 0;
|
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -1199,7 +1204,7 @@ int lfs_file_open(lfs_t *lfs, lfs_file_t *file,
|
||||||
entry.d.elen = sizeof(entry.d) - 4;
|
entry.d.elen = sizeof(entry.d) - 4;
|
||||||
entry.d.alen = 0;
|
entry.d.alen = 0;
|
||||||
entry.d.nlen = strlen(path);
|
entry.d.nlen = strlen(path);
|
||||||
entry.d.u.file.head = -1;
|
entry.d.u.file.head = 0xffffffff;
|
||||||
entry.d.u.file.size = 0;
|
entry.d.u.file.size = 0;
|
||||||
err = lfs_dir_append(lfs, &cwd, &entry, path);
|
err = lfs_dir_append(lfs, &cwd, &entry, path);
|
||||||
if (err) {
|
if (err) {
|
||||||
|
|
@ -1221,7 +1226,7 @@ int lfs_file_open(lfs_t *lfs, lfs_file_t *file,
|
||||||
file->pos = 0;
|
file->pos = 0;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if (flags & LFS_O_TRUNC) {
|
if (flags & LFS_O_TRUNC) {
|
||||||
file->head = -1;
|
file->head = 0xffffffff;
|
||||||
file->size = 0;
|
file->size = 0;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -1455,7 +1460,7 @@ lfs_ssize_t lfs_file_read(lfs_t *lfs, lfs_file_t *file,
|
||||||
// check if we need a new block
|
// check if we need a new block
|
||||||
if (!(file->flags & LFS_F_READING) ||
|
if (!(file->flags & LFS_F_READING) ||
|
||||||
file->off == lfs->cfg->block_size) {
|
file->off == lfs->cfg->block_size) {
|
||||||
int err = lfs_index_find(lfs, &file->cache, NULL,
|
int err = lfs_ctz_find(lfs, &file->cache, NULL,
|
||||||
file->head, file->size,
|
file->head, file->size,
|
||||||
file->pos, &file->block, &file->off);
|
file->pos, &file->block, &file->off);
|
||||||
if (err) {
|
if (err) {
|
||||||
|
|
@ -1522,7 +1527,7 @@ lfs_ssize_t lfs_file_write(lfs_t *lfs, lfs_file_t *file,
|
||||||
file->off == lfs->cfg->block_size) {
|
file->off == lfs->cfg->block_size) {
|
||||||
if (!(file->flags & LFS_F_WRITING) && file->pos > 0) {
|
if (!(file->flags & LFS_F_WRITING) && file->pos > 0) {
|
||||||
// find out which block we're extending from
|
// find out which block we're extending from
|
||||||
int err = lfs_index_find(lfs, &file->cache, NULL,
|
int err = lfs_ctz_find(lfs, &file->cache, NULL,
|
||||||
file->head, file->size,
|
file->head, file->size,
|
||||||
file->pos-1, &file->block, &file->off);
|
file->pos-1, &file->block, &file->off);
|
||||||
if (err) {
|
if (err) {
|
||||||
|
|
@ -1535,7 +1540,7 @@ lfs_ssize_t lfs_file_write(lfs_t *lfs, lfs_file_t *file,
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// extend file with new blocks
|
// extend file with new blocks
|
||||||
lfs_alloc_ack(lfs);
|
lfs_alloc_ack(lfs);
|
||||||
int err = lfs_index_extend(lfs, &lfs->rcache, &file->cache,
|
int err = lfs_ctz_extend(lfs, &lfs->rcache, &file->cache,
|
||||||
file->block, file->pos,
|
file->block, file->pos,
|
||||||
&file->block, &file->off);
|
&file->block, &file->off);
|
||||||
if (err) {
|
if (err) {
|
||||||
|
|
@ -1588,13 +1593,13 @@ lfs_soff_t lfs_file_seek(lfs_t *lfs, lfs_file_t *file,
|
||||||
if (whence == LFS_SEEK_SET) {
|
if (whence == LFS_SEEK_SET) {
|
||||||
