Signed-off-by: zhuwenxing <wenxing.zhu@zilliz.com> |
||
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| chaos_objects | ||
| config | ||
| scripts | ||
| testcases | ||
| README.md | ||
| chaos_commons.py | ||
| chaos_test.sh | ||
| checker.py | ||
| cluster-values.yaml | ||
| constants.py | ||
| run.sh | ||
| standalone-values.yaml | ||
| test_chaos.py | ||
| test_chaos_bulk_load.py | ||
| test_chaos_data_consist.py | ||
| test_chaos_memory_stress.py | ||
| test_chaos_multi_replicas.py | ||
README.md
Chaos Tests
Goal
Chaos tests are designed to check the reliability of Milvus.
For instance, if one pod is killed:
- verify that it restarts automatically
- verify that the related operation fails, while the other operations keep working successfully during the absence of the pod
- verify that all the operations work successfully after the pod back to running state
- verify that no data lost
Prerequisite
Chaos tests run in pytest framework, same as e2e tests.
Please refer to Run E2E Tests
Flow Chart
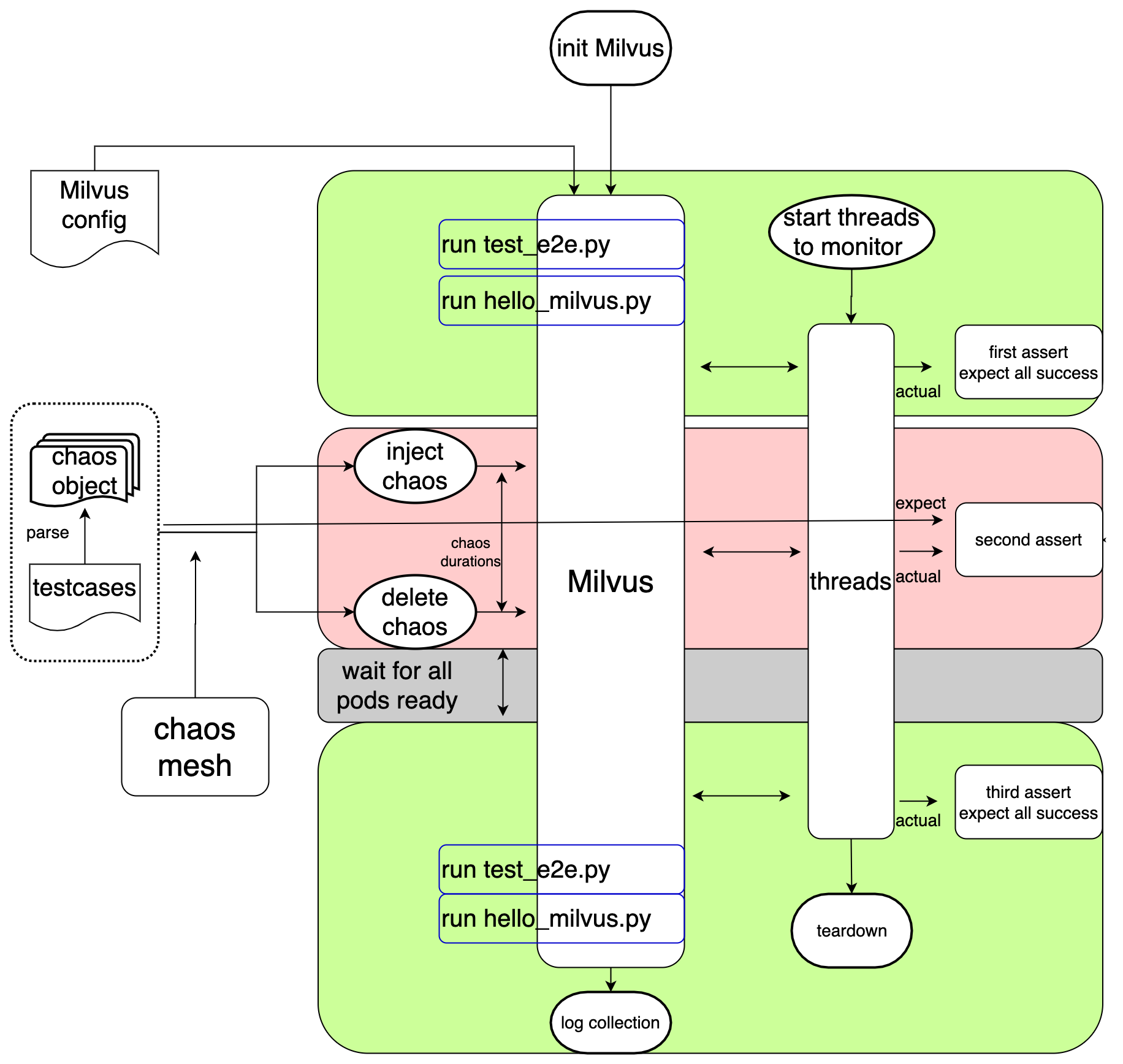
Test Scenarios
Milvus in cluster mode
pod kill
Kill pod every 5s
pod network partition
Two direction(to and from) network isolation between a pod and the rest of the pods
pod failure
Set the pod(querynode, indexnode and datanode)as multiple replicas, make one of them failure, and test milvus's functionality
pod memory stress
Limit the memory resource of pod and generate plenty of stresses over a group of pods
Milvus in standalone mode
-
standalone pod is killed
-
minio pod is killed
How it works
- Test scenarios are designed by different chaos objects
- Every chaos object is defined in one yaml file locates in folder
chaos_objects - Every chaos yaml file specified by
ALL_CHAOS_YAMLSinconstants.pywould be parsed as a parameter and be passed intotest_chaos.py - All expectations of every scenario are defined in
testcases.yamllocates in folderchaos_objects - Chaos Mesh is used to inject chaos into Milvus in
test_chaos.py
Run
Manually
Run a single test scenario manually(take query node pod is killed as instance):
-
update
ALL_CHAOS_YAMLS = 'chaos_querynode_podkill.yaml'inconstants.py -
run the commands below:
cd /milvus/tests/python_client/chaos pytest test_chaos.py --host ${Milvus_IP} -v
Run multiple test scenario in a category manually(take network partition chaos for all pods as instance):
-
update
ALL_CHAOS_YAMLS = 'chaos_*_network_partition.yaml'inconstants.py -
run the commands below:
cd /milvus/tests/python_client/chaos pytest test_chaos.py --host ${Milvus_IP} -v
Automation Scripts
Run test scenario automatically:
- update chaos type and pod in
chaos_test.sh - run the commands below:
cd /milvus/tests/python_client/chaos # in this step, script will install milvus with replicas_num and run testcase bash chaos_test.sh ${pod} ${chaos_type} ${chaos_task} ${replicas_num} # example: bash chaos_test.sh querynode pod_kill chaos-test 2
Github Action
Nightly
still in planning
Todo
- network attack
- clock skew
- IO injection
How to contribute
- Get familiar with chaos engineering and Chaos Mesh
- Design chaos scenarios, preferring to pick from todo list
- Generate yaml file for your chaos scenarios. You can create a chaos experiment in chaos-dashboard, then download the yaml file of it.
- Add yaml file to chaos_objects dir and rename it as
chaos_${component_name}_${chaos_type}.yaml. Make surekubectl apply -f ${your_chaos_yaml_file}can take effect - Add testcase in
testcases.yaml. You should figure out the expectation of milvus during the chaos - Run your added testcase according to
Manuallyabove and check whether it as your expectation