Purpose is to run full set of testcases on each run. Testcases should contain proper cleanup handlers so that they are independent. |
||
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| dns | ||
| tcp | ||
| udp | ||
| README.md | ||
| eth_environment.png | ||
| wifi_environment.png | ||
README.md
Network Socket test plan
This is a test plan for the Mbed OS Socket API. This describes all test cases and their intended behaviors. When an API document is not clear, use this as a reference for implementing correct behavior.
NOTE: Because testing is a moving target, this test plan might define more test cases than Mbed OS implements. Refer to test case priorities for a list of test cases that the target must pass to be compliant with the Mbed OS socket API.
Target API
The target for this plan is to test:
Reference documentation: https://os.mbed.com/docs/latest/reference/network-socket.html
Tools to use
- Mbed OS.
- Standard Mbed OS development tools as described in https://os.mbed.com/docs/latest/tools/index.html.
- Test server.
These test cases themselves do not require any special tooling, other than the test server described in "Test environment" chapter.
Test environment
As a general guideline, network connectivity with public Internet access is required. This satisfies Socket tests, but specific connectivity methods might require some extra configuration or devices within the network.
The test environment consist of DUTs, network connection and the test server. Arm provides a public test server, but it can be installed locally as well, if an isolated test environment is required.
Public test server
Address: echo.mbedcloudtesting.com
Both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses are available from a public DNS service:
$ host echo.mbedcloudtesting.com
echo.mbedcloudtesting.com has address 52.215.34.155
echo.mbedcloudtesting.com has IPv6 address 2a05:d018:21f:3800:8584:60f8:bc9f:e614
Open services in the test server
- Echo protocol, RFC 862 is enabled in both TCP and UDP. Port 7.
- Discard protocol, RFC 863 is enabled in both TCP and UDP. Port 9.
- Character generator protocol, RFC 864 is enabled in both TCP and UDP. Port 19. Output pattern should follow the proposed example pattern in RFC.
- Daytime protocol, RFC 867 in both TCP and UDP. Port 13.
- Time protocol, RFC 868 in both TCP and UDP. Port 37.
Configure the firewall to allow this traffic to access the test server.
Example configuration for Debian/Ubuntu Linux
These services are available on many operating systems, and installing them is out of scope of this document. Below is an example of how to install these services into a Debian/Ubuntu based Linux distribution using standard Inet Daemon:
$ sudo apt install inetutils-inetd
$ nano /etc/inetd.conf
Enable following services from /etc/inetd.conf:
#:INTERNAL: Internal services
discard stream tcp6 nowait root internal
discard dgram udp6 wait root internal
echo stream tcp6 nowait root internal
echo dgram udp6 wait root internal
chargen stream tcp6 nowait root internal
chargen dgram udp6 wait root internal
daytime stream tcp6 nowait root internal
time stream tcp6 nowait root internal
Testing the connectivity
You can connect to the test server with an NMAP tool like this:
$ nmap -sT -p7,9,13,37 echo.mbedcloudtesting.com
Starting Nmap 7.12 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2018-04-05 16:17 EEST
Nmap scan report for echo.mbedcloudtesting.com (52.215.34.155)
Host is up (0.065s latency).
Other addresses for echo.mbedcloudtesting.com (not scanned): 2a05:d018:21f:3800:8584:60f8:bc9f:e614
rDNS record for 52.215.34.155: ec2-52-215-34-155.eu-west-1.compute.amazonaws.com
PORT STATE SERVICE
7/tcp open echo
9/tcp open discard
13/tcp open daytime
37/tcp open time
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.17 seconds
$ sudo nmap -sT -p7,9,13,37 echo.mbedcloudtesting.com
Starting Nmap 7.12 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2018-04-05 16:16 EEST
Nmap scan report for echo.mbedcloudtesting.com (52.215.34.155)
Host is up (0.068s latency).
Other addresses for echo.mbedcloudtesting.com (not scanned): 2a05:d018:21f:3800:8584:60f8:bc9f:e614
rDNS record for 52.215.34.155: ec2-52-215-34-155.eu-west-1.compute.amazonaws.com
PORT STATE SERVICE
7/tcp open echo
9/tcp open discard
13/tcp open daytime
37/tcp open time
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.20 seconds
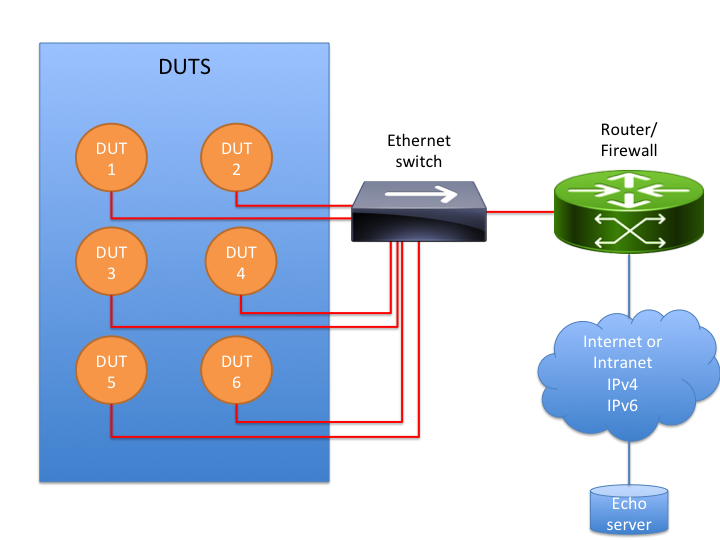
Ethernet test environment
The Ethernet test environment consists of devices, an ethernet switch and an optional firewall that allows connecting to the Echo server.
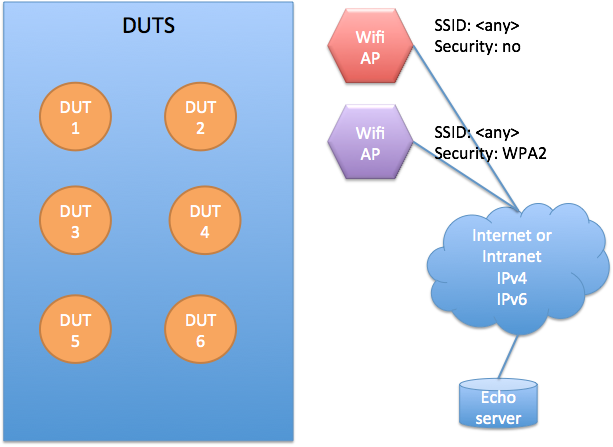
Wi-Fi test environment
The Wi-Fi test environment is equivalent to the Ethernet test environment, except that the Wi-Fi test environment has two separate access points or one with dual SSID. Connectivity to echo server is required, but it can be hosted locally, as specified in the Ethernet environment.
Test case priorities
Please refer to the following table for priorities of test cases. Priorities are labeled as MUST and SHOULD. MUST means this is a requirement and therefore mandatory to pass the test. SHOULD means it is recommended to pass the test if the driver implements the feature in question.
| Test case | Priority | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | UDPSOCKET_OPEN_DESTRUCT | MUST |
| 2 | UDPSOCKET_OPEN_LIMIT | MUST |
| 3 | UDPSOCKET_OPEN_TWICE | MUST |
| 4 | UDPSOCKET_OPEN_CLOSE_REPEAT | MUST |
| 5 | UDPSOCKET_BIND_PORT | SHOULD |
| 6 | UDPSOCKET_BIND_PORT_FAIL | SHOULD |
| 7 | UDPSOCKET_BIND_ADDRESS_PORT | SHOULD |
| 8 | UDPSOCKET_BIND_ADDRESS_NULL | SHOULD |
| 9 | UDPSOCKET_BIND_ADDRESS_INVALID | SHOULD |
| 10 | UDPSOCKET_BIND_WRONG_TYPE | SHOULD |
| 11 | UDPSOCKET_BIND_ADDRESS | SHOULD |
| 12 | UDPSOCKET_BIND_UNOPENED | SHOULD |
| 13 | UDPSOCKET_SENDTO_INVALID | MUST |
| 14 | UDPSOCKET_SENDTO_REPEAT | MUST |
| 15 | UDPSOCKET_BIND_SENDTO | SHOULD |
| 16 | UDPSOCKET_ECHOTEST | MUST |
| 17 | UDPSOCKET_ECHOTEST_NONBLOCK | MUST |
| 18 | UDPSOCKET_RECV_TIMEOUT | SHOULD |
| 19 | UDPSOCKET_SENDTO_TIMEOUT | SHOULD |
| 20 | TCPSOCKET_OPEN_DESTRUCT | MUST |
| 21 | TCPSOCKET_OPEN_LIMIT | MUST |
| 22 | TCPSOCKET_OPEN_TWICE | MUST |
| 23 | TCPSOCKET_OPEN_CLOSE_REPEAT | MUST |
| 24 | TCPSOCKET_BIND_PORT | SHOULD |
| 25 | TCPSOCKET_BIND_PORT_FAIL | SHOULD |
| 26 | TCPSOCKET_BIND_ADDRESS_PORT | SHOULD |
| 27 | TCPSOCKET_BIND_ADDRESS_NULL | SHOULD |
| 28 | TCPSOCKET_BIND_ADDRESS_INVALID | SHOULD |
| 29 | TCPSOCKET_BIND_WRONG_TYPE | SHOULD |
| 30 | TCPSOCKET_BIND_ADDRESS | SHOULD |
| 31 | TCPSOCKET_BIND_UNOPENED | SHOULD |
| 32 | TCPSOCKET_CONNECT_INVALID | MUST |
| 33 | TCPSOCKET_SEND_REPEAT | MUST |
| 34 | TCPSOCKET_ECHOTEST | MUST |
| 35 | TCPSOCKET_ECHOTEST_NONBLOCK | MUST |
| 36 | TCPSOCKET_RECV_TIMEOUT | SHOULD |
| 37 | TCPSOCKET_SEND_TIMEOUT | SHOULD |
| 38 | TCPSOCKET_ENDPOINT_CLOSE | MUST |
| 39 | TCPSERVER_ACCEPT | SHOULD |
| 40 | TCPSERVER_LISTEN | SHOULD |
| 41 | TCPSERVER_LISTEN_WITHOUT_BIND | SHOULD |
| 42 | TCPSERVER_ACCEPT_WITHOUT_LISTEN | SHOULD |
| 43 | UDPSOCKET_ECHOTEST_BURST | MUST |
| 44 | UDPSOCKET_ECHOTEST_BURST_NONBLOCK | MUST |
| 45 | TCPSOCKET_ECHOTEST_BURST | MUST |
| 46 | TCPSOCKET_ECHOTEST_BURST_NONBLOCK | MUST |
| 47 | TCPSOCKET_RECV_100K | MUST |
| 48 | TCPSOCKET_RECV_100K_NONBLOCK | MUST |
| 49 | TCPSOCKET_THREAD_PER_SOCKET_SAFETY | MUST |
| 50 | TCPSOCKET_SETSOCKOPT_KEEPALIVE_VALID | SHOULD |
| 51 | TCPSOCKET_SETSOCKOPT_KEEPALIVE_INVALID | SHOULD |
Building test binaries
For testing the board and driver, test against the Mbed OS master branch to get the most recent, up-to-date test cases and drivers.
To create a build environment:
mbed new network_test
cd network_test
cd mbed-os
git checkout master
cd ..
Also, building socket test cases requires a special macro to
enable all tests, so create an mbed_app.json file with the following
content at minimum:
{
"config": {
"echo-server-addr" : {
"help" : "IP address of echo server",
"value" : "\"echo.mbedcloudtesting.com\""
},
"echo-server-port" : {
"help" : "Port of echo server",
"value" : "7"
}
},
"macros": ["MBED_EXTENDED_TESTS"]
}
Wi-Fi tests require some more configuration, so for Wi-Fi purposes,
the mbed_app.json might look like this:
{
"config": {
"wifi-secure-ssid": {
"help": "WiFi SSID for WPA2 secured network",
"value": "\"test-network\""
},
"wifi-unsecure-ssid": {
"help": "WiFi SSID for unsecure netwrok",
"value": "\"unsecure-test-net\""
},
"wifi-password": {
"help": "WiFi Password",
"value": "\"password\""
},
"wifi-secure-protocol": {
"help": "WiFi security protocol, valid values are WEP, WPA, WPA2, WPA_WPA2",
"value": "\"WPA2\""
},
"wifi-ch-secure": {
"help": "Channel number of secure SSID",
"value": 6
},
"wifi-ch-unsecure": {
"help": "Channel number of unsecure SSID",
"value": 6
},
"ap-mac-secure": {
"help": "BSSID of secure AP in form of AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:FF",
"value": "\"58:8b:f3:99:f2:9c\""
},
"ap-mac-unsecure": {
"help": "BSSID of unsecure AP in form of \"AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:FF\"",
"value": "\"58:8b:f3:99:c2:08\""
},
"max-scan-size": {
"help": "How many networks may appear in Wifi scan result",
"value": 30
},
"echo-server-addr" : {
"help" : "IP address of echo server",
"value" : "\"echo.mbedcloudtesting.com\""
},
"echo-server-port" : {
"help" : "Port of echo server",
"value" : "7"
}
},
"macros": ["MBED_EXTENDED_TESTS"],
"target_overrides": {
"*": {
"target.network-default-interface-type": "WIFI",
"nsapi.default-wifi-ssid": "\"WIFI_SSID\"",
"nsapi.default-wifi-password": "\"WIFI_PASSWORD\"",
"nsapi.default-wifi-security": "WPA_WPA2"
}
}
}
See mbed-os/tools/test_configs folder for examples.
Now build test binaries:
mbed test --compile -t <toolchain> -m <target> -n mbed-os-tests-network-*,mbed-os-tests-netsocket*
Running tests
When device is connected to network, or in case of wireless device near the access point.
mbed test -n mbed-os-tests-network-*,mbed-os-tests-netsocket*
Test cases for Socket class
These test are equal for UDPSocket and TCPSocket but are described here because of identical API and behaviour. Socket class is abstract so it cannot be instantiated, therefore these test cases are implemented using both TCPSocket and UDPSocket.
SOCKET_OPEN_DESTRUCT
Description:
Call Socket::open() and then destruct the socket
Preconditions:
- Network interface and stack are initialised
- Network connection is up
Test steps:
- Create a object by calling
new Socket() - Call
Socket::open(stack) - Call "delete" for the object
- Repeat 1000 times.
Expected result:
Socket::open() should always return NSAPI_ERROR_OK
SOCKET_OPEN_LIMIT
Description:
Call Socket::open() until it runs out of memory or other internal limit
in the stack is reached.
Preconditions:
- Network interface and stack are initialised
- Network connection is up
Test steps:
- Create a object by calling
new Socket() - Call
Socket::open(stack) - repeat until
NSAPI_ERROR_NO_MEMORYorNSAPI_ERROR_NO_SOCKETerror is returned. - Call "delete" for all previously allocated sockets.
- repeat
Expected result:
Should be able to reserve at least 4 sockets. After freeing all sockets, should be able to reserve same number of sockets.
SOCKET_OPEN_TWICE
Description:
Call Socket::open() twice
Preconditions:
- Network interface and stack are initialised
- Network connection is up
Test steps:
- Create a object by calling
new Socket() - Call
Socket::open(stack) - Call
Socket::open(stack) - delete the socket
Expected result:
Socket::open() should first return NSAPI_ERROR_OK and second
call NSAPI_ERROR_PARAMETER.
SOCKET_OPEN_CLOSE_REPEAT
Description:
Call Socket::open() followed by Socket::close() and then again
Socket::open(). Should allow you to reuse the same object.
Preconditions:
- Network interface and stack are initialised
- Network connection is up
Test steps:
- Create a object by calling
new Socket() - Call
Socket::open(stack) - Call
Socket::close(stack) - Call
Socket::open(stack) - Call
Socket::close(stack) - delete the socket
Expected result:
All Socket::open() and Socket::close() calls should return
NSAPI_ERROR_OK.
SOCKET_BIND_PORT
Description:
Call Socket::bind(port)
Preconditions:
- Network interface and stack are initialised
- Network connection is up
Test steps:
- Create a object by calling
new Socket() - Call
Socket::open(stack) - Call
Socket::bind(<any non-used port number>); - destroy socket
Expected result:
All calls return NSAPI_ERROR_OK
SOCKET_BIND_PORT_FAIL
Description:
Call Socket::bind(port) on port number that is already used
Preconditions:
- Network interface and stack are initialised
- Network connection is up
Test steps:
- Create a object by calling
new Socket() - Call
Socket::open(stack) - Call
Socket::bind(<any non-used port number>); - Repeat 1-3 for a new socket.
- destroy both sockets
Expected result:
Second Socket::bind() should return NSAPI_ERROR_PARAMETER
SOCKET_BIND_ADDRESS_PORT
Description:
Call Socket::bind(addr, port)
Preconditions:
- Network interface and stack are initialised
- Network connection is up
Test steps:
- Create a object by calling
new Socket() - Call
Socket::open(stack) - Get address by calling NetworkInterface::get_ip_address();
- Call
Socket::bind(address, <any non-used port number>); - destroy socket
Expected result:
All calls return NSAPI_ERROR_OK
SOCKET_BIND_ADDRESS_NULL
Description:
Call Socket::bind(NULL, port)
Preconditions:
- Network interface and stack are initialised
- Network connection is up
Test steps:
- Create a object by calling
new Socket() - Call
Socket::open(stack) - Call
Socket::bind(NULL, <any non-used port number>); - destroy socket
Expected result:
Socket::bind() should return NSAPI_ERROR_OK
SOCKET_BIND_ADDRESS_INVALID
Description:
Call Socket::bind(address, port) with and address that is not assigned
to us.
Preconditions:
- Network interface and stack are initialised
- Network connection is up
Test steps:
-
Create a object by calling
new Socket() -
Call
Socket::open(stack) -
Check whether device is IPv4 or IPv6 connected.
- For IPv4: Call
Socket::bind("190.2.3.4", <any non-used port number>); - For IPv6: Call
Socket::bind("fe80::ff01", <any non-used port number>);
- For IPv4: Call
-
destroy socket
Expected result:
Socket::bind() should return NSAPI_ERROR_PARAMETER
SOCKET_BIND_ADDRESS_WRONG_TYPE
Description:
Call Socket::bind(SocketAddress) with and address that is not wrong type
for the connection.
Preconditions:
- Network interface and stack are initialised
- Network connection is up
Test steps:
-
Create a object by calling
new Socket() -
Call
Socket::open(stack) -
Check whether device is IPv4 or IPv6 connected.
- For IPv4: Create
SocketAddress("fe80::ff01", <any non-used port number>); - For IPv6: Create
SocketAddress("190.2.3.4", <any non-used port number>);
- For IPv4: Create
-
Call
Socket::bind(address); -
destroy socket
Expected result:
Socket::bind() should return NSAPI_ERROR_PARAMETER
SOCKET_BIND_ADDRESS
Description:
Call Socket::bind(SocketAddress)
Preconditions:
- Network interface and stack are initialised
- Network connection is up
Test steps:
- Create a object by calling
new Socket() - Call
Socket::open(stack) - Get address by calling NetworkInterface::get_ip_address();
- Create a SocketAddress object using this address and any non-used port number.
- Call
Socket::bind(address); - destroy socket
Expected result:
All calls return NSAPI_ERROR_OK
SOCKET_BIND_UNOPENED
Description:
Call Socket::bind() on socket that has not been opened
Preconditions:
- Network interface and stack are initialised
- Network connection is up
Test steps:
- Create a object by calling
new Socket() - Call
Socket::bind(<any non-used port number>); - destroy socket
Expected result:
NSAPI_ERROR_NO_SOCKET
Test cases for UDPSocket class
UDPSOCKET_OPEN_DESTRUCT
Description: Run SOCKET_OPEN_DESTRUCT for UDPSocket
UDPSOCKET_OPEN_LIMIT
Description: Run SOCKET_OPEN_LIMIT for UDPSocket
UDPSOCKET_OPEN_TWICE
Description: Run SOCKET_OPEN_TWICE for UDPSocket
UDPSOCKET_OPEN_CLOSE_REPEAT
Description: Run SOCKET_OPEN_CLOSE_REPEAT for UDPSocket
UDPSOCKET_BIND_PORT
Description: Run SOCKET_BIND_PORT for UDPSocket
UDPSOCKET_BIND_PORT_FAIL
Description: Run SOCKET_BIND_PORT_FAIL for UDPSocket
UDPSOCKET_BIND_ADDRESS_PORT
Description: Run SOCKET_BIND_ADDRESS_PORT for UDPSocket
UDPSOCKET_BIND_ADDRESS_NULL
Description: Run SOCKET_BIND_ADDRESS_NULL for UDPSocket
UDPSOCKET_BIND_ADDRESS_INVALID
Description: Run SOCKET_BIND_ADDRESS_INVALID for UDPSocket
UDPSOCKET_BIND_WRONG_TYPE
Description: Run SOCKET_BIND_WRONG_TYPE for UDPSocket
UDPSOCKET_BIND_ADDRESS
Description: Run SOCKET_BIND_ADDRESS for UDPSocket
UDPSOCKET_BIND_UNOPENED
Description: Run SOCKET_BIND_UNOPENED for UDPSocket
UDPSOCKET_SENDTO_INVALID
Description:
Call UDPSocket::sendto() with invalid parameters.
Preconditions:
- Network interface and stack are initialised
- Network connection is up
- UDPSocket is open
Test steps:
- Call
UDPSocket:sendto( NULL, 9, NULL, 0); - Call
UDPSocket:sendto( "", 9, NULL, 0); - Call
UDPSocket:sendto( "", 0, NULL, 0); - Call
UDPSocket:sendto(NULL, 9, "hello", 5); - Call
UDPSocket:sendto(NULL, 0, "hello", 5); - Call
UDPSocket:sendto("echo.mbedcloudtesting.com", 9,NULL, 0); - Call
UDPSocket:sendto("echo.mbedcloudtesting.com", 9, "hello", 5); - destroy the socket
Expected result:
All sendto() calls should return some error code except:
- step 6 should return 5
- step 7 should return 0
- step 8 should return 5
UDPSOCKET_SENDTO_REPEAT
Description:
Repeatedly send small packets.
Preconditions:
- Network interface and stack are initialised
- Network connection is up
- UDPSocket is open
Test steps:
- Call
UDPSocket:sendto("echo.mbedcloudtesting.com", 9, "hello", 5); - repeat 100 times
- Fail if
NSAPI_ERROR_NO_MEMORYis returned two times in a row, wait 1 second before retry - destroy the socket
Expected result:
All sendto() calls should return 5.
UDPSOCKET_BIND_SENDTO
Description:
Bind the socket to specific port before sending. Verify from DUT2 that packet was coming from correct port.
Requires two devices with LAN connectivity (Eth, WiFi or mesh). For Cellular or WAN connectivity, skip this test.
Preconditions:
- Network interface and stack are initialised
- Network connection is up
- UDPSocket is open
Test steps:
- DUT1&2: Call
UDPSocket::bind(<unuser port number>); - DUT2: Get devices IP address
- DUT1: Call
UDPSocket::sendto( dut2, port, "hello", 5); - DUT2: Call
UDPSocket::recvfrom(); - destroy the sockets
Expected result:
UDPSocket::bind() should return NSAPI_ERROR_OK.
UDPSocket::sendto() call should return 5.
UDPSocket::recvfrom() should return 5 and port number should match the
one used in bind() call. Data should contain "hello"
UDPSOCKET_ECHOTEST
Description:
Repeatedly send packets to echo server and read incoming packets back. Verify working of different packet sizes.
Preconditions:
- Network interface and stack are initialised
- Network connection is up
- UDPSocket is open
Test steps:
- Call
UDPSocket:sendto("echo.mbedcloudtesting.com", 7, <random packet, size = loop index>, <loop index>); - Wait for incomming packet. If timeout happens, retry sending&receiving, max 3 times.
- Verify incomming content was the same that was sent
- Repeat 1200 times
- destroy the socket
Expected result:
All sendto() calls should return the packet size. All recvfrom() calls should return the same sized packet that was send with same content. Calculate packet loss rate, maximum tolerated packet loss rate is 30%
UDPSOCKET_ECHOTEST_NONBLOCK
Description:
Repeatedly send packets to echo server and read incoming packets back. Verify working of different packet sizes. Use socket in non-blocking mode
Preconditions:
- Network interface and stack are initialised
- Network connection is up
- UDPSocket is open
Test steps:
- Call
UDPSocket::set_blocking(false) - Register event handler with
UDPSocket::sigio() - Create another thread that constantly waits signal from sigio()
handler, when received try
UDPSocket::recvfrom() - Call
UDPSocket:sendto("echo.mbedcloudtesting.com", 7, <random packet, size = loop index>, <loop index>); - Wait for incomming packet for one second. If nothing received retry, max 3 times.
- Verify incomming content was the same that was sent
- Repeat 1200 times
- destroy the socket
Expected result:
All sendto() calls should return the packet size. All recvfrom() calls should return the same sized packet that was send with same content or NSAPI_ERROR_WOULD_BLOCK.
Calculate packet loss rate, maximum tolerated packet loss rate is 30%
UDPSOCKET_RECV_TIMEOUT
Description:
Test whether timeouts are obeyed in UDPSockets.
Preconditions:
- Network interface and stack are initialised
- Network connection is up
Test steps:
-
Call
UDPSocket::set_timeout(100) -
Call
UDPSocket::sendto("echo.mbedcloudtesting.com", 7, <random packet, size = 100>, 100); -
Repeat 5 times
- record a time in millisecond precission
- Call
UDPSocket::recvfrom() - record a time in millisecond precission
-
repeat testcase 10 times.
Expected result:
Each sendto() calls should return 100.
Within each loop, one recvfrom() may return the received packet size
(100). Other calls should return NSAPI_ERROR_WOULD_BLOCK.
When NSAPI_ERROR_WOULD_BLOCK is received, check that time consumed is more that 100 milliseconds but less than 200 milliseconds.
After repeating for 10 times, at least 5 packets must have been received.
UDPSOCKET_SENDTO_TIMEOUT
Description:
Test whether timeouts are obeyed in UDPSockets.
Preconditions:
- Network interface and stack are initialised
- Network connection is up
Test steps:
- Record time
- Call
UDPSocket::sendto("echo.mbedcloudtesting.com", 9, <random packet, size = 100>, 100); - Record time
- Call
UDPSocket::set_timeout(1000) - Call
UDPSocket::sendto("echo.mbedcloudtesting.com", 9, <random packet, size = 100>, 100); - Record time
Expected result:
Each sendto() call should return 100.
All sendto() calls should return faster than 100 milliseconds because UDP sending should not block that long.
Test cases for TCPSocket class
TCPSOCKET_OPEN_DESTRUCT
Description: Run SOCKET_OPEN_DESTRUCT for TCPSocket
TCPSOCKET_OPEN_LIMIT
Description: Run SOCKET_OPEN_LIMIT for TCPSocket
TCPSOCKET_OPEN_TWICE
Description: Run SOCKET_OPEN_TWICE for TCPSocket
TCPSOCKET_OPEN_CLOSE_REPEAT
Description: Run SOCKET_OPEN_CLOSE_REPEAT for TCPSocket
TCPSOCKET_BIND_PORT
Description: Run SOCKET_BIND_PORT for TCPSocket
TCPSOCKET_BIND_PORT_FAIL
Description: Run SOCKET_BIND_PORT_FAIL for TCPSocket
TCPSOCKET_BIND_ADDRESS_PORT
Description: Run SOCKET_BIND_ADDRESS_PORT for TCPSocket
TCPSOCKET_BIND_ADDRESS_NULL
Description: Run SOCKET_BIND_ADDRESS_NULL for TCPSocket
TCPSOCKET_BIND_ADDRESS_INVALID
Description: Run SOCKET_BIND_ADDRESS_INVALID for TCPSocket
TCPSOCKET_BIND_WRONG_TYPE
Description: Run SOCKET_BIND_WRONG_TYPE for TCPSocket
TCPSOCKET_BIND_ADDRESS
Description: Run SOCKET_BIND_ADDRESS for TCPSocket
TCPSOCKET_BIND_UNOPENED
Description: Run SOCKET_BIND_UNOPENED for TCPSocket
TCPSOCKET_CONNECT_INVALID
Description:
Call TCPSocket::connect() with invalid parameters.
Preconditions:
- Network interface and stack are initialised
- Network connection is up
- TCPSocket is open
Test steps:
- Call
TCPSocket:connect( NULL, 9); - Call
TCPSocket:connect( "", 9); - Call
TCPSocket:connect( "", 0); - Call
TCPSocket:connect( "echo.mbedcloudtesting.com", 9); - destroy the socket
Expected result:
All connect() calls should return some error code except the number 5 should return NSAPI_ERROR_OK.
TCPSOCKET_SEND_REPEAT
Description:
Repeatedly send small packets.
Preconditions:
- Network interface and stack are initialised
- Network connection is up
- TCPSocket is open
Test steps:
- Call
TCPSocket::connect("echo.mbedcloudtesting.com", 9); - Call
TCPSocket::send("hello", 5); - repeat 1000 times
- destroy the socket
Expected result:
TCPSocket::connect() should return NSAPI_ERROR_OK
All send() calls should return 5.
TCPSOCKET_ECHOTEST
Description:
Repeatedly send packets to echo server and read incoming packets back. Verify working of different packet sizes.
Preconditions:
- Network interface and stack are initialised
- Network connection is up
- TCPSocket is open
Test steps:
-
Call
TCPSocket::connect("echo.mbedcloudtesting.com", 7); -
Call
TCPSocket::send(<random packet, size = loop index>, <size>);- If less than was returned, size = sent bytes
-
Call
TCPSocket::recv(buffer, <size>); -
Verify incomming content was the same that was sent
-
Repeat 1200 times
-
destroy the socket
Expected result:
All send() calls should return the packet size or less. All recv() calls should return the same sized packet that was send with same content.
NOTE: This is stream so recv() might return less data than what was requested. In this case you need to keep calling recv() until all data that you have sent is returned.
TCPSOCKET_ECHOTEST_NONBLOCK
Description:
Repeatedly send packets to echo server and read incoming packets back. Verify working of different packet sizes. Use socket in non-blocking mode
Preconditions:
- Network interface and stack are initialised
- Network connection is up
- TCPSocket is open
Test steps:
-
Call
TCPSocket::connect("echo.mbedcloudtesting.com", 7); -
Call
TCPSocket::set_blocking(false) -
Register event handler with
TCPSocket::sigio() -
Create another thread that constantly waits signal from
sigio()handler, when received tryTCPSocket::recv(buf+index, <loop index> - index), where index is the amount of data already received. -
Call
TCPSocket:send(<random packet, size = loop index>, <loop index>);- If less than was returned, try immeadiately sending remaining bytes.
- If NSAPI_ERROR_WOULD_BLOCK is returned, wait for sigio() call to happen.
-
Wait for incomming packet for one second.
-
Verify incomming content was the same that was sent, set index for receiving thread to zero.
-
Repeat 1200 times
-
destroy the socket
Expected result:
All send() calls should return the packet size or less. All recv() calls should return NSAPI_ERROR_WOULD_BLOCK or packet size that is equal or less than what has been sent.
TCPSOCKET_RECV_TIMEOUT
Description:
Test whether timeouts are obeyed in TCPSockets.
Preconditions:
- Network interface and stack are initialised
- Network connection is up
- TCPSocket is open
Test steps:
-
Call
TCPSocket::connect("echo.mbedcloudtesting.com", 7); -
Call
TCPSocket::set_timeout(100); -
Call
TCPSocket::send(<random packet, size = 100>;, 100); -
Repeat 5 times
- record a time in millisecond precission
- Call
TCPSocket::recv() - record a time in millisecond precission
-
repeat testcase 10 times.
Expected result:
Each send() call should return 100.
Within each loop, one recv() may return the received packet size (100). Other calls should return NSAPI_ERROR_WOULD_BLOCK.
When NSAPI_ERROR_WOULD_BLOCK is received, check that time consumed is more that 100 milliseconds but less than 200 milliseconds.
TCPSOCKET_SEND_TIMEOUT
Description:
Repeatedly send small packets in a given time limit
Preconditions:
- Network interface and stack are initialised
- Network connection is up
- TCPSocket is open
Test steps:
- Call
TCPSocket:connect("echo.mbedcloudtesting.com", 9); - Call
TCPSocket:set_blocking(false); - Call
TCPSocket:send("hello", 5); - repeat 10 times
- destroy the socket
Expected result:
TCPSocket::connect() should return NSAPI_ERROR_OK
All send() calls should return in less than 800 milliseconds
TCPSOCKET_ENDPOINT_CLOSE
Description:
Test whether we tolerate endpoint closing the connection.
Preconditions:
- Network interface and stack are initialised
- Network connection is up
- TCPSocket is open
Test steps:
- Call
TCPSocket::connect("echo.mbedcloudtesting.com", 13); - Call
TCPSocket::recv(<buffer>, 30); - Repeat until recv() returns 0
- Call
TCPSocket::close(); - delete socket
Expected result: Connect should return NSAPI_ERROR_OK.
First recv() should return more that zero. Something between 10 and 30 bytes (datetime string)
Second recv() should return zero because endpoint closed the connection. (EOF). close() should return NSAPI_ERROR_OK
TCPSOCKET_SETSOCKOPT_KEEPALIVE_VALID
Description:
Test we are able to request setting valid TCP keepalive values
Preconditions:
- Network interface and stack are initialised
- Network connection is up
Test steps:
- Call
TCPSocket::setsockopt(keepalive, [0,1 or 7200]); - Call
TCPSocket::connect("echo.mbedcloudtesting.com", 9); - Call
TCPSocket::getsockopt(keepalive);
Postconditions:
- Call
TCPSocket::close(); - delete socket
Expected result:
TCPSocket::getsockopt(keepalive) returns same value as was set with
TCPSocket::setsockopt() or NSAPI_ERROR_UNSUPPORTED
TCPSOCKET_SETSOCKOPT_KEEPALIVE_INVALID
Description:
Test we are able to detect if an invalid TCP keepalive value is tried to be set
Preconditions:
- Network interface and stack are initialised
- Network connection is up
Test steps:
- Call
TCPSocket::setsockopt(keepalive, [-1 or 7201]); - Call
TCPSocket::getsockopt(keepalive);
Postconditions:
- Call
TCPSocket::close(); - delete socket
Expected result:
TCPSocket::setsockopt(keepalive) returns error code or
NSAPI_ERROR_UNSUPPORTED
TCPSocket::getsockopt() returns 0 or NSAPI_ERROR_UNSUPPORTED
Test cases for TCPServer class
These tests require two devices under test and connectivity between them. Therefore they can only be ran with LAN connectivity (Eth, Wifi or Mesh) or if there is no firewall between devices.
TCPSERVER_ACCEPT
Description:
Test that TCPServer::bind(), TCPServer::listen()
and TCPServer::accept() works.
Requires 2 devices.
Preconditions:
- Network interface and stack are initialised
- Network connection is up
Test steps:
- DUT1:
TCPServer::bind(<port>) - DUT1:
TCPServer::listen() - DUT1: Create a new
TCPSocket - DUT1:
TCPServer::accept() - DUT2: Create a new
TCPSocket - DUT2:
TCPSocket::connect(<dut1>, <port>) - DUT1: should receive new socket from accept(),
call
TCPSocket::send("hello",5)for it - DUT2: call
TCPSocket::recv(buffer, 5) - DUT2: Verify that it received "hello"
- destroy all sockets.
Expected result:
On DUT1 accept() call blocks until connection is received. Other calls should return NSAPI_ERROR_OK
On DUT2 all calls should return NSAPI_ERROR_OK
TCPSERVER_LISTEN
Description:
Test that TCPServer::listen() has the backlog functionality.
Requires 2 devices.
Preconditions:
- Network interface and stack are initialised
- Network connection is up
Test steps:
-
DUT1:
TCPServer::bind(<port>) -
DUT1:
TCPServer::listen(2) -
loop 2 times:
- DUT2: Create a new TCPSocket
- DUT2:
TCPSocket::connect(<dut1>, <port>)
-
loop 2 times:
- DUT1: Create a new TCPSocket
- DUT1:
TCPServer::accept() - DUT1: should receive new socket from accept(),
call
TCPSocket::send("hello",5)for it
-
DUT2: call
TCPSocket::recv(buffer, 5)for both socket. -
DUT2: Verify that it received "hello"
-
destroy all sockets.
Expected result:
DUT2 should receive connection before the server have called accept(), because backlog must be minimum of 2.
TCPSERVER_LISTEN_WITHOUT_BIND
Description:
Call TCPServer::listen() without calling bind() first. Should fail,
because no listening port have been defined.
Preconditions:
- Network interface and stack are initialised
- Network connection is up
Test steps:
- Create TCPServer
- Call
TCPServer::listen()
Expected result:
Should return NSAPI_ERROR_UNSUPPORTED, NSAPI_ERROR_PARAMETER, NSAPI_ERROR_NO_ADDRESS or NSAPI_ERROR_DEVICE_ERROR
TCPSERVER_ACCEPT_WITHOUT_LISTEN
Description:
Call TCPServer::accept() without calling listen() first. Should fail,
because socket is not listening for connections.
Preconditions:
- Network interface and stack are initialised
- Network connection is up
Test steps:
- Create TCPServer
- Call
TCPServer::bind(<unused port number>) - Create new TCPSocket.
- Call
TCPServer::accept()
Expected result:
Should return NSAPI_ERROR_UNSUPPORTED, NSAPI_ERROR_PARAMETER or NSAPI_ERROR_DEVICE_ERROR
Performance tests
UDPSOCKET_ECHOTEST_BURST
Description:
Send burst of packets to echo server and read incoming packets back.
Preconditions:
- Network interface and stack are initialised
- Network connection is up
- UDPSocket is open
Test steps:
- Call
UDPSocket:sendto("echo.mbedcloudtesting.com", 7, <random packet, size = 100>, 100); - Call
UDPSocket:sendto("echo.mbedcloudtesting.com", 7, <random packet, size = 200>, 200); - Call
UDPSocket:sendto("echo.mbedcloudtesting.com", 7, <random packet, size = 300>, 300); - Call
UDPSocket:sendto("echo.mbedcloudtesting.com", 7, <random packet, size = 120>, 120); - Call
UDPSocket:sendto("echo.mbedcloudtesting.com", 7, <random packet, size = 500>, 500); - Wait for incomming packets for five second.
- Verify incomming content was the same that was sent. Allow packet reordering.
- Repeat 100 times
- destroy the socket
Expected result:
All sendto() calls should return the packet size.
All recvfrom() calls should return the same sized packet that was send with same content. Allow packet reordering.
Calculate packet loss rate, maximum tolerated packet loss rate is 30%
Calculate number of succesfull rounds, it should be higher than 70
UDPSOCKET_ECHOTEST_BURST_NONBLOCK
Description:
Send burst of packets to echo server and read incoming packets back. Use socket in non-blocking mode
Preconditions:
- Network interface and stack are initialised
- Network connection is up
- UDPSocket is open
Test steps:
- Call
UDPSocket::set_blocking(false) - Register event handler with
UDPSocket::sigio() - Create another thread that constantly waits signal from sigio()
handler, when received try
UDPSocket::recvfrom() - Call
UDPSocket:sendto("echo.mbedcloudtesting.com", 7, <random packet, size = 100>, 100); - Call
UDPSocket:sendto("echo.mbedcloudtesting.com", 7, <random packet, size = 200>, 200); - Call
UDPSocket:sendto("echo.mbedcloudtesting.com", 7, <random packet, size = 300>, 300); - Call
UDPSocket:sendto("echo.mbedcloudtesting.com", 7, <random packet, size = 120>, 120); - Call
UDPSocket:sendto("echo.mbedcloudtesting.com", 7, <random packet, size = 500>, 500); - Wait for incomming packets for five second.
- Verify incomming content was the same that was sent. Allow packet reordering.
- Repeat 100 times
- destroy the socket
Expected result:
All sendto() calls should return the packet size.
All recvfrom() calls should return the same sized packet that was send with same content. Allow packet reordering.
Calculate packet loss rate, maximum tolerated packet loss rate is 30%
Calculate number of succesfull rounds, it should be higher than 70
TCPSOCKET_ECHOTEST_BURST
Description:
Send burst of packets to echo server and read incoming packets back.
Preconditions:
- Network interface and stack are initialised
- Network connection is up
- TCPSocket is open
Test steps:
- Call
TCPSocket::connect("echo.mbedcloudtesting.com", 7); - Call
TCPSocket::send(<random packet, size = 100>, 100); - Call
TCPSocket::send(<random packet, size = 200>, 200); - Call
TCPSocket::send(<random packet, size = 300>, 300); - Call
TCPSocket::send(<random packet, size = 120>, 120); - Call
TCPSocket::send(<random packet, size = 500>, 500); - Call
TCPSocket::recv(buf, 1220) - Verify incomming content was the same that was sent.
- Repeat 100 times
- destroy the socket
Expected result:
All send() calls should return the packet size.
NOTE: This is stream so recv() might return less data than what was requested. In this case you need to keep calling recv() with remaining size until all data that you have sent is returned.
Consecutive calls to recv() should return all the data that has been send. Total amount of returned must match 1220.
TCPSOCKET_ECHOTEST_BURST_NONBLOCK
Description:
Send burst of packets to echo server and read incoming packets back. Use socket in non-blocking mode
Preconditions:
- Network interface and stack are initialised
- Network connection is up
- TCPSocket is open
Test steps:
-
Register event handler with
TCPSocket::sigio() -
Call
TCPSocket::connect("echo.mbedcloudtesting.com", 7); -
Call
TCPSocket::set_blocking(false) -
Create another thread that constantly waits signal from sigio() handler, when received try
TCPSocket::recv() -
For randomly generated packets, sized 100, 200, 300, 120 and 500 do
- Call
TCPSocket::send(packet, size); - If less than size is sent, repeat with remaining.
- If NSAPI_ERROR_WOULD_BLOCK returned, wait for next sigio()
- Call
-
Wait for incomming packets for five second.
-
Verify incomming content was the same that was sent. Allow recv() to return smaller piezes.
-
Repeat 100 times
-
destroy the socket
Expected result:
All send() calls should return NSAPI_ERROR_WOULD_BLOCK or size which is equal or less than requested.
All recv() calls should return value that is less or equal to what have been sent. With consecutive calls, size should match.
When recv() returns NSAPI_ERROR_WOULD_BLOCK wait for next sigio() event. No other error codes allowed.
TCPSOCKET_RECV_100K
Description:
Download 100kB of data
Preconditions:
- Network interface and stack are initialised
- Network connection is up
- TCPSocket is open
Test steps:
- Call
TCPSocket::connect("echo.mbedcloudtesting.com", 19); - Call
TCPSocket::recv(buffer, 100); - Verify input according to known pattern.
- Loop until 100kB of data received.
- close socket.
Expected result:
Each recv() call should return equal or less than 100 bytes of data. No errors should be returned.
Measure time taken for receiving, report speed
TCPSOCKET_RECV_100K_NONBLOCK
Description:
Download 100kB of data
Preconditions:
- Network interface and stack are initialised
- Network connection is up
- TCPSocket is open
Test steps:
-
Call
TCPSocket::connect("echo.mbedcloudtesting.com", 19); -
Call
TCPSocket::set_blocking(false) -
Create another thread that constantly waits signal from sigio() handler, when received try
TCPSocket::recv()- Call
TCPSocket::recv(buffer, 100); - Verify input according to known pattern.
- Call
-
Wait until 100kB of data received.
-
close socket.
Expected result:
Each recv() call should return equal or less than 100 bytes of data or NSAPI_ERROR_WOULD_BLOCK in which case thread should wait for another sigio(). No errors should be returned.
Measure time taken for receiving, report speed
TCPSOCKET_THREAD_PER_SOCKET_SAFETY
Description:
Run two threads which both exercise the underlying stack and driver through a dedicated socket
Preconditions:
- Network interface and stack are initialised
- Network connection is up
- 2 TCPSockets are open and one additional thread has been created
- Both threads get their own socket instance
Test steps:
-
Call
TCPSocket::connect("echo.mbedcloudtesting.com", 7)in both threads - in the main thread executing the test case and on the additional one; -
On main thread
- For randomly generated packets, sized 1001, 901, 801,...,101,1
do
- Call
TCPSocket::send(packet, size); - Verify incoming content was the same that was sent. Allow recv() to return smaller piezes.
- Call
- For randomly generated packets, sized 1001, 901, 801,...,101,1
do
-
Simultaneously with the earlier step do on the additional thread
- For randomly generated packets, sized 10 do
- Call
TCPSocket::send(packet, size); - Verify incomming content was the same that was sent. Allow recv() to return smaller piezes.
- stop the thread if inconsistensies were found and report it to main thread
- Call
- For randomly generated packets, sized 10 do
-
Kill the additional thread
-
Close and destroy the sockets
Expected result:
Echo server returns data to both threads and received data matches to send data. The additional thread isn't stopped prematurely
Subset for driver test
For physical layer driver (emac, PPP):
- TCPSERVER_ACCEPT
- TCPSERVER_LISTEN
- TCPSOCKET_ECHOTEST
- TCPSOCKET_ECHOTEST_BURST
- TCPSOCKET_ECHOTEST_BURST_NONBLOCK
- TCPSOCKET_ECHOTEST_NONBLOCK
- TCPSOCKET_RECV_100K
- TCPSOCKET_RECV_100K_NONBLOCK
- TCPSOCKET_RECV_TIMEOUT
- TCPSOCKET_SEND_REPEAT
- UDPSOCKET_BIND_SENDTO
- UDPSOCKET_ECHOTEST
- UDPSOCKET_ECHOTEST_NONBLOCK
- UDPSOCKET_RECV_TIMEOUT
- UDPSOCKET_SENDTO_INVALID
- UDPSOCKET_SENDTO_REPEAT
- UDPSOCKET_SENDTO_TIMEOUT
For socket layer driver (AT-driven, external IP stack):
All Socket, UDPSocket, TCPSocket and TCPServer testcases.