file->pos = off;
|
file->pos = off;
|
||||||
} else if (whence == LFS_SEEK_CUR) {
|
} else if (whence == LFS_SEEK_CUR) {
|
||||||
if (-off > file->pos) {
|
if ((lfs_off_t)-off > file->pos) {
|
||||||
return LFS_ERR_INVAL;
|
return LFS_ERR_INVAL;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
file->pos = file->pos + off;
|
file->pos = file->pos + off;
|
||||||
} else if (whence == LFS_SEEK_END) {
|
} else if (whence == LFS_SEEK_END) {
|
||||||
if (-off > file->size) {
|
if ((lfs_off_t)-off > file->size) {
|
||||||
return LFS_ERR_INVAL;
|
return LFS_ERR_INVAL;
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -2070,7 +2075,7 @@ int lfs_traverse(lfs_t *lfs, int (*cb)(void*, lfs_block_t), void *data) {
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
dir.off += lfs_entry_size(&entry);
|
dir.off += lfs_entry_size(&entry);
|
||||||
if ((0x70 & entry.d.type) == (0x70 & LFS_TYPE_REG)) {
|
if ((0x70 & entry.d.type) == (0x70 & LFS_TYPE_REG)) {
|
||||||
int err = lfs_index_traverse(lfs, &lfs->rcache, NULL,
|
int err = lfs_ctz_traverse(lfs, &lfs->rcache, NULL,
|
||||||
entry.d.u.file.head, entry.d.u.file.size, cb, data);
|
entry.d.u.file.head, entry.d.u.file.size, cb, data);
|
||||||
if (err) {
|
if (err) {
|
||||||
return err;
|
return err;
|
||||||
|
|
@ -2089,7 +2094,7 @@ int lfs_traverse(lfs_t *lfs, int (*cb)(void*, lfs_block_t), void *data) {
|
||||||
// iterate over any open files
|
// iterate over any open files
|
||||||
for (lfs_file_t *f = lfs->files; f; f = f->next) {
|
for (lfs_file_t *f = lfs->files; f; f = f->next) {
|
||||||
if (f->flags & LFS_F_DIRTY) {
|
if (f->flags & LFS_F_DIRTY) {
|
||||||
int err = lfs_index_traverse(lfs, &lfs->rcache, &f->cache,
|
int err = lfs_ctz_traverse(lfs, &lfs->rcache, &f->cache,
|
||||||
f->head, f->size, cb, data);
|
f->head, f->size, cb, data);
|
||||||
if (err) {
|
if (err) {
|
||||||
return err;
|
return err;
|
||||||
|
|
@ -2097,7 +2102,7 @@ int lfs_traverse(lfs_t *lfs, int (*cb)(void*, lfs_block_t), void *data) {
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if (f->flags & LFS_F_WRITING) {
|
if (f->flags & LFS_F_WRITING) {
|
||||||
int err = lfs_index_traverse(lfs, &lfs->rcache, &f->cache,
|
int err = lfs_ctz_traverse(lfs, &lfs->rcache, &f->cache,
|
||||||
f->block, f->pos, cb, data);
|
f->block, f->pos, cb, data);
|
||||||
if (err) {
|
if (err) {
|
||||||
return err;
|
return err;
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -41,6 +41,10 @@ static inline uint32_t lfs_npw2(uint32_t a) {
|
||||||
return 32 - __builtin_clz(a-1);
|
return 32 - __builtin_clz(a-1);
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
static inline uint32_t lfs_popc(uint32_t a) {
|
||||||
|
return __builtin_popcount(a);
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
static inline int lfs_scmp(uint32_t a, uint32_t b) {
|
static inline int lfs_scmp(uint32_t a, uint32_t b) {
|
||||||
return (int)(unsigned)(a - b);
|
return (int)(unsigned)(a - b);
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue