migrated all v1 and v2 images to new image structure
parent
7666510726
commit
075c585ff8
|
|
@ -13,7 +13,7 @@ menu:
|
|||
Chronograf is InfluxData's open source web application.
|
||||
Use Chronograf with the other components of the [TICK stack](https://www.influxdata.com/products/) to visualize your monitoring data and easily create alerting and automation rules.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Key features
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ When you enter the InfluxDB HTTP bind address in the `Connection String` input,
|
|||
If it is a data node, Chronograf automatically adds the `Meta Service Connection URL` input to the connection details form.
|
||||
Enter the HTTP bind address of one of your cluster's meta nodes into that input and Chronograf takes care of the rest.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Note that the example above assumes that you do not have authentication enabled.
|
||||
If you have authentication enabled, the form requires username and password information.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -17,11 +17,11 @@ To create an InfluxDB connection in the Chronograf UI:
|
|||
1. Open Chronograf and click **Configuration** (wrench icon) in the navigation menu.
|
||||
2. Click **Add Connection**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
3. Enter values for the following fields:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
* **Connection String**: Enter the hostname or IP address of the InfluxDB instance and the port. The field is prefilled with `http://localhost:8086`.
|
||||
* **Name**: Enter the name for this connection.
|
||||
|
|
@ -134,11 +134,11 @@ To create a Kapacitor connection using the Chronograf UI:
|
|||
1. Open Chronograf and click **Configuration** (wrench icon) in the navigation menu.
|
||||
2. Next to an existing [InfluxDB connection](#managing-influxdb-connections-using-the-chronograf-ui), click **Add Kapacitor Connection** if there are no existing Kapacitor connections or select **Add Kapacitor Connection** in the **Kapacitor Connection** dropdown list.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
3. In the **Connection Details** section, enter values for the following fields:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
* **Kapacitor URL**: Enter the hostname or IP address of the Kapacitor instance and the port. The field is prefilled with `http://localhost:9092`.
|
||||
* **Name**: Enter the name for this connection.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ This allows you to recreate robust dashboards without having to manually configu
|
|||
2. Hover over the dashboard you would like to export and click the "Export"
|
||||
button that appears to the right.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.6/dashboard-export.png" alt="Exporting a Chronograf dashboard" style="width:100%;max-width:912px"/>
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-dashboard-export.png" alt="Exporting a Chronograf dashboard" style="width:100%;max-width:912px"/>
|
||||
|
||||
This downloads a JSON file containing dashboard information including template variables,
|
||||
cells and cell information such as the query, cell-sizing, color scheme, visualization type, etc.
|
||||
|
|
@ -35,13 +35,13 @@ cells and cell information such as the query, cell-sizing, color scheme, visuali
|
|||
|
||||
The newly imported dashboard will be included in your list of dashboards.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Reconciling unmatched sources
|
||||
If the data sources defined in the imported dashboard JSON file do not match any of your local sources,
|
||||
you will have to reconcile each of the unmatched sources during the import process.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Required user roles
|
||||
Depending on the role of your user, there are some restrictions on importing and exporting dashboards:
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -88,7 +88,7 @@ On the **Chronograf Admin** page:
|
|||
* Change user passwords
|
||||
* Assign admin and remove admin permissions to or from a user
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
InfluxDB users are either admin users or non-admin users.
|
||||
See InfluxDB's [authentication and authorization](/influxdb/latest/query_language/authentication_and_authorization/#user-types-and-privileges) documentation for more information about those user types.
|
||||
|
|
@ -129,7 +129,7 @@ On the `Admin` page:
|
|||
* Create, edit, and delete roles
|
||||
* Assign and remove roles to or from a user
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### User types
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -306,4 +306,4 @@ For example, the image below contains three roles: `CREATOR`, `DESTROYER`, and `
|
|||
`CREATOR` includes two permissions (`CreateDatbase` and `CreateUserAndRole`) and is assigned to one user (`chrononut`).
|
||||
`DESTROYER` also includes two permissions (`DropDatabase` and `DropData`) and is assigned to two users (`chrononut` and `chronelda`).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -25,7 +25,7 @@ The following sections describe the Chronograf features that relate to the web a
|
|||
In the web admin interface, users chose the target database in the top right corner and selected from a set of query templates in the `Query Templates` dropdown.
|
||||
The templates included queries with no user-provided values (example: [`SHOW MEASUREMENTS`](/influxdb/latest/query_language/schema_exploration/#show-measurements)) and queries with user-provided values (example: [`SHOW TAG KEYS FROM "<measurement_name>"`](/influxdb/latest/query_language/schema_exploration/#show-tag-keys)).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Chronograf
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -33,7 +33,7 @@ In Chronograf, the same `Query Templates` dropdown appears in the Data Explorer.
|
|||
To use query templates, select a query from the set of available queries and insert the relevant user-provided values.
|
||||
Note that unlike the web admin interface, Chronograf does not have a database dropdown; the query must specify the target database.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Writing data
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -41,7 +41,7 @@ Note that unlike the web admin interface, Chronograf does not have a database dr
|
|||
|
||||
To write data to InfluxDB, users selected the target database in the top right corner, clicked the `Write Data` icon, and entered their [line protocol](/influxdb/latest/concepts/glossary/#line-protocol) in the text input:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Chronograf
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -49,7 +49,7 @@ In versions 1.3.2.0+, Chronograf's Data Explorer offers the same write functiona
|
|||
To write data to InfluxDB, click the `Write Data` icon at the top of the Data Explorer page and select your target database.
|
||||
Next, enter your line protocol in the main text box and click the `Write` button.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Database and retention policy management
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -57,7 +57,7 @@ Next, enter your line protocol in the main text box and click the `Write` button
|
|||
|
||||
In the web admin interface, the `Query Template` dropdown was the only way to manage databases and [retention policies](/influxdb/latest/concepts/glossary/#retention-policy-rp) (RP):
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Chronograf
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -65,7 +65,7 @@ In Chronograf, the `Admin` page includes a complete user interface for database
|
|||
The `Admin` page allows users to view, create, and delete databases and RPs without having to learn the relevant query syntax.
|
||||
The GIF below shows the process of creating a database, creating an RP, and deleting that database.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Note that, like the web admin interface, Chronograf's [`Query Templates` dropdown](#chronograf) includes the database- and RP-related queries.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -75,7 +75,7 @@ Note that, like the web admin interface, Chronograf's [`Query Templates` dropdow
|
|||
|
||||
In the web admin interface, the `Query Template` dropdown was the only way to manage users:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Chronograf
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -89,6 +89,6 @@ The `Admin` page allows users to:
|
|||
* Create, edit, and delete roles (available in InfluxDB Enterprise only)
|
||||
* Assign and remove roles to or from a user (available in InfluxDB Enterprise only)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Note that, like the web admin interface, Chronograf's [`Query Templates` dropdown](#chronograf) includes the user-related queries.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -31,7 +31,7 @@ In the Databases tab:
|
|||
|
||||
#### Step 1: Locate the `chronograf` database and click on the infinity symbol (∞)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 2: Enter a different duration
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -50,7 +50,7 @@ Those alerts no longer appear in your InfluxDB instance or on Chronograf's Alert
|
|||
Looking at the image below and assuming that the current time is 19:00 on April 27, 2017, only the first three alerts would appear in your alert history; they occurred within the previous hour (18:00 through 19:00).
|
||||
The fourth alert, which occurred on the same day at 16:58:50, is outside the previous hour and would no longer appear in the InfluxDB `chronograf` database or on the Chronograf Alert History page.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## TICKscript management
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -69,4 +69,4 @@ You cannot edit pre-existing tasks on the Chronograf Alert Rules page.
|
|||
The `mytick` task in the image below is a pre-existing task; its name appears on the Alert Rules page but you cannot click on it or edit its TICKscript in the interface.
|
||||
Currently, you must manually edit your existing tasks and TICKscripts on your machine.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -18,21 +18,21 @@ Logs data is a first class citizen in InfluxDB and is populated using available
|
|||
## Viewing logs in Chronograf
|
||||
Chronograf has a dedicated log viewer accessed by clicking the "Log Viewer" button in the left navigation.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.6/logs-nav-log-viewer.png" alt="Log viewer in the left nav" style="width:100%;max-width:209px;"/>
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-logs-nav-log-viewer.png" alt="Log viewer in the left nav" style="width:100%;max-width:209px;"/>
|
||||
|
||||
The log viewer provides a detailed histogram showing the time-based distribution of log entries color-coded by log severity.
|
||||
It also includes a live stream of logs that can be searched, filtered, and paused to analyze specific time ranges.
|
||||
Logs are pulled from the `syslog` measurement.
|
||||
_Other log inputs and alternate log measurement options will be available in future updates._
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.6/logs-log-viewer.png" alt="Chronograf log viewer" style="width:100%;max-width:1016px;"/>
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-logs-log-viewer.png" alt="Chronograf log viewer" style="width:100%;max-width:1016px;"/>
|
||||
|
||||
### Searching and filtering logs
|
||||
Logs are searched using keywords or regular expressions.
|
||||
They can also be filtered by clicking values in the log table such as `severity` or `facility`.
|
||||
Any tag values included with the log entry can be used as a filter.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
> **Note:** The log search field is case-sensitive.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -45,13 +45,13 @@ Timeframe selection allows you to go to to a specific event and see logs both pr
|
|||
When viewing logs from a previous time window, first select the target time, then select the offset.
|
||||
The offset is used to define the upper and lower thresholds of the window from which logs are pulled.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Configuring the log viewer
|
||||
The log viewer can be customized to fit your specific needs.
|
||||
Open the log viewer configuration options by clicking the gear button in the top right corner of the log viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.6/logs-log-viewer-config-options.png" alt="Log viewer configuration options" style="width:100%;max-width:819px;"/>
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-logs-log-viewer-config-options.png" alt="Log viewer configuration options" style="width:100%;max-width:819px;"/>
|
||||
|
||||
### Severity colors
|
||||
Every log severity is assigned a color which is used in the display of log entries.
|
||||
|
|
@ -68,15 +68,15 @@ Below are the options and how they appear in the log table:
|
|||
|
||||
| Severity Format | Display |
|
||||
| --------------- |:------- |
|
||||
| Dot | <img src="/img/chronograf/v1.6/logs-serverity-fmt-dot.png" alt="Log serverity format 'Dot'" style="display:inline;max-height:24px;"/> |
|
||||
| Dot + Text | <img src="/img/chronograf/v1.6/logs-serverity-fmt-dot-text.png" alt="Log serverity format 'Dot + Text'" style="display:inline;max-height:24px;"/> |
|
||||
| Text | <img src="/img/chronograf/v1.6/logs-serverity-fmt-text.png" alt="Log serverity format 'Text'" style="display:inline;max-height:24px;"/> |
|
||||
| Dot | <img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-logs-serverity-fmt-dot.png" alt="Log serverity format 'Dot'" style="display:inline;max-height:24px;"/> |
|
||||
| Dot + Text | <img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-logs-serverity-fmt-dot-text.png" alt="Log serverity format 'Dot + Text'" style="display:inline;max-height:24px;"/> |
|
||||
| Text | <img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-logs-serverity-fmt-text.png" alt="Log serverity format 'Text'" style="display:inline;max-height:24px;"/> |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Logs in dashboards
|
||||
An incredibly powerful way to analyze log data is by creating dashboards that include log data.
|
||||
This is possible by using the [Table visualization type](/chronograf/v1.6/guides/visualization-types/#table) to display log data in your dashboard.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
This type of visualization allows you to quickly identify anomalies in other metrics and see logs associated with those anomalies.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ The following screenshot of five graph views displays annotations for a single p
|
|||
The text and timestamp for the single point in time can be seem above the annotation line in the graph view on the lower right.
|
||||
The annotation displays "`Deploy v3.8.1-2`" and the time "`2018/28/02 15:59:30:00`".
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**To add and edit an annotation:**
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -18,11 +18,11 @@ Dashboards in Chronograf can be cloned (or copied) to be used to create a dashbo
|
|||
|
||||
1. On the **Dashboards** page, hover your cursor over the listing of the dashboard that you want to clone and click the **Clone** button that appears.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The cloned dashboard opens and displays the name of the original dashboard with `(clone)` after it.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You can now change the dashboard name and customize the dashboard.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -34,10 +34,10 @@ Cells in Chronograf dashboards can be cloned, or copied, to quickly create a cel
|
|||
|
||||
1. On the dashboard cell that you want to make a copy of, click the **Clone** icon and then confirm by clicking **Clone Cell**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
2. The cloned cell appears in the dashboard displaying the nameof the original cell with `(clone)` after it.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You can now change the cell name and customize the cell.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -58,7 +58,7 @@ For example, Chronograf's Slack integration allows users to specify a default ch
|
|||
Configure Chronograf to send alert messages to a HipChat room.
|
||||
The sections below describe each configuration option.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Subdomain
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -88,7 +88,7 @@ The following steps describe how to create the API access token:
|
|||
|
||||
Your token appears in the table just above the **Create new token** section:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Kafka
|
||||
|
|
@ -226,7 +226,7 @@ Click **Add Another Config** to add additional Slack alert endpoints. Each addit
|
|||
Configure Chronograf to send alert messages to an existing Telegram bot.
|
||||
The sections below describe each configuration option.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Telegram bot
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ This guide shows you how to create custom Chronograf dashboards.
|
|||
|
||||
By the end of this guide, you'll be aware of the tools available to you for creating dashboards similar to this example:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Requirements
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -36,7 +36,7 @@ Click **Name This Dashboard** and type a new name. In this guide, "ChronoDash" i
|
|||
In the first cell, titled "Untitled Cell", click **Edit**
|
||||
to open the cell editor mode.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Step 3: Create your query
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -51,13 +51,13 @@ Those defaults are configurable using the query builder or by manually editing t
|
|||
|
||||
In addition, the time range (`:dashboardTime:`) is [configurable on the dashboard](#step-6-configure-your-dashboard).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Step 4: Choose your visualization type
|
||||
|
||||
Chronograf supports many different [visualization types](/chronograf/latest/guides/visualization-types/). To choose a visualization type, click **Visualization** and select **Step-Plot Graph**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Step 5: Save your cell
|
||||
Click **Save** (the green checkmark icon) to save your cell.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -38,12 +38,12 @@ See the [Configuring Kapacitor Event Handlers](/chronograf/latest/guides/configu
|
|||
|
||||
Navigate to the **Manage Tasks** page under **Alerting** in the left navigation, then click **+ Build Alert Rule** in the top right corner.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The **Manage Tasks** page is used to create and edit your Chronograf alert rules.
|
||||
The steps below guide you through the process of creating a Chronograf alert rule.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Step 1: Name the alert rule
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -72,7 +72,7 @@ Navigate through databases, measurements, fields, and tags to select the relevan
|
|||
|
||||
In this example, select the `telegraf` [database](/influxdb/latest/concepts/glossary/#database), the `autogen` [retention policy](/influxdb/latest/concepts/glossary/#retention-policy-rp), the `cpu` [measurement](/influxdb/latest/concepts/glossary/#measurement), and the `usage_idle` [field](/influxdb/latest/concepts/glossary/#field).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Step 4: Define the rule condition
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -80,7 +80,7 @@ Define the threshold condition.
|
|||
Condition options are determined by the [alert type](#step-2-select-the-alert-type).
|
||||
For this example, the alert conditions are if `usage_idle` is less than `80`.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The graph shows a preview of the relevant data and the threshold number.
|
||||
By default, the graph shows data from the past 15 minutes.
|
||||
|
|
@ -98,7 +98,7 @@ Each handler has unique configurable options.
|
|||
|
||||
For this example, choose the **slack** alert handler and enter the desired options.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
> Multiple alert handlers can be added to send alerts to multiple endpoints.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -111,7 +111,7 @@ As you type your alert message, clicking the data templates will insert them at
|
|||
|
||||
In this example, use the alert message, `Your idle CPU usage is {{.Level}} at {{ index .Fields "value" }}.`.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*View the Kapacitor documentation for more information about [message template data](/kapacitor/latest/nodes/alert_node/#message).*
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -120,7 +120,7 @@ In this example, use the alert message, `Your idle CPU usage is {{.Level}} at {{
|
|||
Click **Save Rule** in the top right corner and navigate to the **Manage Tasks** page to see your rule.
|
||||
Notice that you can easily enable and disable the rule by toggling the checkbox in the **Enabled** column.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Next, move on to the section below to experience your alert rule in action.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -149,10 +149,10 @@ Assuming the first step was successful, `#ohnos` should reveal at least two aler
|
|||
* The first alert message indicates that your idle CPU usage was `CRITICAL`, meaning it dipped below `80%`.
|
||||
* The second alert message indicates that your idle CPU usage returned to an `OK` level of `80%` or above.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You can also see alerts on the **Alert History** page available under **Alerting** in the left navigation.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
That's it! You've successfully used Chronograf to configure an alert rule to monitor your idle CPU usage and send notifications to Slack.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -25,7 +25,7 @@ You can use either [predefined template variables](#predefined-template-variable
|
|||
or [custom template variables](#create-custom-template-variables).
|
||||
Variable values are then selected in your dashboard user-interface (UI).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Predefined template variables
|
||||
Chronograf includes predefined template variables controlled by elements in the Chrongraf UI.
|
||||
|
|
@ -38,7 +38,7 @@ These template variables can be used in any of your cells' queries.
|
|||
### dashboardTime
|
||||
The `:dashboardTime:` template variable is controlled by the "time" dropdown in your Chronograf dashboard.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.6/template-vars-time-dropdown.png" style="width:100%;max-width:549px;" alt="Dashboard time selector"/>
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-template-vars-time-dropdown.png" style="width:100%;max-width:549px;" alt="Dashboard time selector"/>
|
||||
|
||||
If using relative times, it represents the time offset specified in the dropdown (-5m, -15m, -30m, etc.) and assumes time is relative to "now".
|
||||
If using absolute times defined by the date picker, `:dashboardTime:` is populated with lower threshold.
|
||||
|
|
@ -56,7 +56,7 @@ WHERE time > :dashboardTime:
|
|||
### upperDashboardTime
|
||||
The `:upperDashboardTime:` template variable is defined by the upper time limit specified using the date picker.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.6/template-vars-date-picker.png" style="width:100%;max-width:762px;" alt="Dashboard date picker"/>
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-template-vars-date-picker.png" style="width:100%;max-width:762px;" alt="Dashboard date picker"/>
|
||||
|
||||
It will inherit `now()` when using relative time frames or the upper time limit when using absolute timeframes.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -69,7 +69,7 @@ WHERE time > :dashboardTime: AND time < :upperDashboardTime:
|
|||
### interval
|
||||
The `:interval:` template variable is defined by the interval dropdown in the Chronograf dashboard.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.6/template-vars-interval-dropdown.png" style="width:100%;max-width:549px;" alt="Dashboard interval selector"/>
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-template-vars-interval-dropdown.png" style="width:100%;max-width:549px;" alt="Dashboard interval selector"/>
|
||||
|
||||
In cell queries, it should be used in the `GROUP BY time()` clause that accompanies aggregate functions:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -95,7 +95,7 @@ To create a template variable:
|
|||
If using the CSV or Map types, upload or input the CSV with the desired values in the appropriate format then select a default value.
|
||||
5. Click **Create**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Once created, the template variable can be used in any of your cell's queries or titles
|
||||
and a dropdown for the variable will be included at the top of your dashboard.
|
||||
|
|
@ -251,7 +251,7 @@ key3,value3
|
|||
key4,value4
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.6/template-vars-map-dropdown.png" style="width:100%;max-width:140px;" alt="Map variable dropdown"/>
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-template-vars-map-dropdown.png" style="width:100%;max-width:140px;" alt="Map variable dropdown"/>
|
||||
|
||||
> If values are meant to be used as string field values, wrap them in single quote ([required by InfluxQL](/influxdb/latest/troubleshooting/frequently-asked-questions/#when-should-i-single-quote-and-when-should-i-double-quote-in-queries)). This only pertains to values. String keys do not matter.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -285,7 +285,7 @@ The customer names would populate your template variable dropdown rather than th
|
|||
Vary part of a query with a customized meta query that pulls a specific array of values from InfluxDB.
|
||||
These variables allow you to pull a highly customized array of potential values and offer advanced functionality such as [filtering values based on other template variables](#filtering-template-variables-with-other-template-variables).
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.6/template-vars-custom-meta-query.png" style="width:100%;max-width:667px;" alt="Custom meta query"/>
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-template-vars-custom-meta-query.png" style="width:100%;max-width:667px;" alt="Custom meta query"/>
|
||||
|
||||
_**Example custom meta query variable in a cell query**_
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
|
|
@ -330,7 +330,7 @@ For example, let's say you want to list all the field keys associated with a mea
|
|||
|
||||
1. Create a template variable named `:measurementVar:` _(the name "measurement" is [reserved]( #reserved-variable-names))_ that uses the [Measurements](#measurements) variable type to pull in all measurements from the `telegraf` database.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.6/template-vars-measurement-var.png" style="width:100%;max-width:667px;" alt="measurementVar"/>
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-template-vars-measurement-var.png" style="width:100%;max-width:667px;" alt="measurementVar"/>
|
||||
|
||||
2. Create a template variable named `:fieldKey:` that uses the [custom meta query](#custom-meta-query) variable type.
|
||||
The following meta query pulls a list of field keys based on the existing `:measurementVar:` template variable.
|
||||
|
|
@ -339,7 +339,7 @@ The following meta query pulls a list of field keys based on the existing `:meas
|
|||
SHOW FIELD KEYS ON telegraf FROM :measurementVar:
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.6/template-vars-fieldkey.png" style="width:100%;max-width:667px;" alt="fieldKey"/>
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-template-vars-fieldkey.png" style="width:100%;max-width:667px;" alt="fieldKey"/>
|
||||
|
||||
3. Create a new dashboard cell that uses the `:fieldKey:` and `:measurementVar` template variables in its query.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -349,7 +349,7 @@ The following meta query pulls a list of field keys based on the existing `:meas
|
|||
|
||||
The resulting dashboard will work like this:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Defining template variables in the URL
|
||||
Chronograf uses URL query parameters (also known as query string parameters) to set both display options and template variables in the URL.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ Chronograf and the other components of the TICK stack are supported on several o
|
|||
|
||||
Before we begin, here's an overview of the final monitoring setup:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The diagram above shows an InfluxDB Enterprise cluster that consists of three meta nodes (M) and three data nodes (D).
|
||||
Each data node has its own [Telegraf](/telegraf/latest/) instance (T).
|
||||
|
|
@ -233,7 +233,7 @@ Chronograf can be downloaded from the [InfluxData downloads page](https://portal
|
|||
To access Chronograf, go to http://localhost:8888.
|
||||
The welcome page includes instructions for connecting Chronograf to that instance.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
For the `Connection String`, enter the hostname or IP of your InfluxDB OSS instance, and be sure to include the default port: `8086`.
|
||||
Next, name your data source; this can be anything you want.
|
||||
|
|
@ -245,17 +245,17 @@ Chronograf works with the Telegraf data in your InfluxDB OSS instance.
|
|||
The `Host List` page shows your data node's hostnames, their statuses, CPU usage, load, and their configured applications.
|
||||
In this case, you've only enabled the system stats input plugin so `system` is the single application that appears in the `Apps` column.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Click `system` to see the Chronograf canned dashboard for that application.
|
||||
Keep an eye on your data nodes by viewing that dashboard for each hostname:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Next, check out the Data Explorer to create a customized graph with the monitoring data.
|
||||
In the image below, the Chronograf query editor is used to visualize the idle CPU usage data for each data node:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Create more customized graphs and save them to a dashboard on the Dashboard page in Chronograf.
|
||||
See the [Creating Chronograf dashboards](/chronograf/latest/guides/create-a-dashboard/) guide for more information.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -13,7 +13,7 @@ Presentation mode allows you to view Chronograf in full screen, hiding the left
|
|||
## Entering presentation mode manually
|
||||
To enter presentation mode manually, click the icon in the upper right:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/chronograf-presentation-mode.png" style="width:100%; max-width:500px"/>
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-presentation-mode.png" style="width:100%; max-width:500px"/>
|
||||
|
||||
To exit presentation mode, press `ESC`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ menu:
|
|||
|
||||
Chronograf's dashboard views support the following visualization types, which can be selected in the **Visualization Type** selection view.
|
||||
|
||||
[Visualization Type selector](/img/chronograf/chrono-viz-types-selector.png)
|
||||
[Visualization Type selector](/img/chronograf/1-6-viz-types-selector.png)
|
||||
|
||||
Each of the available visualization types and available user controls are described below.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -30,11 +30,11 @@ For information on adding and displaying annotations in graph views, see [Adding
|
|||
|
||||
The **Line Graph** view displays a time series in a line graph.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Line Graph Controls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Use the **Line Graph Controls** to specify the following:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -53,18 +53,18 @@ Use the **Line Graph Controls** to specify the following:
|
|||
|
||||
#### Line Graph example
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Stacked Graph
|
||||
|
||||
The **Stacked Graph** view displays multiple time series bars as segments stacked on top of each other.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Stacked Graph Controls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Use the **Stacked Graph Controls** to specify the following:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -83,18 +83,18 @@ Use the **Stacked Graph Controls** to specify the following:
|
|||
|
||||
#### Stacked Graph example
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Step-Plot Graph
|
||||
|
||||
The **Step-Plot Graph** view displays a time series in a staircase graph.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Step-Plot Graph Controls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Use the **Step-Plot Graph Controls** to specify the following:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -111,7 +111,7 @@ Use the **Step-Plot Graph Controls** to specify the following:
|
|||
|
||||
#### Step-Plot Graph example
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Bar Graph
|
||||
|
|
@ -120,11 +120,11 @@ The **Bar Graph** view displays the specified time series using a bar chart.
|
|||
|
||||
To select this view, click the Bar Graph selector icon.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Bar Graph Controls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Use the **Bar Graph Controls** to specify the following:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -141,7 +141,7 @@ Use the **Bar Graph Controls** to specify the following:
|
|||
|
||||
#### Bar Graph example
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Line Graph + Single Stat
|
||||
|
|
@ -150,11 +150,11 @@ The **Line Graph + Single Stat** view displays the specified time series in a li
|
|||
|
||||
To select this view, click the **Line Graph + Single Stat** view option.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Line Graph + Single Stat Controls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Use the **Line Graph + Single Stat Controls** to specify the following:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -171,13 +171,13 @@ Use the **Line Graph + Single Stat Controls** to specify the following:
|
|||
|
||||
#### Line Graph + Single Stat example
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Single Stat
|
||||
|
||||
The **Single Stat** view displays the most recent value of the specified time series as a numerical value.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If a cell's query includes a [`GROUP BY` tag](/influxdb/latest/query_language/data_exploration/#group-by-tags) clause, Chronograf sorts the different [series](/influxdb/latest/concepts/glossary/#series) lexicographically and shows the most recent [field value](/influxdb/latest/concepts/glossary/#field-value) associated with the first series.
|
||||
For example, if a query groups by the `name` [tag key](/influxdb/latest/concepts/glossary/#tag-key) and `name` has two [tag values](/influxdb/latest/concepts/glossary/#tag-value) (`chronelda` and `chronz`), Chronograf shows the most recent field value associated with the `chronelda` series.
|
||||
|
|
@ -203,11 +203,11 @@ The **Gauge** view displays the single value most recent value for a time series
|
|||
|
||||
To select this view, click the Gauge selector icon.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Gauge Controls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Use the **Gauge Controls** to specify the following:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -221,17 +221,17 @@ Use the **Gauge Controls** to specify the following:
|
|||
|
||||
#### Gauge example
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Table
|
||||
|
||||
The **Table** panel displays the results of queries in a tabular view, which is sometimes easier to analyze than graph views of data.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Table Controls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Use the **Table Controls** to specify the following:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -255,4 +255,4 @@ Use the **Table Controls** to specify the following:
|
|||
|
||||
#### Table view example
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ When you enter the InfluxDB HTTP bind address in the `Connection String` input,
|
|||
If it is a data node, Chronograf automatically adds the `Meta Service Connection URL` input to the connection details form.
|
||||
Enter the HTTP bind address of one of your cluster's meta nodes into that input and Chronograf takes care of the rest.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Note that the example above assumes that you do not have authentication enabled.
|
||||
If you have authentication enabled, the form requires username and password information.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ menu:
|
|||
Chronograf is InfluxData's open source web application.
|
||||
Use Chronograf with the other components of the [TICK stack](https://www.influxdata.com/products/) to visualize your monitoring data and easily create alerting and automation rules.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Key features
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ When you enter the InfluxDB HTTP bind address in the `Connection String` input,
|
|||
If it is a data node, Chronograf automatically adds the `Meta Service Connection URL` input to the connection details form.
|
||||
Enter the HTTP bind address of one of your cluster's meta nodes into that input and Chronograf takes care of the rest.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Note that the example above assumes that you do not have authentication enabled.
|
||||
If you have authentication enabled, the form requires username and password information.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -23,10 +23,10 @@ To create an InfluxDB connection in the Chronograf UI:
|
|||
|
||||
1. Open Chronograf and click **Configuration** (wrench icon) in the navigation menu.
|
||||
2. Click **Add Connection**.
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
3. Enter values for the following fields:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.7/influxdb-connection-config.png" style="width:100%; max-width:600px;">
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-7-influxdb-connection-config.png" style="width:100%; max-width:600px;">
|
||||
|
||||
* **Connection URL**: Enter the hostname or IP address of the InfluxDB instance and the port. The field is prefilled with `http://localhost:8086`.
|
||||
* **Connection Name**: Enter the name for this connection.
|
||||
|
|
@ -167,11 +167,11 @@ To create a Kapacitor connection using the Chronograf UI:
|
|||
|
||||
1. Open Chronograf and click **Configuration** (wrench icon) in the navigation menu.
|
||||
2. Next to an existing [InfluxDB connection](#managing-influxdb-connections-using-the-chronograf-ui), click **Add Kapacitor Connection** if there are no existing Kapacitor connections or select **Add Kapacitor Connection** in the **Kapacitor Connection** dropdown list.
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
3. In the **Connection Details** section, enter values for the following fields:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.7/kapacitor-connection-config.png" style="width:100%; max-width:600px;">
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-7-kapacitor-connection-config.png" style="width:100%; max-width:600px;">
|
||||
|
||||
* **Kapacitor URL**: Enter the hostname or IP address of the Kapacitor instance and the port. The field is prefilled with `http://localhost:9092`.
|
||||
* **Name**: Enter the name for this connection.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ This allows you to recreate robust dashboards without having to manually configu
|
|||
2. Hover over the dashboard you would like to export and click the "Export"
|
||||
button that appears to the right.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.7/dashboard-export.png" alt="Exporting a Chronograf dashboard" style="width:100%;max-width:912px"/>
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-dashboard-export.png" alt="Exporting a Chronograf dashboard" style="width:100%;max-width:912px"/>
|
||||
|
||||
This downloads a JSON file containing dashboard information including template variables,
|
||||
cells and cell information such as the query, cell-sizing, color scheme, visualization type, etc.
|
||||
|
|
@ -35,13 +35,13 @@ cells and cell information such as the query, cell-sizing, color scheme, visuali
|
|||
|
||||
The newly imported dashboard will be included in your list of dashboards.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Reconciling unmatched sources
|
||||
If the data sources defined in the imported dashboard JSON file do not match any of your local sources,
|
||||
you will have to reconcile each of the unmatched sources during the import process.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Required user roles
|
||||
Depending on the role of your user, there are some restrictions on importing and exporting dashboards:
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -88,7 +88,7 @@ On the **Chronograf Admin** page:
|
|||
* Change user passwords
|
||||
* Assign admin and remove admin permissions to or from a user
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
InfluxDB users are either admin users or non-admin users.
|
||||
See InfluxDB's [authentication and authorization](/influxdb/latest/administration/authentication_and_authorization/#user-types-and-privileges) documentation for more information about those user types.
|
||||
|
|
@ -129,7 +129,7 @@ On the `Admin` page:
|
|||
* Create, edit, and delete roles
|
||||
* Assign and remove roles to or from a user
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### User types
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -306,4 +306,4 @@ For example, the image below contains three roles: `CREATOR`, `DESTROYER`, and `
|
|||
`CREATOR` includes two permissions (`CreateDatbase` and `CreateUserAndRole`) and is assigned to one user (`chrononut`).
|
||||
`DESTROYER` also includes two permissions (`DropDatabase` and `DropData`) and is assigned to two users (`chrononut` and `chronelda`).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -25,7 +25,7 @@ The following sections describe the Chronograf features that relate to the web a
|
|||
In the web admin interface, users chose the target database in the top right corner and selected from a set of query templates in the `Query Templates` dropdown.
|
||||
The templates included queries with no user-provided values (example: [`SHOW MEASUREMENTS`](/influxdb/latest/query_language/schema_exploration/#show-measurements)) and queries with user-provided values (example: [`SHOW TAG KEYS FROM "<measurement_name>"`](/influxdb/latest/query_language/schema_exploration/#show-tag-keys)).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Chronograf
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -33,7 +33,7 @@ In Chronograf, the same `Query Templates` dropdown appears in the Data Explorer.
|
|||
To use query templates, select a query from the set of available queries and insert the relevant user-provided values.
|
||||
Note that unlike the web admin interface, Chronograf does not have a database dropdown; the query must specify the target database.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Writing data
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -41,7 +41,7 @@ Note that unlike the web admin interface, Chronograf does not have a database dr
|
|||
|
||||
To write data to InfluxDB, users selected the target database in the top right corner, clicked the `Write Data` icon, and entered their [line protocol](/influxdb/latest/concepts/glossary/#influxdb-line-protocol) in the text input:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Chronograf
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -49,7 +49,7 @@ In versions 1.3.2.0+, Chronograf's Data Explorer offers the same write functiona
|
|||
To write data to InfluxDB, click the `Write Data` icon at the top of the Data Explorer page and select your target database.
|
||||
Next, enter your line protocol in the main text box and click the `Write` button.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Database and retention policy management
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -57,7 +57,7 @@ Next, enter your line protocol in the main text box and click the `Write` button
|
|||
|
||||
In the web admin interface, the `Query Template` dropdown was the only way to manage databases and [retention policies](/influxdb/latest/concepts/glossary/#retention-policy-rp) (RP):
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Chronograf
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -65,7 +65,7 @@ In Chronograf, the `Admin` page includes a complete user interface for database
|
|||
The `Admin` page allows users to view, create, and delete databases and RPs without having to learn the relevant query syntax.
|
||||
The GIF below shows the process of creating a database, creating an RP, and deleting that database.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Note that, like the web admin interface, Chronograf's [`Query Templates` dropdown](#chronograf) includes the database- and RP-related queries.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -75,7 +75,7 @@ Note that, like the web admin interface, Chronograf's [`Query Templates` dropdow
|
|||
|
||||
In the web admin interface, the `Query Template` dropdown was the only way to manage users:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Chronograf
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -89,6 +89,6 @@ The `Admin` page allows users to:
|
|||
* Create, edit, and delete roles (available in InfluxEnterprise only)
|
||||
* Assign and remove roles to or from a user (available in InfluxEnterprise only)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Note that, like the web admin interface, Chronograf's [`Query Templates` dropdown](#chronograf) includes the user-related queries.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -31,7 +31,7 @@ In the Databases tab:
|
|||
|
||||
#### Step 1: Locate the `chronograf` database and click on the infinity symbol (∞)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 2: Enter a different duration
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -50,7 +50,7 @@ Those alerts no longer appear in your InfluxDB instance or on Chronograf's Alert
|
|||
Looking at the image below and assuming that the current time is 19:00 on April 27, 2017, only the first three alerts would appear in your alert history; they occurred within the previous hour (18:00 through 19:00).
|
||||
The fourth alert, which occurred on the same day at 16:58:50, is outside the previous hour and would no longer appear in the InfluxDB `chronograf` database or on the Chronograf Alert History page.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## TICKscript management
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -69,4 +69,4 @@ You cannot edit pre-existing tasks on the Chronograf Alert Rules page.
|
|||
The `mytick` task in the image below is a pre-existing task; its name appears on the Alert Rules page but you cannot click on it or edit its TICKscript in the interface.
|
||||
Currently, you must manually edit your existing tasks and TICKscripts on your machine.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -18,14 +18,14 @@ Logs data is a first class citizen in InfluxDB and is populated using available
|
|||
## Viewing logs in Chronograf
|
||||
Chronograf has a dedicated log viewer accessed by clicking the **Log Viewer** button in the left navigation.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.7/logs-nav-log-viewer.png" alt="Log viewer in the left nav" style="width:100%;max-width:209px;"/>
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-logs-nav-log-viewer.png" alt="Log viewer in the left nav" style="width:100%;max-width:209px;"/>
|
||||
|
||||
The log viewer provides a detailed histogram showing the time-based distribution of log entries color-coded by log severity.
|
||||
It also includes a live stream of logs that can be searched, filtered, and paused to analyze specific time ranges.
|
||||
Logs are pulled from the `syslog` measurement.
|
||||
_Other log inputs and alternate log measurement options will be available in future updates._
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/log-viewer-overview.png" alt="Chronograf log viewer" style="width:100%;max-width:1016px;"/>
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-7-log-viewer-overview.png" alt="Chronograf log viewer" style="width:100%;max-width:1016px;"/>
|
||||
|
||||
### Searching and filtering logs
|
||||
Search for logs using keywords or regular expressions.
|
||||
|
|
@ -34,7 +34,7 @@ Any tag values included with the log entry can be used as a filter.
|
|||
|
||||
You can also use search operators to filter your results. For example, if you want to find results with a severity of critical that don't mention RSS, you can enter: `severity == crit` and `-RSS`.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
> **Note:** The log search field is case-sensitive.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -45,13 +45,13 @@ In the log viewer, you can select time ranges from which to view logs.
|
|||
By default, logs are streamed and displayed relative to "now," but it is possible to view logs from a past window of time.
|
||||
timeframe selection allows you to go to to a specific event and see logs for a time window both preceding and following that event. The default window is one minute, meaning the graph shows logs from thirty seconds before and the target time. Click the dropdown menu change the window.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Configuring the log viewer
|
||||
The log viewer can be customized to fit your specific needs.
|
||||
Open the log viewer configuration options by clicking the gear button in the top right corner of the log viewer. Once done, click **Save** to apply the changes.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.7/logs-log-viewer-config-options.png" alt="Log viewer configuration options" style="width:100%;max-width:819px;"/>
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-logs-log-viewer-config-options.png" alt="Log viewer configuration options" style="width:100%;max-width:819px;"/>
|
||||
|
||||
### Severity colors
|
||||
Every log severity is assigned a color which is used in the display of log entries.
|
||||
|
|
@ -67,9 +67,9 @@ Below are the options and how they appear in the log table:
|
|||
|
||||
| Severity Format | Display |
|
||||
| --------------- |:------- |
|
||||
| Dot | <img src="/img/chronograf/v1.7/logs-serverity-fmt-dot.png" alt="Log serverity format 'Dot'" style="display:inline;max-height:24px;"/> |
|
||||
| Dot + Text | <img src="/img/chronograf/v1.7/logs-serverity-fmt-dot-text.png" alt="Log serverity format 'Dot + Text'" style="display:inline;max-height:24px;"/> |
|
||||
| Text | <img src="/img/chronograf/v1.7/logs-serverity-fmt-text.png" alt="Log serverity format 'Text'" style="display:inline;max-height:24px;"/> |
|
||||
| Dot | <img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-logs-serverity-fmt-dot.png" alt="Log serverity format 'Dot'" style="display:inline;max-height:24px;"/> |
|
||||
| Dot + Text | <img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-logs-serverity-fmt-dot-text.png" alt="Log serverity format 'Dot + Text'" style="display:inline;max-height:24px;"/> |
|
||||
| Text | <img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-logs-serverity-fmt-text.png" alt="Log serverity format 'Text'" style="display:inline;max-height:24px;"/> |
|
||||
|
||||
### Truncate or wrap log messages
|
||||
By default, text in Log Viewer columns is truncated if it exceeds the column width. You can choose to wrap the text instead to display the full content of each cell.
|
||||
|
|
@ -82,6 +82,6 @@ To copy the complete, untruncated log message, select the message cell and click
|
|||
An incredibly powerful way to analyze log data is by creating dashboards that include log data.
|
||||
This is possible by using the [Table visualization type](/chronograf/v1.7/guides/visualization-types/#table) to display log data in your dashboard.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
This type of visualization allows you to quickly identify anomalies in other metrics and see logs associated with those anomalies.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ The following screenshot of five graph views displays annotations for a single p
|
|||
The text and timestamp for the single point in time can be seem above the annotation line in the graph view on the lower right.
|
||||
The annotation displays "`Deploy v3.8.1-2`" and the time "`2018/28/02 15:59:30:00`".
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**To add an annotation using the Chronograf user interface:**
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -18,11 +18,11 @@ Dashboards in Chronograf can be cloned (or copied) to be used to create a dashbo
|
|||
|
||||
1. On the **Dashboards** page, hover your cursor over the listing of the dashboard that you want to clone and click the **Clone** button that appears.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The cloned dashboard opens and displays the name of the original dashboard with `(clone)` after it.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You can now change the dashboard name and customize the dashboard.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -34,10 +34,10 @@ Cells in Chronograf dashboards can be cloned, or copied, to quickly create a cel
|
|||
|
||||
1. On the dashboard cell that you want to make a copy of, click the **Clone** icon and then confirm by clicking **Clone Cell**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
2. The cloned cell appears in the dashboard displaying the nameof the original cell with `(clone)` after it.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You can now change the cell name and customize the cell.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -253,7 +253,7 @@ Click **Add Another Config** to add additional Slack alert endpoints. Each addit
|
|||
Configure Chronograf to send alert messages to an existing Telegram bot.
|
||||
The sections below describe each configuration option.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Telegram bot
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -17,7 +17,7 @@ Chronograf offers a complete dashboard solution for visualizing your data and mo
|
|||
|
||||
By the end of this guide, you'll be aware of the tools available to you for creating dashboards similar to this example:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Requirements
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -39,7 +39,7 @@ Click **Name This Dashboard** and type a new name. In this guide, "ChronoDash" i
|
|||
In the first cell, titled "Untitled Cell", click **Edit**
|
||||
to open the cell editor mode.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Step 3: Create your query
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -54,13 +54,13 @@ Those defaults are configurable using the query builder or by manually editing t
|
|||
|
||||
In addition, the time range (`:dashboardTime:`) is [configurable on the dashboard](#step-6-configure-your-dashboard).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Step 4: Choose your visualization type
|
||||
|
||||
Chronograf supports many different [visualization types](/chronograf/latest/guides/visualization-types/). To choose a visualization type, click **Visualization** and select **Step-Plot Graph**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Step 5: Save your cell
|
||||
Click **Save** (the green checkmark icon) to save your cell.
|
||||
|
|
@ -95,10 +95,10 @@ Now, you're ready to experiment and complete your dashboard by creating, editing
|
|||
|
||||
Select from a variety of dashboard templates to import and customize based on which Telegraf plugins you have enabled, such as the following examples:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.7/protoboard-kubernetes.png" style="width:100%; max-width:600px;">
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.7/protoboard-mysql.png" style="width:100%; max-width:600px;">
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.7/protoboard-system.png" style="width:100%; max-width:600px;">
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.7/protoboard-vsphere.png" style="width:100%; max-width:600px;">
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-7-protoboard-kubernetes.png" style="width:100%; max-width:600px;">
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-7-protoboard-mysql.png" style="width:100%; max-width:600px;">
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-7-protoboard-system.png" style="width:100%; max-width:600px;">
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-7-protoboard-vsphere.png" style="width:100%; max-width:600px;">
|
||||
|
||||
**To import dashboard templates:**
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -106,7 +106,7 @@ Select from a variety of dashboard templates to import and customize based on wh
|
|||
2. In the **InfluxDB Connection** window, enter or verify your connection details and click **Add** or **Update Connection**.
|
||||
3. In the **Dashboards** window, select from the available dashboard templates to import based on which Telegraf plugins you have enabled.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.7/protoboard-select.png" style="width:100%; max-width:500px;">
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-7-protoboard-select.png" style="width:100%; max-width:500px;">
|
||||
4. Click **Create (x) Dashboards**.
|
||||
5. Edit, clone, or configure the dashboards as needed.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -38,12 +38,12 @@ See the [Configuring Kapacitor Event Handlers](/chronograf/latest/guides/configu
|
|||
|
||||
Navigate to the **Manage Tasks** page under **Alerting** in the left navigation, then click **+ Build Alert Rule** in the top right corner.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The **Manage Tasks** page is used to create and edit your Chronograf alert rules.
|
||||
The steps below guide you through the process of creating a Chronograf alert rule.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Step 1: Name the alert rule
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -72,7 +72,7 @@ Navigate through databases, measurements, fields, and tags to select the relevan
|
|||
|
||||
In this example, select the `telegraf` [database](/influxdb/latest/concepts/glossary/#database), the `autogen` [retention policy](/influxdb/latest/concepts/glossary/#retention-policy-rp), the `cpu` [measurement](/influxdb/latest/concepts/glossary/#measurement), and the `usage_idle` [field](/influxdb/latest/concepts/glossary/#field).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Step 4: Define the rule condition
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -80,7 +80,7 @@ Define the threshold condition.
|
|||
Condition options are determined by the [alert type](#step-2-select-the-alert-type).
|
||||
For this example, the alert conditions are if `usage_idle` is less than `80`.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The graph shows a preview of the relevant data and the threshold number.
|
||||
By default, the graph shows data from the past 15 minutes.
|
||||
|
|
@ -98,7 +98,7 @@ Each handler has unique configurable options.
|
|||
|
||||
For this example, choose the **slack** alert handler and enter the desired options.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
> Multiple alert handlers can be added to send alerts to multiple endpoints.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -111,7 +111,7 @@ As you type your alert message, clicking the data templates will insert them at
|
|||
|
||||
In this example, use the alert message, `Your idle CPU usage is {{.Level}} at {{ index .Fields "value" }}.`.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*View the Kapacitor documentation for more information about [message template data](/kapacitor/latest/nodes/alert_node/#message).*
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -120,7 +120,7 @@ In this example, use the alert message, `Your idle CPU usage is {{.Level}} at {{
|
|||
Click **Save Rule** in the top right corner and navigate to the **Manage Tasks** page to see your rule.
|
||||
Notice that you can easily enable and disable the rule by toggling the checkbox in the **Enabled** column.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Next, move on to the section below to experience your alert rule in action.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -149,10 +149,10 @@ Assuming the first step was successful, `#ohnos` should reveal at least two aler
|
|||
* The first alert message indicates that your idle CPU usage was `CRITICAL`, meaning it dipped below `80%`.
|
||||
* The second alert message indicates that your idle CPU usage returned to an `OK` level of `80%` or above.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You can also see alerts on the **Alert History** page available under **Alerting** in the left navigation.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
That's it! You've successfully used Chronograf to configure an alert rule to monitor your idle CPU usage and send notifications to Slack.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -25,7 +25,7 @@ You can use either [predefined template variables](#predefined-template-variable
|
|||
or [custom template variables](#create-custom-template-variables).
|
||||
Variable values are then selected in your dashboard user-interface (UI).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Predefined template variables
|
||||
Chronograf includes predefined template variables controlled by elements in the Chrongraf UI.
|
||||
|
|
@ -38,7 +38,7 @@ These template variables can be used in any of your cells' queries.
|
|||
### dashboardTime
|
||||
The `:dashboardTime:` template variable is controlled by the "time" dropdown in your Chronograf dashboard.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.7/template-vars-time-dropdown.png" style="width:100%;max-width:549px;" alt="Dashboard time selector"/>
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-template-vars-time-dropdown.png" style="width:100%;max-width:549px;" alt="Dashboard time selector"/>
|
||||
|
||||
If using relative times, it represents the time offset specified in the dropdown (-5m, -15m, -30m, etc.) and assumes time is relative to "now".
|
||||
If using absolute times defined by the date picker, `:dashboardTime:` is populated with lower threshold.
|
||||
|
|
@ -56,7 +56,7 @@ WHERE time > :dashboardTime:
|
|||
### upperDashboardTime
|
||||
The `:upperDashboardTime:` template variable is defined by the upper time limit specified using the date picker.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.7/template-vars-date-picker.png" style="width:100%;max-width:762px;" alt="Dashboard date picker"/>
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-template-vars-date-picker.png" style="width:100%;max-width:762px;" alt="Dashboard date picker"/>
|
||||
|
||||
It will inherit `now()` when using relative time frames or the upper time limit when using absolute timeframes.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -69,7 +69,7 @@ WHERE time > :dashboardTime: AND time < :upperDashboardTime:
|
|||
### interval
|
||||
The `:interval:` template variable is defined by the interval dropdown in the Chronograf dashboard.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.7/template-vars-interval-dropdown.png" style="width:100%;max-width:549px;" alt="Dashboard interval selector"/>
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-template-vars-interval-dropdown.png" style="width:100%;max-width:549px;" alt="Dashboard interval selector"/>
|
||||
|
||||
In cell queries, it should be used in the `GROUP BY time()` clause that accompanies aggregate functions:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -95,7 +95,7 @@ To create a template variable:
|
|||
If using the CSV or Map types, upload or input the CSV with the desired values in the appropriate format then select a default value.
|
||||
5. Click **Create**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Once created, the template variable can be used in any of your cell's queries or titles
|
||||
and a dropdown for the variable will be included at the top of your dashboard.
|
||||
|
|
@ -251,7 +251,7 @@ key3,value3
|
|||
key4,value4
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.7/template-vars-map-dropdown.png" style="width:100%;max-width:140px;" alt="Map variable dropdown"/>
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-template-vars-map-dropdown.png" style="width:100%;max-width:140px;" alt="Map variable dropdown"/>
|
||||
|
||||
> If values are meant to be used as string field values, wrap them in single quote ([required by InfluxQL](/influxdb/latest/troubleshooting/frequently-asked-questions/#when-should-i-single-quote-and-when-should-i-double-quote-in-queries)). This only pertains to values. String keys do not matter.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -285,7 +285,7 @@ The customer names would populate your template variable dropdown rather than th
|
|||
Vary part of a query with a customized meta query that pulls a specific array of values from InfluxDB.
|
||||
These variables allow you to pull a highly customized array of potential values and offer advanced functionality such as [filtering values based on other template variables](#filtering-template-variables-with-other-template-variables).
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.7/template-vars-custom-meta-query.png" style="width:100%;max-width:667px;" alt="Custom meta query"/>
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-template-vars-custom-meta-query.png" style="width:100%;max-width:667px;" alt="Custom meta query"/>
|
||||
|
||||
_**Example custom meta query variable in a cell query**_
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
|
|
@ -330,7 +330,7 @@ For example, let's say you want to list all the field keys associated with a mea
|
|||
|
||||
1. Create a template variable named `:measurementVar:` _(the name "measurement" is [reserved]( #reserved-variable-names))_ that uses the [Measurements](#measurements) variable type to pull in all measurements from the `telegraf` database.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.7/template-vars-measurement-var.png" style="width:100%;max-width:667px;" alt="measurementVar"/>
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-template-vars-measurement-var.png" style="width:100%;max-width:667px;" alt="measurementVar"/>
|
||||
|
||||
2. Create a template variable named `:fieldKey:` that uses the [custom meta query](#custom-meta-query) variable type.
|
||||
The following meta query pulls a list of field keys based on the existing `:measurementVar:` template variable.
|
||||
|
|
@ -339,7 +339,7 @@ The following meta query pulls a list of field keys based on the existing `:meas
|
|||
SHOW FIELD KEYS ON telegraf FROM :measurementVar:
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.7/template-vars-fieldkey.png" style="width:100%;max-width:667px;" alt="fieldKey"/>
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-template-vars-fieldkey.png" style="width:100%;max-width:667px;" alt="fieldKey"/>
|
||||
|
||||
3. Create a new dashboard cell that uses the `:fieldKey:` and `:measurementVar` template variables in its query.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -349,7 +349,7 @@ The following meta query pulls a list of field keys based on the existing `:meas
|
|||
|
||||
The resulting dashboard will work like this:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Defining template variables in the URL
|
||||
Chronograf uses URL query parameters (also known as query string parameters) to set both display options and template variables in the URL.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ Chronograf and the other components of the TICK stack are supported on several o
|
|||
|
||||
Before we begin, here's an overview of the final monitoring setup:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The diagram above shows an InfluxEnterprise cluster that consists of three meta nodes (M) and three data nodes (D).
|
||||
Each data node has its own [Telegraf](/telegraf/latest/) instance (T).
|
||||
|
|
@ -233,7 +233,7 @@ Chronograf can be downloaded from the [InfluxData downloads page](https://portal
|
|||
To access Chronograf, go to http://localhost:8888.
|
||||
The welcome page includes instructions for connecting Chronograf to that instance.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
For the `Connection String`, enter the hostname or IP of your InfluxDB OSS instance, and be sure to include the default port: `8086`.
|
||||
Next, name your data source; this can be anything you want.
|
||||
|
|
@ -245,17 +245,17 @@ Chronograf works with the Telegraf data in your InfluxDB OSS instance.
|
|||
The `Host List` page shows your data node's hostnames, their statuses, CPU usage, load, and their configured applications.
|
||||
In this case, you've only enabled the system stats input plugin so `system` is the single application that appears in the `Apps` column.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Click `system` to see the Chronograf canned dashboard for that application.
|
||||
Keep an eye on your data nodes by viewing that dashboard for each hostname:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Next, check out the Data Explorer to create a customized graph with the monitoring data.
|
||||
In the image below, the Chronograf query editor is used to visualize the idle CPU usage data for each data node:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Create more customized graphs and save them to a dashboard on the Dashboard page in Chronograf.
|
||||
See the [Creating Chronograf dashboards](/chronograf/latest/guides/create-a-dashboard/) guide for more information.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -13,7 +13,7 @@ Presentation mode allows you to view Chronograf in full screen, hiding the left
|
|||
## Entering presentation mode manually
|
||||
To enter presentation mode manually, click the icon in the upper right:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/chronograf-presentation-mode.png" style="width:100%; max-width:500px"/>
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-presentation-mode.png" style="width:100%; max-width:500px"/>
|
||||
|
||||
To exit presentation mode, press `ESC`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -11,7 +11,7 @@ Explore and visualize your data in the **Data Explorer**. For both InfluxQL and
|
|||
|
||||
To open the **Data Explorer**, click the **Explore** icon in the navigation bar:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.7/data-explorer-icon.png" style="width:100%; max-width:400px; margin:2em 0; display: block;">
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-7-data-explorer-icon.png" style="width:100%; max-width:400px; margin:2em 0; display: block;">
|
||||
|
||||
## Select local time or UTC (Coordinated Universal Time)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -47,7 +47,7 @@ Flux is InfluxData's new functional data scripting language designed for queryin
|
|||
|
||||
* To get started with your query, click the **Script Wizard**. In the wizard, you can select a bucket, measurement, fields and an aggregate.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.7/flux-script-wizard.png" style="width:100%; max-width:400px; margin:2em 0; display:block;">
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-7-flux-script-wizard.png" style="width:100%; max-width:400px; margin:2em 0; display:block;">
|
||||
|
||||
For example, if you make the above selections, the wizard inserts the following script:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -75,9 +75,9 @@ To add your query and graph to a dashboard:
|
|||
1. Click **Send to Dashboard** in the upper right.
|
||||
2. In the **Target Dashboard(s)** dropdown, select at least one existing dashboard to send the cell to, or select **Send to a New Dashboard**.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/send-to-dashboard-target.png" style="width:100%; max-width:597px; margin:2em 0; display: block;">
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-7-send-to-dashboard-target.png" style="width:100%; max-width:597px; margin:2em 0; display: block;">
|
||||
|
||||
3. Enter a name for the new cell and, if you created a new dashboard, the new dashboard.
|
||||
4. Click **Send to Dashboard(s)**.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.7/send-to-dashboard-send.png" style="width:100%; max-width:597px; display:block; margin:2em 0;">
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-7-send-to-dashboard-send.png" style="width:100%; max-width:597px; display:block; margin:2em 0;">
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ menu:
|
|||
|
||||
Chronograf's dashboard views support the following visualization types, which can be selected in the **Visualization Type** selection view of the [Data Explorer](/chronograf/latest/querying-data) .
|
||||
|
||||
[Visualization Type selector](/img/chronograf/chrono-viz-types-selector.png)
|
||||
[Visualization Type selector](/img/chronograf/1-6-viz-types-selector.png)
|
||||
|
||||
Each of the available visualization types and available user controls are described below.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -31,11 +31,11 @@ For information on adding and displaying annotations in graph views, see [Adding
|
|||
|
||||
The **Line Graph** view displays a time series in a line graph.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Line Graph Controls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Use the **Line Graph Controls** to specify the following:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -54,18 +54,18 @@ Use the **Line Graph Controls** to specify the following:
|
|||
|
||||
#### Line Graph example
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Stacked Graph
|
||||
|
||||
The **Stacked Graph** view displays multiple time series bars as segments stacked on top of each other.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Stacked Graph Controls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Use the **Stacked Graph Controls** to specify the following:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -84,18 +84,18 @@ Use the **Stacked Graph Controls** to specify the following:
|
|||
|
||||
#### Stacked Graph example
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Step-Plot Graph
|
||||
|
||||
The **Step-Plot Graph** view displays a time series in a staircase graph.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Step-Plot Graph Controls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Use the **Step-Plot Graph Controls** to specify the following:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -112,7 +112,7 @@ Use the **Step-Plot Graph Controls** to specify the following:
|
|||
|
||||
#### Step-Plot Graph example
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Bar Graph
|
||||
|
|
@ -121,11 +121,11 @@ The **Bar Graph** view displays the specified time series using a bar chart.
|
|||
|
||||
To select this view, click the Bar Graph selector icon.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Bar Graph Controls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Use the **Bar Graph Controls** to specify the following:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -142,7 +142,7 @@ Use the **Bar Graph Controls** to specify the following:
|
|||
|
||||
#### Bar Graph example
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Line Graph + Single Stat
|
||||
|
|
@ -151,11 +151,11 @@ The **Line Graph + Single Stat** view displays the specified time series in a li
|
|||
|
||||
To select this view, click the **Line Graph + Single Stat** view option.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Line Graph + Single Stat Controls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Use the **Line Graph + Single Stat Controls** to specify the following:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -172,13 +172,13 @@ Use the **Line Graph + Single Stat Controls** to specify the following:
|
|||
|
||||
#### Line Graph + Single Stat example
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Single Stat
|
||||
|
||||
The **Single Stat** view displays the most recent value of the specified time series as a numerical value.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If a cell's query includes a [`GROUP BY` tag](/influxdb/latest/query_language/data_exploration/#group-by-tags) clause, Chronograf sorts the different [series](/influxdb/latest/concepts/glossary/#series) lexicographically and shows the most recent [field value](/influxdb/latest/concepts/glossary/#field-value) associated with the first series.
|
||||
For example, if a query groups by the `name` [tag key](/influxdb/latest/concepts/glossary/#tag-key) and `name` has two [tag values](/influxdb/latest/concepts/glossary/#tag-value) (`chronelda` and `chronz`), Chronograf shows the most recent field value associated with the `chronelda` series.
|
||||
|
|
@ -204,11 +204,11 @@ The **Gauge** view displays the single value most recent value for a time series
|
|||
|
||||
To select this view, click the Gauge selector icon.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Gauge Controls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Use the **Gauge Controls** to specify the following:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -222,17 +222,17 @@ Use the **Gauge Controls** to specify the following:
|
|||
|
||||
#### Gauge example
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Table
|
||||
|
||||
The **Table** panel displays the results of queries in a tabular view, which is sometimes easier to analyze than graph views of data.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Table Controls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Use the **Table Controls** to specify the following:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -256,17 +256,17 @@ Use the **Table Controls** to specify the following:
|
|||
|
||||
#### Table view example
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Note
|
||||
|
||||
The **Note** panel displays Markdown-formatted text with your graph.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Note Controls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Enter your text in the **Add a Note** panel, using Markdown to format the text.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -274,4 +274,4 @@ Enable the **Display note in cell when query returns no results** option to disp
|
|||
|
||||
#### Note view example
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ When you enter the InfluxDB HTTP bind address in the `Connection String` input,
|
|||
If it is a data node, Chronograf automatically adds the `Meta Service Connection URL` input to the connection details form.
|
||||
Enter the HTTP bind address of one of your cluster's meta nodes into that input and Chronograf takes care of the rest.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Note that the example above assumes that you do not have authentication enabled.
|
||||
If you have authentication enabled, the form requires username and password information.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ menu:
|
|||
Chronograf is InfluxData's open source web application.
|
||||
Use Chronograf with the other components of the [TICK stack](https://www.influxdata.com/products/) to visualize your monitoring data and easily create alerting and automation rules.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Key features
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ When you enter the InfluxDB HTTP bind address in the `Connection String` input,
|
|||
If it is a data node, Chronograf automatically adds the `Meta Service Connection URL` input to the connection details form.
|
||||
Enter the HTTP bind address of one of your cluster's meta nodes into that input and Chronograf takes care of the rest.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Note that the example above assumes that you do not have authentication enabled.
|
||||
If you have authentication enabled, the form requires username and password information.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -17,7 +17,7 @@ Have an existing Chronograf configuration store that you want to use with a Chro
|
|||
|
||||
## Architecture
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/svgs/chronograf-ha-architecture.svg" alt="Chronograf high-availability architecture" style="width:100%;max-width:500px"/>
|
||||
{{< svg "/static/img/chronograf/1-8-ha-architecture.svg" >}}
|
||||
|
||||
## Install and start etcd
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -23,10 +23,10 @@ To create an InfluxDB connection in the Chronograf UI:
|
|||
|
||||
1. Open Chronograf and click **Configuration** (wrench icon) in the navigation menu.
|
||||
2. Click **Add Connection**.
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
3. Enter values for the following fields:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.8/influxdb-connection-config.png" style="width:100%; max-width:600px;">
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-7-influxdb-connection-config.png" style="width:100%; max-width:600px;">
|
||||
|
||||
* **Connection URL**: Enter the hostname or IP address of the InfluxDB instance and the port. The field is prefilled with `http://localhost:8086`.
|
||||
* **Connection Name**: Enter the name for this connection.
|
||||
|
|
@ -167,11 +167,11 @@ To create a Kapacitor connection using the Chronograf UI:
|
|||
|
||||
1. Open Chronograf and click **Configuration** (wrench icon) in the navigation menu.
|
||||
2. Next to an existing [InfluxDB connection](#managing-influxdb-connections-using-the-chronograf-ui), click **Add Kapacitor Connection** if there are no existing Kapacitor connections or select **Add Kapacitor Connection** in the **Kapacitor Connection** dropdown list.
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
3. In the **Connection Details** section, enter values for the following fields:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.8/kapacitor-connection-config.png" style="width:100%; max-width:600px;">
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-7-kapacitor-connection-config.png" style="width:100%; max-width:600px;">
|
||||
|
||||
* **Kapacitor URL**: Enter the hostname or IP address of the Kapacitor instance and the port. The field is prefilled with `http://localhost:9092`.
|
||||
* **Name**: Enter the name for this connection.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ This allows you to recreate robust dashboards without having to manually configu
|
|||
2. Hover over the dashboard you would like to export and click the "Export"
|
||||
button that appears to the right.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.8/dashboard-export.png" alt="Exporting a Chronograf dashboard" style="width:100%;max-width:912px"/>
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-dashboard-export.png" alt="Exporting a Chronograf dashboard" style="width:100%;max-width:912px"/>
|
||||
|
||||
This downloads a JSON file containing dashboard information including template variables,
|
||||
cells and cell information such as the query, cell-sizing, color scheme, visualization type, etc.
|
||||
|
|
@ -35,13 +35,13 @@ cells and cell information such as the query, cell-sizing, color scheme, visuali
|
|||
|
||||
The newly imported dashboard will be included in your list of dashboards.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Reconciling unmatched sources
|
||||
If the data sources defined in the imported dashboard JSON file do not match any of your local sources,
|
||||
you will have to reconcile each of the unmatched sources during the import process.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Required user roles
|
||||
Depending on the role of your user, there are some restrictions on importing and exporting dashboards:
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -88,7 +88,7 @@ On the **Chronograf Admin** page:
|
|||
* Change user passwords
|
||||
* Assign admin and remove admin permissions to or from a user
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
InfluxDB users are either admin users or non-admin users.
|
||||
See InfluxDB's [authentication and authorization](/influxdb/latest/administration/authentication_and_authorization/#user-types-and-privileges) documentation for more information about those user types.
|
||||
|
|
@ -129,7 +129,7 @@ On the `Admin` page:
|
|||
* Create, edit, and delete roles
|
||||
* Assign and remove roles to or from a user
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### User types
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -306,4 +306,4 @@ For example, the image below contains three roles: `CREATOR`, `DESTROYER`, and `
|
|||
`CREATOR` includes two permissions (`CreateDatbase` and `CreateUserAndRole`) and is assigned to one user (`chrononut`).
|
||||
`DESTROYER` also includes two permissions (`DropDatabase` and `DropData`) and is assigned to two users (`chrononut` and `chronelda`).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -31,7 +31,7 @@ In the Databases tab:
|
|||
|
||||
#### Step 1: Locate the `chronograf` database and click on the infinity symbol (∞)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 2: Enter a different duration
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -50,7 +50,7 @@ Those alerts no longer appear in your InfluxDB instance or on Chronograf's Alert
|
|||
Looking at the image below and assuming that the current time is 19:00 on April 27, 2017, only the first three alerts would appear in your alert history; they occurred within the previous hour (18:00 through 19:00).
|
||||
The fourth alert, which occurred on the same day at 16:58:50, is outside the previous hour and would no longer appear in the InfluxDB `chronograf` database or on the Chronograf Alert History page.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## TICKscript management
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -69,4 +69,4 @@ You cannot edit pre-existing tasks on the Chronograf Alert Rules page.
|
|||
The `mytick` task in the image below is a pre-existing task; its name appears on the Alert Rules page but you cannot click on it or edit its TICKscript in the interface.
|
||||
Currently, you must manually edit your existing tasks and TICKscripts on your machine.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -18,14 +18,14 @@ Logs data is a first class citizen in InfluxDB and is populated using available
|
|||
## Viewing logs in Chronograf
|
||||
Chronograf has a dedicated log viewer accessed by clicking the **Log Viewer** button in the left navigation.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.8/logs-nav-log-viewer.png" alt="Log viewer in the left nav" style="width:100%;max-width:209px;"/>
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-logs-nav-log-viewer.png" alt="Log viewer in the left nav" style="width:100%;max-width:209px;"/>
|
||||
|
||||
The log viewer provides a detailed histogram showing the time-based distribution of log entries color-coded by log severity.
|
||||
It also includes a live stream of logs that can be searched, filtered, and paused to analyze specific time ranges.
|
||||
Logs are pulled from the `syslog` measurement.
|
||||
_Other log inputs and alternate log measurement options will be available in future updates._
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/log-viewer-overview.png" alt="Chronograf log viewer" style="width:100%;max-width:1016px;"/>
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-7-log-viewer-overview.png" alt="Chronograf log viewer" style="width:100%;max-width:1016px;"/>
|
||||
|
||||
### Searching and filtering logs
|
||||
Search for logs using keywords or regular expressions.
|
||||
|
|
@ -34,7 +34,7 @@ Any tag values included with the log entry can be used as a filter.
|
|||
|
||||
You can also use search operators to filter your results. For example, if you want to find results with a severity of critical that don't mention RSS, you can enter: `severity == crit` and `-RSS`.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
> **Note:** The log search field is case-sensitive.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -45,13 +45,13 @@ In the log viewer, you can select time ranges from which to view logs.
|
|||
By default, logs are streamed and displayed relative to "now," but it is possible to view logs from a past window of time.
|
||||
timeframe selection allows you to go to to a specific event and see logs for a time window both preceding and following that event. The default window is one minute, meaning the graph shows logs from thirty seconds before and the target time. Click the dropdown menu change the window.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Configuring the log viewer
|
||||
The log viewer can be customized to fit your specific needs.
|
||||
Open the log viewer configuration options by clicking the gear button in the top right corner of the log viewer. Once done, click **Save** to apply the changes.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.8/logs-log-viewer-config-options.png" alt="Log viewer configuration options" style="width:100%;max-width:819px;"/>
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-logs-log-viewer-config-options.png" alt="Log viewer configuration options" style="width:100%;max-width:819px;"/>
|
||||
|
||||
### Severity colors
|
||||
Every log severity is assigned a color which is used in the display of log entries.
|
||||
|
|
@ -67,9 +67,9 @@ Below are the options and how they appear in the log table:
|
|||
|
||||
| Severity Format | Display |
|
||||
| --------------- |:------- |
|
||||
| Dot | <img src="/img/chronograf/v1.8/logs-serverity-fmt-dot.png" alt="Log serverity format 'Dot'" style="display:inline;max-height:24px;"/> |
|
||||
| Dot + Text | <img src="/img/chronograf/v1.8/logs-serverity-fmt-dot-text.png" alt="Log serverity format 'Dot + Text'" style="display:inline;max-height:24px;"/> |
|
||||
| Text | <img src="/img/chronograf/v1.8/logs-serverity-fmt-text.png" alt="Log serverity format 'Text'" style="display:inline;max-height:24px;"/> |
|
||||
| Dot | <img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-logs-serverity-fmt-dot.png" alt="Log serverity format 'Dot'" style="display:inline;max-height:24px;"/> |
|
||||
| Dot + Text | <img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-logs-serverity-fmt-dot-text.png" alt="Log serverity format 'Dot + Text'" style="display:inline;max-height:24px;"/> |
|
||||
| Text | <img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-logs-serverity-fmt-text.png" alt="Log serverity format 'Text'" style="display:inline;max-height:24px;"/> |
|
||||
|
||||
### Truncate or wrap log messages
|
||||
By default, text in Log Viewer columns is truncated if it exceeds the column width. You can choose to wrap the text instead to display the full content of each cell.
|
||||
|
|
@ -82,6 +82,6 @@ To copy the complete, untruncated log message, select the message cell and click
|
|||
An incredibly powerful way to analyze log data is by creating dashboards that include log data.
|
||||
This is possible by using the [Table visualization type](/chronograf/v1.8/guides/visualization-types/#table) to display log data in your dashboard.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
This type of visualization allows you to quickly identify anomalies in other metrics and see logs associated with those anomalies.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ The following screenshot of five graph views displays annotations for a single p
|
|||
The text and timestamp for the single point in time can be seem above the annotation line in the graph view on the lower right.
|
||||
The annotation displays "`Deploy v3.8.1-2`" and the time "`2018/28/02 15:59:30:00`".
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**To add an annotation using the Chronograf user interface:**
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -18,11 +18,11 @@ Dashboards in Chronograf can be cloned (or copied) to be used to create a dashbo
|
|||
|
||||
1. On the **Dashboards** page, hover your cursor over the listing of the dashboard that you want to clone and click the **Clone** button that appears.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The cloned dashboard opens and displays the name of the original dashboard with `(clone)` after it.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You can now change the dashboard name and customize the dashboard.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -34,10 +34,10 @@ Cells in Chronograf dashboards can be cloned, or copied, to quickly create a cel
|
|||
|
||||
1. On the dashboard cell that you want to make a copy of, click the **Clone** icon and then confirm by clicking **Clone Cell**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
2. The cloned cell appears in the dashboard displaying the nameof the original cell with `(clone)` after it.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You can now change the cell name and customize the cell.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -253,7 +253,7 @@ Click **Add Another Config** to add additional Slack alert endpoints. Each addit
|
|||
Configure Chronograf to send alert messages to an existing Telegram bot.
|
||||
The sections below describe each configuration option.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Telegram bot
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ Chronograf offers a complete dashboard solution for visualizing your data and mo
|
|||
|
||||
By the end of this guide, you'll be aware of the tools available to you for creating dashboards similar to this example:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Requirements
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -38,7 +38,7 @@ Click **Name This Dashboard** and type a new name. In this guide, "ChronoDash" i
|
|||
In the first cell, titled "Untitled Cell", click **Edit**
|
||||
to open the cell editor mode.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Step 3: Create your query
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -53,13 +53,13 @@ Those defaults are configurable using the query builder or by manually editing t
|
|||
|
||||
In addition, the time range (`:dashboardTime:` and `:upperDashboardTime:`) are [configurable on the dashboard](#step-6-configure-your-dashboard).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Step 4: Choose your visualization type
|
||||
|
||||
Chronograf supports many different [visualization types](/chronograf/latest/guides/visualization-types/). To choose a visualization type, click **Visualization** and select **Step-Plot Graph**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Step 5: Save your cell
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -102,10 +102,10 @@ Now, you're ready to experiment and complete your dashboard by creating, editing
|
|||
|
||||
Select from a variety of dashboard templates to import and customize based on which Telegraf plugins you have enabled, such as the following examples:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.8/protoboard-kubernetes.png" style="width:100%; max-width:600px;">
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.8/protoboard-mysql.png" style="width:100%; max-width:600px;">
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.8/protoboard-system.png" style="width:100%; max-width:600px;">
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.8/protoboard-vsphere.png" style="width:100%; max-width:600px;">
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-7-protoboard-kubernetes.png" style="width:100%; max-width:600px;">
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-7-protoboard-mysql.png" style="width:100%; max-width:600px;">
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-7-protoboard-system.png" style="width:100%; max-width:600px;">
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-7-protoboard-vsphere.png" style="width:100%; max-width:600px;">
|
||||
|
||||
**To import dashboard templates:**
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -113,7 +113,7 @@ Select from a variety of dashboard templates to import and customize based on wh
|
|||
2. In the **InfluxDB Connection** window, enter or verify your connection details and click **Add** or **Update Connection**.
|
||||
3. In the **Dashboards** window, select from the available dashboard templates to import based on which Telegraf plugins you have enabled.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.8/protoboard-select.png" style="width:100%; max-width:500px;">
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-7-protoboard-select.png" style="width:100%; max-width:500px;">
|
||||
4. Click **Create (x) Dashboards**.
|
||||
5. Edit, clone, or configure the dashboards as needed.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -38,12 +38,12 @@ See the [Configuring Kapacitor Event Handlers](/chronograf/latest/guides/configu
|
|||
|
||||
Navigate to the **Manage Tasks** page under **Alerting** in the left navigation, then click **+ Build Alert Rule** in the top right corner.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The **Manage Tasks** page is used to create and edit your Chronograf alert rules.
|
||||
The steps below guide you through the process of creating a Chronograf alert rule.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Step 1: Name the alert rule
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -72,7 +72,7 @@ Navigate through databases, measurements, fields, and tags to select the relevan
|
|||
|
||||
In this example, select the `telegraf` [database](/influxdb/latest/concepts/glossary/#database), the `autogen` [retention policy](/influxdb/latest/concepts/glossary/#retention-policy-rp), the `cpu` [measurement](/influxdb/latest/concepts/glossary/#measurement), and the `usage_idle` [field](/influxdb/latest/concepts/glossary/#field).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Step 4: Define the rule condition
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -80,7 +80,7 @@ Define the threshold condition.
|
|||
Condition options are determined by the [alert type](#step-2-select-the-alert-type).
|
||||
For this example, the alert conditions are if `usage_idle` is less than `80`.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The graph shows a preview of the relevant data and the threshold number.
|
||||
By default, the graph shows data from the past 15 minutes.
|
||||
|
|
@ -98,7 +98,7 @@ Each handler has unique configurable options.
|
|||
|
||||
For this example, choose the **slack** alert handler and enter the desired options.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
> Multiple alert handlers can be added to send alerts to multiple endpoints.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -111,7 +111,7 @@ As you type your alert message, clicking the data templates will insert them at
|
|||
|
||||
In this example, use the alert message, `Your idle CPU usage is {{.Level}} at {{ index .Fields "value" }}.`.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*View the Kapacitor documentation for more information about [message template data](/kapacitor/latest/nodes/alert_node/#message).*
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -120,7 +120,7 @@ In this example, use the alert message, `Your idle CPU usage is {{.Level}} at {{
|
|||
Click **Save Rule** in the top right corner and navigate to the **Manage Tasks** page to see your rule.
|
||||
Notice that you can easily enable and disable the rule by toggling the checkbox in the **Enabled** column.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Next, move on to the section below to experience your alert rule in action.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -149,10 +149,10 @@ Assuming the first step was successful, `#ohnos` should reveal at least two aler
|
|||
* The first alert message indicates that your idle CPU usage was `CRITICAL`, meaning it dipped below `80%`.
|
||||
* The second alert message indicates that your idle CPU usage returned to an `OK` level of `80%` or above.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You can also see alerts on the **Alert History** page available under **Alerting** in the left navigation.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
That's it! You've successfully used Chronograf to configure an alert rule to monitor your idle CPU usage and send notifications to Slack.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -25,7 +25,7 @@ You can use either [predefined template variables](#predefined-template-variable
|
|||
or [custom template variables](#create-custom-template-variables).
|
||||
Variable values are then selected in your dashboard user-interface (UI).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Predefined template variables
|
||||
Chronograf includes predefined template variables controlled by elements in the Chrongraf UI.
|
||||
|
|
@ -38,7 +38,7 @@ These template variables can be used in any of your cells' queries.
|
|||
### dashboardTime
|
||||
The `:dashboardTime:` template variable is controlled by the "time" dropdown in your Chronograf dashboard.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.8/template-vars-time-dropdown.png" style="width:100%;max-width:549px;" alt="Dashboard time selector"/>
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-template-vars-time-dropdown.png" style="width:100%;max-width:549px;" alt="Dashboard time selector"/>
|
||||
|
||||
If using relative times, it represents the time offset specified in the dropdown (-5m, -15m, -30m, etc.) and assumes time is relative to "now".
|
||||
If using absolute times defined by the date picker, `:dashboardTime:` is populated with lower threshold.
|
||||
|
|
@ -56,7 +56,7 @@ WHERE time > :dashboardTime:
|
|||
### upperDashboardTime
|
||||
The `:upperDashboardTime:` template variable is defined by the upper time limit specified using the date picker.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.8/template-vars-date-picker.png" style="width:100%;max-width:762px;" alt="Dashboard date picker"/>
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-template-vars-date-picker.png" style="width:100%;max-width:762px;" alt="Dashboard date picker"/>
|
||||
|
||||
It will inherit `now()` when using relative time frames or the upper time limit when using absolute timeframes.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -70,7 +70,7 @@ WHERE time > :dashboardTime: AND time < :upperDashboardTime:
|
|||
|
||||
The `:interval:` template variable is defined by the interval dropdown in the Chronograf dashboard.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.8/template-vars-interval-dropdown.png" style="width:100%;max-width:549px;" alt="Dashboard interval selector"/>
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-template-vars-interval-dropdown.png" style="width:100%;max-width:549px;" alt="Dashboard interval selector"/>
|
||||
|
||||
In cell queries, it should be used in the `GROUP BY time()` clause that accompanies aggregate functions:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -251,7 +251,7 @@ key3,value3
|
|||
key4,value4
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.8/template-vars-map-dropdown.png" style="width:100%;max-width:140px;" alt="Map variable dropdown"/>
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-template-vars-map-dropdown.png" style="width:100%;max-width:140px;" alt="Map variable dropdown"/>
|
||||
|
||||
> If values are meant to be used as string field values, wrap them in single quote ([required by InfluxQL](/influxdb/latest/troubleshooting/frequently-asked-questions/#when-should-i-single-quote-and-when-should-i-double-quote-in-queries)). This only pertains to values. String keys do not matter.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -285,7 +285,7 @@ The customer names would populate your template variable dropdown rather than th
|
|||
Vary part of a query with a customized meta query that pulls a specific array of values from InfluxDB.
|
||||
These variables allow you to pull a highly customized array of potential values and offer advanced functionality such as [filtering values based on other template variables](#filtering-template-variables-with-other-template-variables).
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.8/template-vars-custom-meta-query.png" style="width:100%;max-width:667px;" alt="Custom meta query"/>
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-template-vars-custom-meta-query.png" style="width:100%;max-width:667px;" alt="Custom meta query"/>
|
||||
|
||||
_**Example custom meta query variable in a cell query**_
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
|
|
@ -331,7 +331,7 @@ For example, let's say you want to list all the field keys associated with a mea
|
|||
|
||||
1. Create a template variable named `:measurementVar:` _(the name "measurement" is [reserved]( #reserved-variable-names))_ that uses the [Measurements](#measurements) variable type to pull in all measurements from the `telegraf` database.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.8/template-vars-measurement-var.png" style="width:100%;max-width:667px;" alt="measurementVar"/>
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-template-vars-measurement-var.png" style="width:100%;max-width:667px;" alt="measurementVar"/>
|
||||
|
||||
2. Create a template variable named `:fieldKey:` that uses the [custom meta query](#custom-meta-query) variable type.
|
||||
The following meta query pulls a list of field keys based on the existing `:measurementVar:` template variable.
|
||||
|
|
@ -340,7 +340,7 @@ The following meta query pulls a list of field keys based on the existing `:meas
|
|||
SHOW FIELD KEYS ON telegraf FROM :measurementVar:
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.8/template-vars-fieldkey.png" style="width:100%;max-width:667px;" alt="fieldKey"/>
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-template-vars-fieldkey.png" style="width:100%;max-width:667px;" alt="fieldKey"/>
|
||||
|
||||
3. Create a new dashboard cell that uses the `:fieldKey:` and `:measurementVar` template variables in its query.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -350,7 +350,7 @@ The following meta query pulls a list of field keys based on the existing `:meas
|
|||
|
||||
The resulting dashboard will work like this:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Defining template variables in the URL
|
||||
Chronograf uses URL query parameters (also known as query string parameters) to set both display options and template variables in the URL.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ Chronograf and the other components of the TICK stack are supported on several o
|
|||
|
||||
Before we begin, here's an overview of the final monitoring setup:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The diagram above shows an InfluxEnterprise cluster that consists of three meta nodes (M) and three data nodes (D).
|
||||
Each data node has its own [Telegraf](/telegraf/latest/) instance (T).
|
||||
|
|
@ -259,7 +259,7 @@ Chronograf can be downloaded from the [InfluxData downloads page](https://portal
|
|||
To access Chronograf, go to http://localhost:8888.
|
||||
The welcome page includes instructions for connecting Chronograf to that instance.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
For the `Connection String`, enter the hostname or IP of your InfluxDB OSS instance, and be sure to include the default port: `8086`.
|
||||
Next, name your data source; this can be anything you want.
|
||||
|
|
@ -271,17 +271,17 @@ Chronograf works with the Telegraf data in your InfluxDB OSS instance.
|
|||
The `Host List` page shows your data node's hostnames, their statuses, CPU usage, load, and their configured applications.
|
||||
In this case, you've only enabled the system stats input plugin so `system` is the single application that appears in the `Apps` column.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Click `system` to see the Chronograf canned dashboard for that application.
|
||||
Keep an eye on your data nodes by viewing that dashboard for each hostname:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Next, check out the Data Explorer to create a customized graph with the monitoring data.
|
||||
In the image below, the Chronograf query editor is used to visualize the idle CPU usage data for each data node:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Create more customized graphs and save them to a dashboard on the Dashboard page in Chronograf.
|
||||
See the [Creating Chronograf dashboards](/chronograf/latest/guides/create-a-dashboard/) guide for more information.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -13,7 +13,7 @@ Presentation mode allows you to view Chronograf in full screen, hiding the left
|
|||
## Entering presentation mode manually
|
||||
To enter presentation mode manually, click the icon in the upper right:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/chronograf-presentation-mode.png" style="width:100%; max-width:500px"/>
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-6-presentation-mode.png" style="width:100%; max-width:500px"/>
|
||||
|
||||
To exit presentation mode, press `ESC`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -11,7 +11,7 @@ Explore and visualize your data in the **Data Explorer**. For both InfluxQL and
|
|||
|
||||
To open the **Data Explorer**, click the **Explore** icon in the navigation bar:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.8/data-explorer-icon.png" style="width:100%; max-width:400px; margin:2em 0; display: block;">
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-7-data-explorer-icon.png" style="width:100%; max-width:400px; margin:2em 0; display: block;">
|
||||
|
||||
## Select local time or UTC (Coordinated Universal Time)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -47,7 +47,7 @@ Flux is InfluxData's new functional data scripting language designed for queryin
|
|||
|
||||
* To get started with your query, click the **Script Wizard**. In the wizard, you can select a bucket, measurement, fields and an aggregate.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.8/flux-script-wizard.png" style="width:100%; max-width:400px; margin:2em 0; display:block;">
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-7-flux-script-wizard.png" style="width:100%; max-width:400px; margin:2em 0; display:block;">
|
||||
|
||||
For example, if you make the above selections, the wizard inserts the following script:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -75,9 +75,9 @@ To add your query and graph to a dashboard:
|
|||
1. Click **Send to Dashboard** in the upper right.
|
||||
2. In the **Target Dashboard(s)** dropdown, select at least one existing dashboard to send the cell to, or select **Send to a New Dashboard**.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/send-to-dashboard-target.png" style="width:100%; max-width:597px; margin:2em 0; display: block;">
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-7-send-to-dashboard-target.png" style="width:100%; max-width:597px; margin:2em 0; display: block;">
|
||||
|
||||
3. Enter a name for the new cell and, if you created a new dashboard, the new dashboard.
|
||||
4. Click **Send to Dashboard(s)**.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/v1.8/send-to-dashboard-send.png" style="width:100%; max-width:597px; display:block; margin:2em 0;">
|
||||
<img src="/img/chronograf/1-7-send-to-dashboard-send.png" style="width:100%; max-width:597px; display:block; margin:2em 0;">
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ menu:
|
|||
|
||||
Chronograf's dashboard views support the following visualization types, which can be selected in the **Visualization Type** selection view of the [Data Explorer](/chronograf/latest/querying-data) .
|
||||
|
||||
[Visualization Type selector](/img/chronograf/chrono-viz-types-selector.png)
|
||||
[Visualization Type selector](/img/chronograf/1-6-viz-types-selector.png)
|
||||
|
||||
Each of the available visualization types and available user controls are described below.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -31,11 +31,11 @@ For information on adding and displaying annotations in graph views, see [Adding
|
|||
|
||||
The **Line Graph** view displays a time series in a line graph.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Line Graph Controls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Use the **Line Graph Controls** to specify the following:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -54,18 +54,18 @@ Use the **Line Graph Controls** to specify the following:
|
|||
|
||||
#### Line Graph example
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Stacked Graph
|
||||
|
||||
The **Stacked Graph** view displays multiple time series bars as segments stacked on top of each other.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Stacked Graph Controls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Use the **Stacked Graph Controls** to specify the following:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -84,18 +84,18 @@ Use the **Stacked Graph Controls** to specify the following:
|
|||
|
||||
#### Stacked Graph example
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Step-Plot Graph
|
||||
|
||||
The **Step-Plot Graph** view displays a time series in a staircase graph.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Step-Plot Graph Controls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Use the **Step-Plot Graph Controls** to specify the following:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -112,7 +112,7 @@ Use the **Step-Plot Graph Controls** to specify the following:
|
|||
|
||||
#### Step-Plot Graph example
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Bar Graph
|
||||
|
|
@ -121,11 +121,11 @@ The **Bar Graph** view displays the specified time series using a bar chart.
|
|||
|
||||
To select this view, click the Bar Graph selector icon.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Bar Graph Controls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Use the **Bar Graph Controls** to specify the following:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -142,7 +142,7 @@ Use the **Bar Graph Controls** to specify the following:
|
|||
|
||||
#### Bar Graph example
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Line Graph + Single Stat
|
||||
|
|
@ -151,11 +151,11 @@ The **Line Graph + Single Stat** view displays the specified time series in a li
|
|||
|
||||
To select this view, click the **Line Graph + Single Stat** view option.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Line Graph + Single Stat Controls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Use the **Line Graph + Single Stat Controls** to specify the following:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -172,13 +172,13 @@ Use the **Line Graph + Single Stat Controls** to specify the following:
|
|||
|
||||
#### Line Graph + Single Stat example
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Single Stat
|
||||
|
||||
The **Single Stat** view displays the most recent value of the specified time series as a numerical value.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If a cell's query includes a [`GROUP BY` tag](/influxdb/latest/query_language/data_exploration/#group-by-tags) clause, Chronograf sorts the different [series](/influxdb/latest/concepts/glossary/#series) lexicographically and shows the most recent [field value](/influxdb/latest/concepts/glossary/#field-value) associated with the first series.
|
||||
For example, if a query groups by the `name` [tag key](/influxdb/latest/concepts/glossary/#tag-key) and `name` has two [tag values](/influxdb/latest/concepts/glossary/#tag-value) (`chronelda` and `chronz`), Chronograf shows the most recent field value associated with the `chronelda` series.
|
||||
|
|
@ -204,11 +204,11 @@ The **Gauge** view displays the single value most recent value for a time series
|
|||
|
||||
To select this view, click the Gauge selector icon.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Gauge Controls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Use the **Gauge Controls** to specify the following:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -222,17 +222,17 @@ Use the **Gauge Controls** to specify the following:
|
|||
|
||||
#### Gauge example
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Table
|
||||
|
||||
The **Table** panel displays the results of queries in a tabular view, which is sometimes easier to analyze than graph views of data.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Table Controls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Use the **Table Controls** to specify the following:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -256,17 +256,17 @@ Use the **Table Controls** to specify the following:
|
|||
|
||||
#### Table view example
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Note
|
||||
|
||||
The **Note** panel displays Markdown-formatted text with your graph.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Note Controls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Enter your text in the **Add a Note** panel, using Markdown to format the text.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -274,4 +274,4 @@ Enable the **Display note in cell when query returns no results** option to disp
|
|||
|
||||
#### Note view example
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ When you enter the InfluxDB HTTP bind address in the `Connection String` input,
|
|||
If it is a data node, Chronograf automatically adds the `Meta Service Connection URL` input to the connection details form.
|
||||
Enter the HTTP bind address of one of your cluster's meta nodes into that input and Chronograf takes care of the rest.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Note that the example above assumes that you do not have authentication enabled.
|
||||
If you have authentication enabled, the form requires username and password information.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -17,19 +17,19 @@ Use InfluxDB Enterprise to:
|
|||
|
||||
* Monitor your cluster
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
* Manage queries
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
* Manage users
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
* Explore and visualize your data
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you're interested in working with InfluxDB Enterprise, visit
|
||||
[InfluxPortal](https://portal.influxdata.com/) to sign up, get a license key,
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -17,19 +17,19 @@ Use InfluxDB Enterprise to:
|
|||
|
||||
* Monitor your cluster
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
* Manage queries
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
* Manage users
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
* Explore and visualize your data
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you're interested in working with InfluxDB Enterprise, visit
|
||||
[InfluxPortal](https://portal.influxdata.com/) to sign up, get a license key,
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -27,11 +27,11 @@ To deploy InfluxDB Enterprise on platforms other than GCP, please see [InfluxDB
|
|||
|
||||
To deploy an InfluxDB Enterprise cluster, log in to your Google Cloud Platform account and navigate to [InfluxData's InfluxDB Enterprise (BYOL)](https://console.cloud.google.com/partner/editor/influxdata-public/influxdb-enterprise-byol) solution in the GCP Marketplace.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Click __Launch on compute engine__ to open up the configuration page.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Copy the InfluxDB Enterprise license key to the __InfluxDB Enterprise license key__ field or [sign up for a free InfluxDB Enterprise trial for GCP](https://portal.influxdata.com/users/gcp) to obtain a license key.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -39,11 +39,11 @@ Adjust any other fields as desired. The cluster will only be accessible within t
|
|||
|
||||
Click __Deploy__ to launch the InfluxDB Enterprise cluster.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The cluster will take up to five minutes to fully deploy. If the deployment does not complete or reports an error, read through the list of [common deployment errors](https://cloud.google.com/marketplace/docs/troubleshooting).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Your cluster is now deployed!
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -17,19 +17,19 @@ Use InfluxDB Enterprise to:
|
|||
|
||||
* Monitor your cluster
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
* Manage queries
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
* Manage users
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
* Explore and visualize your data
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you're interested in working with InfluxDB Enterprise, visit
|
||||
[InfluxPortal](https://portal.influxdata.com/) to sign up, get a license key,
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -16,19 +16,19 @@ Use InfluxDB Enterprise to:
|
|||
|
||||
* Monitor your cluster
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
* Manage queries
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
* Manage users
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
* Explore and visualize your data
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you're interested in working with InfluxDB Enterprise, visit
|
||||
[InfluxPortal](https://portal.influxdata.com/) to sign up, get a license key,
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -157,7 +157,7 @@ A series cardinality around or above 10 million can cause OOM failures even with
|
|||
|
||||
The increase in RAM needs relative to series cardinality is exponential where the exponent is between one and two:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
# What kind of storage do I need?
|
||||
InfluxDB is designed to run on SSDs. InfluxData does not test on HDDs or networked storage devices, and we do not recommend them for production. Performance is an order of magnitude lower on spinning disk drives and the system may break down under even moderate load. For best results InfluxDB servers must have at least 1000 IOPS on the storage system.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -3040,7 +3040,7 @@ The example focuses the following subsample of the [`NOAA_water_database` data](
|
|||
SELECT "water_level" FROM "NOAA_water_database"."autogen"."h2o_feet" WHERE "location"='santa_monica' AND time >= '2015-08-22 22:12:00' AND time <= '2015-08-28 03:00:00'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
##### Step 1: Match the Trends of the Raw Data
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
|
|
@ -3060,7 +3060,7 @@ match the time range of the raw data.
|
|||
|
||||
The blue line shows the results of the query:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
##### Step 2: Determine the Seasonal Pattern
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
|
|
@ -3070,7 +3070,7 @@ query in step 1.
|
|||
Focusing on the blue line in the graph below, the pattern in the `water_level` data repeats about every 25 hours and 15 minutes.
|
||||
There are four data points per season, so `4` is the seasonal pattern argument.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
##### Step 3: Apply the HOLT_WINTERS() function
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
|
|
@ -3087,7 +3087,7 @@ The second argument in the `HOLT_WINTERS_WITH_FIT()` function (`4`) is the seaso
|
|||
|
||||
The blue line shows the results of the query:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Common Issues with `HOLT_WINTERS()`
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ HTTP API that comes with every InfluxDB package.
|
|||
Use `influx` to write data (manually or from a file), query data interactively,
|
||||
and view query output in different formats:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Go straight to the documentation on:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -157,7 +157,7 @@ A series cardinality around or above 10 million can cause OOM failures even with
|
|||
|
||||
The increase in RAM needs relative to series cardinality is exponential where the exponent is between one and two:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
# What kind of storage do I need?
|
||||
InfluxDB is designed to run on SSDs. InfluxData does not test on HDDs or networked storage devices, and we do not recommend them for production. Performance is an order of magnitude lower on spinning disk drives and the system may break down under even moderate load. For best results InfluxDB servers must have at least 1000 IOPS on the storage system.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -3040,7 +3040,7 @@ The example focuses the following subsample of the [`NOAA_water_database` data](
|
|||
SELECT "water_level" FROM "NOAA_water_database"."autogen"."h2o_feet" WHERE "location"='santa_monica' AND time >= '2015-08-22 22:12:00' AND time <= '2015-08-28 03:00:00'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
##### Step 1: Match the Trends of the Raw Data
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
|
|
@ -3060,7 +3060,7 @@ match the time range of the raw data.
|
|||
|
||||
The blue line shows the results of the query:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
##### Step 2: Determine the Seasonal Pattern
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
|
|
@ -3070,7 +3070,7 @@ query in step 1.
|
|||
Focusing on the blue line in the graph below, the pattern in the `water_level` data repeats about every 25 hours and 15 minutes.
|
||||
There are four data points per season, so `4` is the seasonal pattern argument.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
##### Step 3: Apply the HOLT_WINTERS() function
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
|
|
@ -3087,7 +3087,7 @@ The second argument in the `HOLT_WINTERS_WITH_FIT()` function (`4`) is the seaso
|
|||
|
||||
The blue line shows the results of the query:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Common Issues with `HOLT_WINTERS()`
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ HTTP API that comes with every InfluxDB package.
|
|||
Use `influx` to write data (manually or from a file), query data interactively,
|
||||
and view query output in different formats:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Go straight to the documentation on:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -83,7 +83,7 @@ FROM "apple_stand"."autogen"."variety"'>
|
|||
If visualized as a [stacked graph](/chronograf/v1.5/guides/visualization-types/#stacked-graph)
|
||||
in Chronograf, it would look like:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Calculating aggregate percentage per variety
|
||||
The following query calculates the average percentage of the total weight each variety
|
||||
|
|
@ -112,4 +112,4 @@ _**Note the following about this query:**_
|
|||
If visualized as a [stacked graph](/chronograf/v1.5/guides/visualization-types/#stacked-graph)
|
||||
in Chronograf, it would look like:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -3041,7 +3041,7 @@ The example focuses the following subsample of the [`NOAA_water_database` data](
|
|||
SELECT "water_level" FROM "NOAA_water_database"."autogen"."h2o_feet" WHERE "location"='santa_monica' AND time >= '2015-08-22 22:12:00' AND time <= '2015-08-28 03:00:00'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
##### Step 1: Match the Trends of the Raw Data
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
|
|
@ -3061,7 +3061,7 @@ match the time range of the raw data.
|
|||
|
||||
The blue line shows the results of the query:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
##### Step 2: Determine the Seasonal Pattern
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
|
|
@ -3071,7 +3071,7 @@ query in step 1.
|
|||
Focusing on the blue line in the graph below, the pattern in the `water_level` data repeats about every 25 hours and 15 minutes.
|
||||
There are four data points per season, so `4` is the seasonal pattern argument.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
##### Step 3: Apply the HOLT_WINTERS() function
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
|
|
@ -3088,7 +3088,7 @@ The second argument in the `HOLT_WINTERS_WITH_FIT()` function (`4`) is the seaso
|
|||
|
||||
The blue line shows the results of the query:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Common Issues with `HOLT_WINTERS()`
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -19,7 +19,7 @@ HTTP API that comes with every InfluxDB package.
|
|||
Use `influx` to write data (manually or from a file), query data interactively,
|
||||
and view query output in different formats:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Go straight to the documentation on:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -83,7 +83,7 @@ FROM "apple_stand"."autogen"."variety"'>
|
|||
If visualized as a [stacked graph](/chronograf/v1.6/guides/visualization-types/#stacked-graph)
|
||||
in Chronograf, it would look like:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Calculating aggregate percentage per variety
|
||||
The following query calculates the average percentage of the total weight each variety
|
||||
|
|
@ -112,4 +112,4 @@ _**Note the following about this query:**_
|
|||
If visualized as a [stacked graph](/chronograf/v1.6/guides/visualization-types/#stacked-graph)
|
||||
in Chronograf, it would look like:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -6010,7 +6010,7 @@ The example focuses the following subsample of the [`NOAA_water_database` data](
|
|||
SELECT "water_level" FROM "NOAA_water_database"."autogen"."h2o_feet" WHERE "location"='santa_monica' AND time >= '2015-08-22 22:12:00' AND time <= '2015-08-28 03:00:00'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
##### Step 1: Match the Trends of the Raw Data
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
|
|
@ -6030,7 +6030,7 @@ match the time range of the raw data.
|
|||
|
||||
The blue line shows the results of the query:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
##### Step 2: Determine the Seasonal Pattern
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
|
|
@ -6040,7 +6040,7 @@ query in step 1.
|
|||
Focusing on the blue line in the graph below, the pattern in the `water_level` data repeats about every 25 hours and 15 minutes.
|
||||
There are four data points per season, so `4` is the seasonal pattern argument.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
##### Step 3: Apply the HOLT_WINTERS() function
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
|
|
@ -6057,7 +6057,7 @@ The second argument in the `HOLT_WINTERS_WITH_FIT()` function (`4`) is the seaso
|
|||
|
||||
The blue line shows the results of the query:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Common Issues with `HOLT_WINTERS()`
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -19,7 +19,7 @@ HTTP API that comes with every InfluxDB package.
|
|||
Use `influx` to write data (manually or from a file), query data interactively,
|
||||
and view query output in different formats:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Go straight to the documentation on:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -83,7 +83,7 @@ FROM "apple_stand"."autogen"."variety"'>
|
|||
If visualized as a [stacked graph](/chronograf/v1.7/guides/visualization-types/#stacked-graph)
|
||||
in Chronograf, it would look like:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Calculating aggregate percentage per variety
|
||||
The following query calculates the average percentage of the total weight each variety
|
||||
|
|
@ -112,4 +112,4 @@ _**Note the following about this query:**_
|
|||
If visualized as a [stacked graph](/chronograf/v1.7/guides/visualization-types/#stacked-graph)
|
||||
in Chronograf, it would look like:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -6236,7 +6236,7 @@ The example focuses on the following subsample of the [`NOAA_water_database` dat
|
|||
SELECT "water_level" FROM "NOAA_water_database"."autogen"."h2o_feet" WHERE "location"='santa_monica' AND time >= '2015-08-22 22:12:00' AND time <= '2015-08-28 03:00:00'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
###### Step 1: Match the Trends of the Raw Data
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -6256,7 +6256,7 @@ match the time range of the raw data.
|
|||
|
||||
The blue line shows the results of the query:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
###### Step 2: Determine the Seasonal Pattern
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -6266,7 +6266,7 @@ query in step 1.
|
|||
Focusing on the blue line in the graph below, the pattern in the `water_level` data repeats about every 25 hours and 15 minutes.
|
||||
There are four data points per season, so `4` is the seasonal pattern argument.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
###### Step 3: Apply the HOLT_WINTERS() function
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -6283,7 +6283,7 @@ The second argument in the `HOLT_WINTERS_WITH_FIT()` function (`4`) is the seaso
|
|||
|
||||
The blue line shows the results of the query:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Common Issues with `HOLT_WINTERS()`
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -228,7 +228,7 @@ FROM "apple_stand"."autogen"."variety"'>
|
|||
If visualized as a [stacked graph](/chronograf/v1.8/guides/visualization-types/#stacked-graph)
|
||||
in Chronograf, it would look like:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Calculating aggregate percentage per variety
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -258,7 +258,7 @@ _**Note the following about this query:**_
|
|||
If visualized as a [stacked graph](/chronograf/v1.8/guides/visualization-types/#stacked-graph)
|
||||
in Chronograf, it would look like:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
{{% /tab-content %}}
|
||||
{{< /tabs-wrapper >}}
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -115,7 +115,7 @@ In general, more RAM helps queries return faster. Your RAM requirements are prim
|
|||
|
||||
The increase in RAM needs relative to series cardinality is exponential where the exponent is between one and two:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Guidelines per cluster
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -6236,7 +6236,7 @@ The example focuses on the following subsample of the [`NOAA_water_database` dat
|
|||
SELECT "water_level" FROM "NOAA_water_database"."autogen"."h2o_feet" WHERE "location"='santa_monica' AND time >= '2015-08-22 22:12:00' AND time <= '2015-08-28 03:00:00'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
###### Step 1: Match the Trends of the Raw Data
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -6256,7 +6256,7 @@ match the time range of the raw data.
|
|||
|
||||
The blue line shows the results of the query:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
###### Step 2: Determine the Seasonal Pattern
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -6266,7 +6266,7 @@ query in step 1.
|
|||
Focusing on the blue line in the graph below, the pattern in the `water_level` data repeats about every 25 hours and 15 minutes.
|
||||
There are four data points per season, so `4` is the seasonal pattern argument.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
###### Step 3: Apply the HOLT_WINTERS() function
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -6283,7 +6283,7 @@ The second argument in the `HOLT_WINTERS_WITH_FIT()` function (`4`) is the seaso
|
|||
|
||||
The blue line shows the results of the query:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Common Issues with `HOLT_WINTERS()`
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -27,7 +27,7 @@ Find data usage information for the time frame specified in the drop-down at the
|
|||
- **Usage over the specified time period:** A line graph that visualizes usage over the specified time period.
|
||||
- **Rate Limits over the specified time period:** A list of rate limit events over the specified time period.
|
||||
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/2-0-cloud-usage.png" />}}
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/influxdb/2-0-cloud-usage.png" />}}
|
||||
|
||||
## Exceeded rate limits
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -61,7 +61,7 @@ WHERE time > now() - 15m
|
|||
### h3 This is a header3
|
||||
This is a paragraph. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Nunc rutrum, metus id scelerisque euismod, erat ante suscipit nibh, ac congue enim risus id est. Etiam tristique nisi et tristique auctor. Morbi eu bibendum erat. Sed ullamcorper, dui id lobortis efficitur, mauris odio pharetra neque, vel tempor odio dolor blandit justo.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
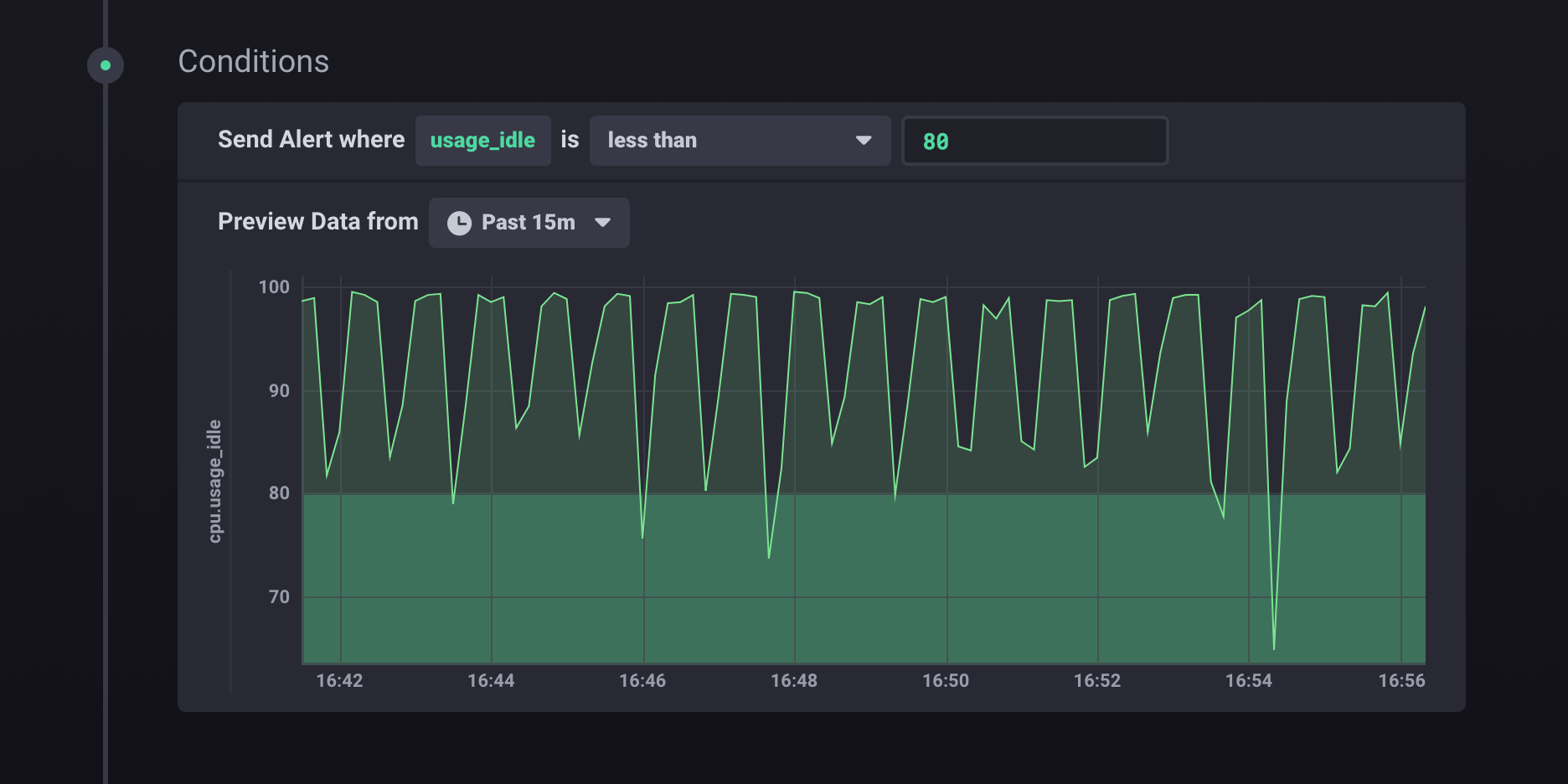
|
||||
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/test-image-2.png" alt="Test Image" />}}
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -23,7 +23,7 @@ This guide covers the different options:
|
|||
## Data Explorer
|
||||
Queries can be built, executed, and visualized in InfluxDB UI's Data Explorer.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Influx REPL
|
||||
The [`influx repl` command](/v2.0/reference/cli/influx/repl) starts an interactive
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -164,7 +164,7 @@ Table: keys: [_start, _stop, _field, _measurement, cpu]
|
|||
|
||||
**Note that the group key is output with each table: `Table: keys: <group-key>`.**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Group by CPU
|
||||
Group the `dataSet` stream by the `cpu` column.
|
||||
|
|
@ -253,7 +253,7 @@ Table: keys: [cpu]
|
|||
|
||||
The visualization remains the same.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Group by time
|
||||
Grouping data by the `_time` column is a good illustration of how grouping changes the structure of your data.
|
||||
|
|
@ -378,7 +378,7 @@ Table: keys: [_time]
|
|||
Because each timestamp is structured as a separate table, when visualized, all
|
||||
points that share the same timestamp appear connected.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
{{% note %}}
|
||||
With some further processing, you could calculate the average CPU usage across all CPUs per point
|
||||
|
|
@ -670,7 +670,7 @@ Table: keys: [_time, cpu]
|
|||
|
||||
When visualized, tables appear as individual, unconnected points.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Grouping by `cpu` and `_time` is a good illustration of how grouping works.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -76,7 +76,7 @@ logarithmicBins(start: 1.0, factor: 2.0, count: 10, infinity: true)
|
|||
The [Histogram visualization type](/v2.0/visualize-data/visualization-types/histogram/)
|
||||
automatically converts query results into a binned and segmented histogram.
|
||||
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/2-0-visualizations-histogram-example.png" alt="Histogram visualization" />}}
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/influxdb/2-0-visualizations-histogram-example.png" alt="Histogram visualization" />}}
|
||||
|
||||
Use the [Histogram visualization controls](/v2.0/visualize-data/visualization-types/histogram/#histogram-controls)
|
||||
to specify the number of bins and define groups in bins.
|
||||
|
|
@ -190,4 +190,4 @@ from(bucket: "example-bucket")
|
|||
In the Histogram visualization options, select `_time` as the **X Column**
|
||||
and `severity` as the **Group By** option:
|
||||
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/2-0-visualizations-histogram-errors.png" alt="Logs by severity histogram" />}}
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/influxdb/2-0-visualizations-histogram-errors.png" alt="Logs by severity histogram" />}}
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -184,7 +184,7 @@ sql.from(
|
|||
|
||||
Use the variable to manipulate queries in your dashboards.
|
||||
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/2-0-sql-dashboard-variable.png" alt="Dashboard variable from SQL query results" />}}
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/influxdb/2-0-sql-dashboard-variable.png" alt="Dashboard variable from SQL query results" />}}
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -187,7 +187,7 @@ Table: keys: [_start, _stop, _field, _measurement]
|
|||
|
||||
When visualized in the InfluxDB UI, each window table is displayed in a different color.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Aggregate data
|
||||
[Aggregate functions](/v2.0/reference/flux/stdlib/built-in/transformations/aggregates) take the values
|
||||
|
|
@ -249,7 +249,7 @@ Table: keys: [_start, _stop, _field, _measurement]
|
|||
Because each data point is contained in its own table, when visualized,
|
||||
they appear as single, unconnected points.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Recreate the time column
|
||||
**Notice the `_time` column is not in the [aggregated output tables](#mean-output-tables).**
|
||||
|
|
@ -343,7 +343,7 @@ Table: keys: [_start, _stop, _field, _measurement]
|
|||
|
||||
With the aggregate values in a single table, data points in the visualization are connected.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Summing up
|
||||
You have now created a Flux query that windows and aggregates data.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -83,7 +83,7 @@ from(bucket:"example-bucket")
|
|||
As data is gathered into windows of time, each window is output as its own table.
|
||||
When visualized, each table is assigned a unique color.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Aggregate windowed data
|
||||
Flux aggregate functions take the `_value`s in each table and aggregate them in some way.
|
||||
|
|
@ -104,7 +104,7 @@ from(bucket:"example-bucket")
|
|||
As rows in each window are aggregated, their output table contains only a single row with the aggregate value.
