



# Keel - automated Kubernetes deployments for the rest of us
* Website [https://keel.sh](https://keel.sh)
* Slack - [kubernetes.slack.com](https://kubernetes.slack.com) look for channel #keel
Keel is a tool for automating [Kubernetes](https://kubernetes.io/) deployment updates. Keel is stateless, robust and lightweight.
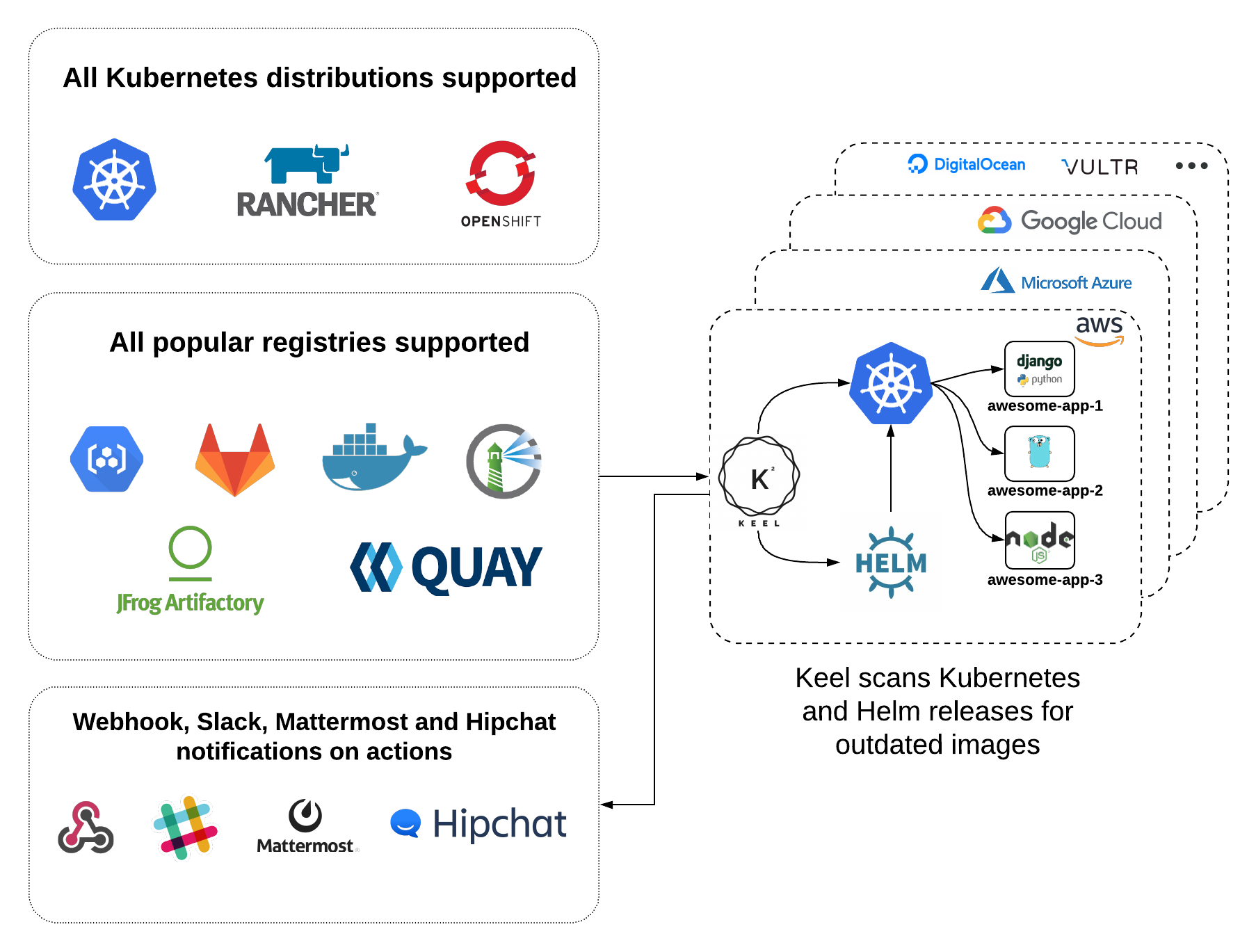
Keel provides several key features:
* __[Kubernetes](https://kubernetes.io/) and [Helm](https://helm.sh) providers__ - Keel has direct integrations with Kubernetes and Helm.
* __No CLI/API__ - tired of `f***ctl` for everything? Keel doesn't have one. Gets job done through labels, annotations, charts.
* __Semver policies__ - specify update policy for each deployment/Helm release individually.
* __Automatic [Google Container Registry](https://cloud.google.com/container-registry/) configuration__ - Keel automatically sets up topic and subscriptions for your deployment images by periodically scanning your environment.
* __[Native, DockerHub, Quay and Azure container registry webhooks](https://keel.sh/docs/#triggers) support__ - once webhook is received impacted deployments will be identified and updated.
* __[Polling](https://keel.sh/docs/#polling)__ - when webhooks and pubsub aren't available - Keel can still be useful by checking Docker Registry for new tags (if current tag is semver) or same tag SHA digest change (ie: `latest`).
