



# Keel - automated Kubernetes deployments for the rest of us
* Website [https://keel.sh](https://keel.sh)
* Slack - [kubernetes.slack.com](https://kubernetes.slack.com) look for channel #keel
Keel is a tool for automating [Kubernetes](https://kubernetes.io/) deployment updates. Keel is stateless, robust and lightweight.
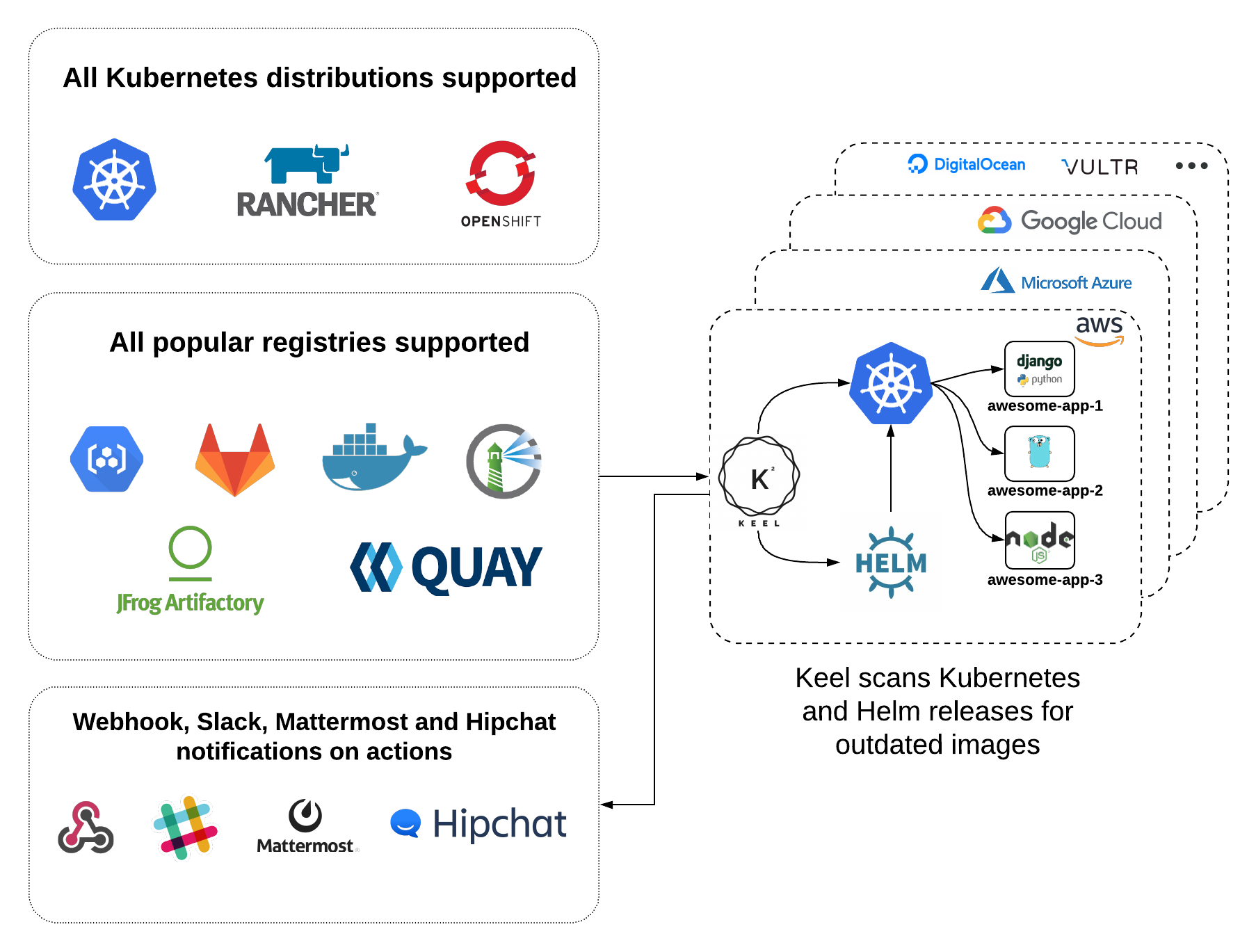
Keel provides several key features:
* __[Kubernetes](https://kubernetes.io/) and [Helm](https://helm.sh) providers__ - Keel has direct integrations with Kubernetes and Helm.
* __No CLI/API__ - tired of `f***ctl` for everything? Keel doesn't have one. Gets job done through labels, annotations, charts.
* __Semver policies__ - specify update policy for each deployment/Helm release individually.
* __Automatic [Google Container Registry](https://cloud.google.com/container-registry/) configuration__ - Keel automatically sets up topic and subscriptions for your deployment images by periodically scanning your environment.
* __[Native, DockerHub, Quay and Azure container registry webhooks](https://keel.sh/docs/#triggers) support__ - once webhook is received impacted deployments will be identified and updated.
* __[Polling](https://keel.sh/docs/#polling)__ - when webhooks and pubsub aren't available - Keel can still be useful by checking Docker Registry for new tags (if current tag is semver) or same tag SHA digest change (ie: `latest`).
* __Notifications__ - out of the box Keel has Slack, Hipchat, Mattermost and standard webhook notifications, more info [here](https://keel.sh/docs/#notifications)
### Support
Support Keel's development by:
* Star this repository
* [Follow on Twitter](https://twitter.com/keel_hq)
### Helm quick start
Prerequisites:
* [Helm](https://docs.helm.sh/using_helm/#installing-helm)
* Kubernetes
You need to add this Chart repo to Helm:
```bash
helm repo add keel https://keel-hq.github.io/keel/
helm repo update
```
Install through Helm (with Helm provider enabled by default):
```bash
helm upgrade --install keel --namespace=kube-system keel/keel
```
If you work mostly with regular Kubernetes manifests, you can install Keel without Helm provider support:
```bash
helm upgrade --install keel --namespace=keel keel/keel --set helmProvider.enabled="false"
```
To install for Helm v3, set helmProvider.version="v3" (default is "v2"):
```bash
helm install keel keel/keel --set helmProvider.version="v3"
```
To install using terraform:
```terraform
resource "helm_release" "keel" {
provider = helm.helm
name = "keel"
namespace = "keel"
repository = "https://keel-hq.github.io/keel"
chart = "keel"
version = "v1.0.4"
set {
name = "basicauth.enabled"
value = "true"
}
set {
name = "basicauth.user"
value = "admin"
}
set {
name = "basicauth.password"
value = "admin"
}
set {
name = "image.repository"
value = "keelhq/keel"
}
set {
name = "image.tag"
value = "0.19.1"
}
}
```
That's it, see [Configuration](https://github.com/keel-hq/keel#configuration) section now.
### Quick Start
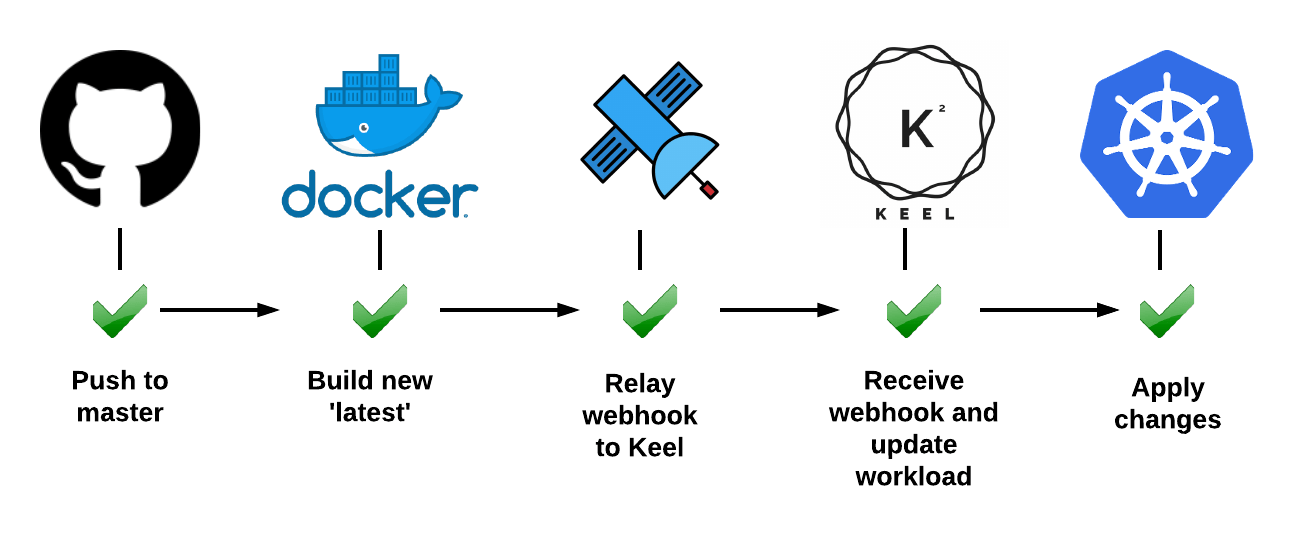
A step-by-step guide to install Keel on your Kubernetes cluster is viewable on the Keel website:
[https://keel.sh/examples/#example-1-push-to-deploy](https://keel.sh/examples/#example-1-push-to-deploy)
### Configuration
Once Keel is deployed, you only need to specify update policy on your deployment file or Helm chart:
```yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: wd
namespace: default
labels:
name: "wd"
annotations:
keel.sh/policy: minor # <-- policy name according to https://semver.org/
keel.sh/trigger: poll # <-- actively query registry, otherwise defaults to webhooks
spec:
template:
metadata:
name: wd
labels:
app: wd
spec:
containers:
- image: karolisr/webhook-demo:0.0.8
imagePullPolicy: Always
name: wd
command: ["/bin/webhook-demo"]