|
||||
Windowed tables are all still separate and, when visualized, will appear as single, unconnected points.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Add times to your aggregates
|
||||
As values are aggregated, the resulting tables do not have a `_time` column because
|
||||
|
|
@ -150,7 +150,7 @@ from(bucket:"example-bucket")
|
|||
|
||||
Once ungrouped and combined into a single table, the aggregate data points will appear connected in your visualization.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Helper functions
|
||||
This may seem like a lot of coding just to build a query that aggregates data, however going through the
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -33,7 +33,7 @@ For details on using the Data Explorer, see [Explore metrics](/v2.0/visualize-da
|
|||
|
||||
Click the timezone dropdown to select a timezone to use for the dashboard. Select either the local time (default) or UTC.
|
||||
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/2-0-controls-timezone.png" alt="Select timezone" />}}
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/influxdb/2-0-controls-timezone.png" alt="Select timezone" />}}
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
### Select auto-refresh interval
|
||||
|
|
@ -51,7 +51,7 @@ Click the refresh button (**{{< icon "refresh" >}}**) to manually refresh the da
|
|||
|
||||
1. Select from the time range options in the dropdown menu.
|
||||
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/2-0-controls-time-range.png" alt="Select time range" />}}
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/influxdb/2-0-controls-time-range.png" alt="Select time range" />}}
|
||||
|
||||
2. Select **Custom Time Range** to enter a custom time range with precision up to nanoseconds.
|
||||
The default time range is 5 minutes.
|
||||
|
|
@ -69,4 +69,4 @@ Click the fullscreen icon (**{{< icon "fullscreen" >}}**) to enter presentation
|
|||
### Toggle dark mode and light mode
|
||||
Click the moon or sun icons to toggle your dashboard between **dark mode** and **light mode.**
|
||||
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/2-0-controls-dark-light-mode.png" alt="Dark & light mode"/>}}
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/influxdb/2-0-controls-dark-light-mode.png" alt="Dark & light mode"/>}}
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -51,7 +51,7 @@ See [Get started with Flux](/v2.0/query-data/get-started) to learn more about Fl
|
|||
|
||||
- Select an available [visualization types](/v2.0/visualize-data/visualization-types/) from the dropdown menu in the upper-left:
|
||||
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/2-0-visualizations-dropdown.png" title="Visualization dropdown" />}}
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/influxdb/2-0-visualizations-dropdown.png" title="Visualization dropdown" />}}
|
||||
|
||||
## Control your dashboard cell
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -62,7 +62,7 @@ To open the cell editor overlay, click the gear icon in the upper right of a cel
|
|||
|
||||
Toggle the **View Raw Data** {{< icon "toggle" >}} option to see your data in table format instead of a graph. Use this option when data can't be visualized using a visualization type.
|
||||
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/beta-8-raw-data.png" alt="View raw data" />}}
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/influxdb/2-0-controls-view-raw-data.png" alt="View raw data" />}}
|
||||
|
||||
### Save as CSV
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -72,7 +72,7 @@ Click the CSV icon to save the cells contents as a CSV file.
|
|||
|
||||
Select how frequently to refresh the dashboard's data. By default, refreshing is paused.
|
||||
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/beta-8-interval-dropdown.png" alt="Select refresh interval" />}}
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/influxdb-influxdb/2-0-controls-refresh-interval.png" alt="Select refresh interval" />}}
|
||||
|
||||
### Manually refresh dashboard
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -82,7 +82,7 @@ Click the refresh button ({{< icon "refresh" >}}) to manually refresh the dashbo
|
|||
|
||||
1. Select from the time range options in the dropdown menu.
|
||||
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/2-0-controls-time-range.png" alt="Select time range" />}}
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/influxdb/2-0-controls-time-range.png" alt="Select time range" />}}
|
||||
|
||||
2. Select **Custom Time Range** to enter a custom time range with precision up to nanoseconds.
|
||||
The default time range is 5m.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -61,7 +61,7 @@ configure your InfluxDB connection:
|
|||
- **Default Bucket**: The default [bucket](/v2.0/organizations/buckets/) to use in Flux queries.
|
||||
- **Min time interval**: The [Grafana minimum time interval](https://grafana.com/docs/grafana/latest/features/datasources/influxdb/#min-time-interval).
|
||||
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/2-0-visualize-grafana.png" />}}
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/influxdb/2-0-visualize-grafana.png" />}}
|
||||
|
||||
2. Click **Save & Test**. Grafana attempts to connect to the InfluxDB 2.0 datasource
|
||||
and returns the results of the test.
|
||||
|
|
@ -100,7 +100,7 @@ configure your InfluxDB connection:
|
|||
- **HTTP Method**: Select **GET**.
|
||||
- **Min time interval**: The [Grafana minimum time interval](https://grafana.com/docs/grafana/latest/features/datasources/influxdb/#min-time-interval).
|
||||
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/2-0-visualize-grafana-influxql.png" />}}
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/influxdb/2-0-visualize-grafana-influxql.png" />}}
|
||||
|
||||
5. Click **Save & Test**. Grafana attempts to connect to the InfluxDB 2.0 datasource
|
||||
and returns the results of the test.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -35,7 +35,7 @@ Only [user templates](/v2.0/visualize-data/templates/#dashboard-template-types)
|
|||
|
||||
3. Select **User Templates**.
|
||||
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/2-0-templates-type-select.png" alt="Select User Templates" />}}
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/influxdb/2-0-templates-type-select.png" alt="Select User Templates" />}}
|
||||
|
||||
4. Hover over the template you want to clone and click **{{< icon "clone" >}}**.
|
||||
5. Click **Clone** to confirm. The cloned template appears in your list.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ To create a new dashboard from an InfluxDB dashboard template:
|
|||
|
||||
3. Select the [template type](/v2.0/visualize-data/templates/#dashboard-template-types).
|
||||
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/2-0-templates-type-select.png" alt="Select User Templates" />}}
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/influxdb/2-0-templates-type-select.png" alt="Select User Templates" />}}
|
||||
|
||||
4. Hover over the template you want to use and click **Create**.
|
||||
A notification appears confirming the dashboard was created.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ To view templates in the InfluxDB userface (UI):
|
|||
|
||||
3. Select templates to view:
|
||||
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/2-0-templates-type-select.png" alt="Select User Templates" />}}
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/influxdb/2-0-templates-type-select.png" alt="Select User Templates" />}}
|
||||
|
||||
- **Static Templates:** templates included with InfluxDB.
|
||||
For more information, see [Static templates](#static-templates) below.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -33,7 +33,7 @@ from(bucket: v.bucket)
|
|||
When building Flux queries for dashboard cells, view available dashboard variables
|
||||
in the **Variables** tab next to the Functions tab.
|
||||
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/2-0-variables-data-explorer-view.png" />}}
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/influxdb/2-0-variables-data-explorer-view.png" />}}
|
||||
|
||||
Click a variable name to add it to your query and select a value from the **Value** dropdown.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -30,4 +30,4 @@ View a list of dashboard variables in the InfluxDB user interface (UI) from an o
|
|||
2. Switch to **Script Editor**.
|
||||
3. Click the **Variables** tab to the right of the script editor.
|
||||
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/2-0-variables-data-explorer-view.png" />}}
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/influxdb/2-0-variables-data-explorer-view.png" />}}
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: Gauge visualization
|
||||
list_title: Gauge
|
||||
list_image: /img/2-0-visualizations-gauge-example.png
|
||||
list_image: /img/influxdb/2-0-visualizations-gauge-example.png
|
||||
description: >
|
||||
The Gauge view displays the single value most recent value for a time series in a gauge view.
|
||||
weight: 206
|
||||
|
|
@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ menu:
|
|||
|
||||
The **Gauge** visualization displays the most recent value for a time series in a gauge.
|
||||
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/2-0-visualizations-gauge-example-8.png" alt="Gauge example" />}}
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/influxdb/2-0-visualizations-gauge-example-8.png" alt="Gauge example" />}}
|
||||
|
||||
Select the **Gauge** option from the visualization dropdown in the upper right.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -66,4 +66,4 @@ from(bucket: "example-bucket")
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
###### Visualization options for pressure gauge
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/2-0-visualizations-gauge-pressure-8.png" alt="Pressure guage example" />}}
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/influxdb/2-0-visualizations-gauge-pressure-8.png" alt="Pressure guage example" />}}
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: Graph + Single Stat visualization
|
||||
list_title: Graph + Single Stat
|
||||
list_image: /img/2-0-visualizations-line-graph-single-stat-example.png
|
||||
list_image: /img/influxdb/2-0-visualizations-line-graph-single-stat-example.png
|
||||
description: >
|
||||
The Graph + Single Stat view displays the specified time series in a line graph
|
||||
and overlays the single most recent value as a large numeric value.
|
||||
|
|
@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ related:
|
|||
The **Graph + Single Stat** view displays the specified time series in a line graph
|
||||
and overlays the single most recent value as a large numeric value.
|
||||
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/2-0-visualizations-line-graph-single-stat-example-8.png" alt="Line Graph + Single Stat example" />}}
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/influxdb/2-0-visualizations-line-graph-single-stat-example-8.png" alt="Line Graph + Single Stat example" />}}
|
||||
|
||||
Select the **Graph + Single Stat** option from the visualization dropdown in the upper right.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -95,4 +95,4 @@ from(bucket: "example-bucket")
|
|||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
###### Memory allocations visualization
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/2-0-visualizations-graph-single-stat-mem-8.png" alt="Graph + Single Stat Memory Usage Example" />}}
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/influxdb/2-0-visualizations-graph-single-stat-mem-8.png" alt="Graph + Single Stat Memory Usage Example" />}}
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: Graph visualization
|
||||
list_title: Graph
|
||||
list_image: /img/2-0-visualizations-line-graph-example.png
|
||||
list_image: /img/influxdb/2-0-visualizations-line-graph-example.png
|
||||
description: >
|
||||
The Graph view lets you select from multiple graph types such as line graphs and bar graphs *(Coming)*.
|
||||
weight: 201
|
||||
|
|
@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ menu:
|
|||
The Graph visualization provides several types of graphs, each configured through
|
||||
the [Graph controls](#graph-controls).
|
||||
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/2-0-visualizations-line-graph-example-8.png" alt="Line Graph example" />}}
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/influxdb/2-0-visualizations-line-graph-example-8.png" alt="Line Graph example" />}}
|
||||
|
||||
Select the **Graph** option from the visualization dropdown in the upper right.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -61,13 +61,13 @@ the visualization dropdown.
|
|||
## Graph Examples
|
||||
|
||||
##### Graph with linear interpolation
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/2-0-visualizations-line-graph-example-8.png" alt="Line Graph example" />}}
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/influxdb/2-0-visualizations-line-graph-example-8.png" alt="Line Graph example" />}}
|
||||
|
||||
##### Graph with smooth interpolation
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/2-0-visualizations-line-graph-smooth-example-8.png" alt="Step-Plot Graph example" />}}
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/influxdb/2-0-visualizations-line-graph-smooth-example-8.png" alt="Step-Plot Graph example" />}}
|
||||
|
||||
##### Graph with step interpolation
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/2-0-visualizations-line-graph-step-example-8.png" alt="Step-Plot Graph example" />}}
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/influxdb/2-0-visualizations-line-graph-step-example-8.png" alt="Step-Plot Graph example" />}}
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- ##### Stacked Graph example
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/2-0-visualizations-stacked-graph-example.png" alt="Stacked Graph example" />}} -->
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: Heatmap visualization
|
||||
list_title: Heatmap
|
||||
list_image: /img/2-0-visualizations-heatmap-example.png
|
||||
list_image: /img/influxdb/2-0-visualizations-heatmap-example.png
|
||||
description: >
|
||||
A Heatmap displays the distribution of data on an x and y axes where color
|
||||
represents different concentrations of data points.
|
||||
|
|
@ -19,7 +19,7 @@ related:
|
|||
A **Heatmap** displays the distribution of data on an x and y axes where color
|
||||
represents different concentrations of data points.
|
||||
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/2-0-visualizations-heatmap-example.png" alt="Heatmap example" />}}
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/influxdb/2-0-visualizations-heatmap-example.png" alt="Heatmap example" />}}
|
||||
|
||||
Select the **Heatmap** option from the visualization dropdown in the upper right.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -98,7 +98,7 @@ and `_value_mem` is selected as the [Y Column](#data).
|
|||
The domain for each axis is also customized to account for the scale difference
|
||||
between column values.
|
||||
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/2-0-visualizations-heatmap-correlation.png" alt="Heatmap correlation example" />}}
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/influxdb/2-0-visualizations-heatmap-correlation.png" alt="Heatmap correlation example" />}}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Important notes
|
||||
|
|
@ -110,7 +110,7 @@ However, in certain cases, heatmaps provide better visibility into point density
|
|||
|
||||
For example, the dashboard cells below visualize the same query results:
|
||||
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/2-0-visualizations-heatmap-vs-scatter.png" alt="Heatmap vs Scatter plot" />}}
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/influxdb/2-0-visualizations-heatmap-vs-scatter.png" alt="Heatmap vs Scatter plot" />}}
|
||||
|
||||
The heatmap indicates isolated high point density, which isn't visible in the scatter plot.
|
||||
In the scatter plot visualization, points that share the same X and Y coordinates
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: Histogram visualization
|
||||
list_title: Histogram
|
||||
list_image: /img/2-0-visualizations-histogram-example.png
|
||||
list_image: /img/influxdb/2-0-visualizations-histogram-example.png
|
||||
description: >
|
||||
A histogram is a way to view the distribution of data.
|
||||
The y-axis is dedicated to count, and the x-axis is divided into bins.
|
||||
|
|
@ -17,7 +17,7 @@ menu:
|
|||
A histogram is a way to view the distribution of data.
|
||||
The y-axis is dedicated to count, and the X-axis is divided into bins.
|
||||
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/2-0-visualizations-histogram-example.png" alt="Histogram example" />}}
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/influxdb/2-0-visualizations-histogram-example.png" alt="Histogram example" />}}
|
||||
|
||||
Select the **Histogram** option from the visualization dropdown in the upper right.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -79,4 +79,4 @@ from(bucket: "example-bucket")
|
|||
In the Histogram visualization options, select `_time` as the [X Column](#data)
|
||||
and `severity` as the [Group By](#data) option:
|
||||
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/2-0-visualizations-histogram-errors.png" alt="Errors histogram" />}}
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/influxdb/2-0-visualizations-histogram-errors.png" alt="Errors histogram" />}}
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: Scatter visualization
|
||||
list_title: Scatter
|
||||
list_image: /img/2-0-visualizations-scatter-example.png
|
||||
list_image: /img/influxdb/2-0-visualizations-scatter-example.png
|
||||
description: >
|
||||
The Scatter view uses a scatter plot to display time series data.
|
||||
weight: 208
|
||||
|
|
@ -17,7 +17,7 @@ related:
|
|||
|
||||
The **Scatter** view uses a scatter plot to display time series data.
|
||||
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/2-0-visualizations-scatter-example.png" alt="Scatter plot example" />}}
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/influxdb/2-0-visualizations-scatter-example.png" alt="Scatter plot example" />}}
|
||||
|
||||
Select the **Scatter** option from the visualization dropdown in the upper right.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -93,7 +93,7 @@ union(tables: [cpu, mem])
|
|||
###### Use a scatter plot to visualize correlation
|
||||
In the Scatter visualization controls, points are differentiated based on their group keys.
|
||||
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/2-0-visualizations-scatter-correlation.png" alt="Heatmap correlation example" />}}
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/influxdb/2-0-visualizations-scatter-correlation.png" alt="Heatmap correlation example" />}}
|
||||
|
||||
## Important notes
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -104,7 +104,7 @@ However, in certain cases, scatterplots can "hide" points if they share the same
|
|||
|
||||
For example, the dashboard cells below visualize the same query results:
|
||||
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/2-0-visualizations-heatmap-vs-scatter.png" alt="Heatmap vs Scatter plot" />}}
|
||||
{{< img-hd src="/img/influxdb/2-0-visualizations-heatmap-vs-scatter.png" alt="Heatmap vs Scatter plot" />}}
|
||||
|
||||
The heatmap indicates isolated high point density, which isn't visible in the scatter plot.
|
||||
In the scatter plot visualization, points that share the same X and Y coordinates
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Loading…
Reference in New Issue