* __Notifications__ - out of the box Keel has Slack, Hipchat, Mattermost and standard webhook notifications, more info [here](https://keel.sh/docs/#notifications)
### Support
Support Keel's development by:
* Star this repository
* [Follow on Twitter](https://twitter.com/keel_hq)
### Helm quick start
Prerequisites:
* [Helm](https://docs.helm.sh/using_helm/#installing-helm)
* Kubernetes
You need to add this Chart repo to Helm:
```bash
helm repo add keel https://charts.keel.sh
helm repo update
```
Install through Helm (with Helm provider enabled by default):
```bash
helm upgrade --install keel --namespace=kube-system keel/keel
```
If you work mostly with regular Kubernetes manifests, you can install Keel without Helm provider support:
```bash
helm upgrade --install keel --namespace=keel keel/keel --set helmProvider.enabled="false"
```
To install for Helm v3, set helmProvider.version="v3" (default is "v2"):
```bash
helm install keel keel/keel --set helmProvider.version="v3"
```
That's it, see [Configuration](https://github.com/keel-hq/keel#configuration) section now.
### Quick Start
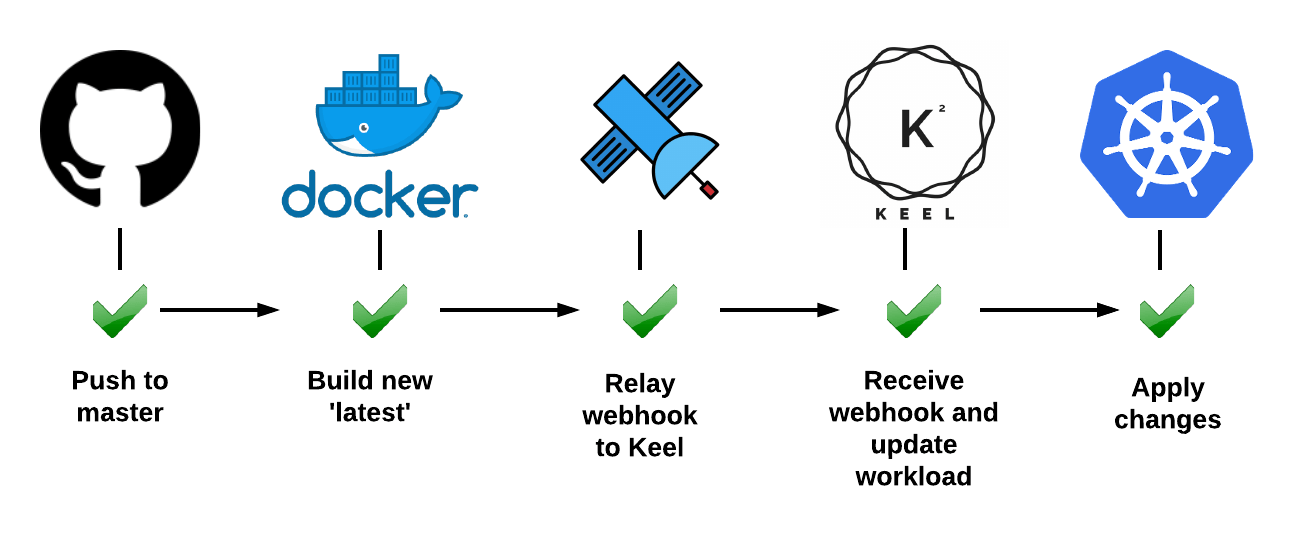
A step-by-step guide to install Keel on your Kubernetes cluster is viewable on the Keel website:
[https://keel.sh/examples/#example-1-push-to-deploy](https://keel.sh/examples/#example-1-push-to-deploy)
### Configuration
Once Keel is deployed, you only need to specify update policy on your deployment file or Helm chart:
```yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: wd
namespace: default
labels:
name: "wd"
annotations:
keel.sh/policy: minor # <-- policy name according to https://semver.org/
keel.sh/trigger: poll # <-- actively query registry, otherwise defaults to webhooks
spec:
template:
metadata:
name: wd
labels:
app: wd
spec:
containers:
- image: karolisr/webhook-demo:0.0.8
imagePullPolicy: Always
name: wd
command: ["/bin/webhook-demo"]
ports:
- containerPort: 8090
```
No additional configuration is required. Enabling continuous delivery for your workloads has never been this easy!
### Documentation
Documentation is viewable on the Keel Website:
[https://keel.sh/docs/#introduction](https://keel.sh/docs/#introduction)
### Contributing
Before starting to work on some big or medium features - raise an issue [here](https://github.com/keel-hq/keel/issues) so we can coordinate our efforts.
We use pull requests, so:
1. Fork this repository
2. Create a branch on your local copy with a sensible name
3. Push to your fork and open a pull request
### Developing Keel
If you wish to work on Keel itself, you will need Go 1.12+ installed. Make sure you put Keel into correct Gopath and `go build` (dependency management is done through [dep](https://github.com/golang/dep)).
To test Keel while developing:
1. Launch a Kubernetes cluster like Minikube or Docker for Mac with Kubernetes.
2. Change config to use it: `kubectl config use-context docker-for-desktop`
3. Build Keel from `cmd/keel` directory.
4. Start Keel with: `keel --no-incluster`. This will use Kubeconfig from your home.
### Running unit tests
Get a test parser (makes output nice):
```bash
go get github.com/mfridman/tparse
```
To run unit tests:
```bash
make test
```
### Running e2e tests
Prerequisites:
- configured kubectl + kubeconfig
- a running cluster (test suite will create testing namespaces and delete them after tests)
- Go environment (will compile Keel before running)
Once prerequisites are ready:
```bash
make e2e
```