ports:
- containerPort: 8090
```
No additional configuration is required. Enabling continuous delivery for your workloads has never been this easy!
### Documentation
Documentation is viewable on the Keel Website:
[https://keel.sh/docs/#introduction](https://keel.sh/docs/#introduction)
### Contributing
Before starting to work on some big or medium features - raise an issue [here](https://github.com/keel-hq/keel/issues) so we can coordinate our efforts.
We use pull requests, so:
1. Fork this repository
2. Create a branch on your local copy with a sensible name
3. Push to your fork and open a pull request
### Developing Keel
If you wish to work on Keel itself, you will need Go 1.12+ installed. Make sure you put Keel into correct Gopath and `go build` (dependency management is done through [dep](https://github.com/golang/dep)).
To test Keel while developing:
1. Launch a Kubernetes cluster like Minikube or Docker for Mac with Kubernetes.
2. Change config to use it: `kubectl config use-context docker-for-desktop`
3. Build Keel from `cmd/keel` directory.
4. Start Keel with: `keel --no-incluster`. This will use Kubeconfig from your home.
### Debugging Keel on Windows
```powershell
# Ensure we have gcc and go
choco upgrade mingw -y
choco upgrade golang -y
# Move and build
cd cmd/keel
go build
$Env:XDG_DATA_HOME = $Env:APPDATA; # Data volume for the local database
$Env:HOME = $Env:USERPROFILE; # This is where the .kube/config will be read from
$Env:KUBERNETES_CONTEXT = "mycontext" #Use if you have more than one context in .kube/config
.\keel --no-incluster
```
### Running unit tests
Get a test parser (makes output nice):
```bash
go get github.com/mfridman/tparse
```
To run unit tests:
```bash
make test
```
### Running e2e tests
Prerequisites:
- configured kubectl + kubeconfig
- a running cluster (test suite will create testing namespaces and delete them after tests)
- Go environment (will compile Keel before running)
Once prerequisites are ready:
```bash
make e2e
```
### Debugging keel inside the container against your remote cluster (Windows)
The repository contains a debug version of keel container ready for remote debugging.
You can start the debug container with powershell (docker desktop needed):
```powershell
.\build.ps1 -StartDebugContainers
```
To connect to your cluster, copy the authentication details from within the keel pod in your cluster from:
```
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount
```
to the serviceaccount folder at the root of the repository and make sure you set the environment variable for the K8S management API endpoint:
```powershell
# This can be configured in envesttings.ps1 to be picked up automatically by the build script
$ENV:KUBERNETES_SERVICE_HOST = "mycluster-o5ff3caf.hcp.myregion.azmk8s.io"
$ENV:KUBERNETES_SERVICE_PORT = "443"
```
And make sure your API server is accesible from your client (VPN, IP whitelisting or whatever you use to secure your cluster management API).
Once started, simply use the debug option in a Go debugger, such as Jetbrains GoLand:
[Debugging a Go application inside a Docker container | The GoLand Blog](https://blog.jetbrains.com/go/2020/05/06/debugging-a-go-application-inside-a-docker-container/)
